![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
276 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Layer of Cortex that is principal efferent for motor related subcortical structures |
Internal pyramidal layer V |
|
|
|
Reduplicative paramnesia localization |
Right parietal and bifrontal |
|
|
|
Moyamoya pathology finding |
Intimal fibroplasia |
|
|
|
Most common cancer metastasizing to the brain |
Non-small cell lung cancer |
|
|
|
Cancer that metastasize to the brain |
Lung, kidney, breast, melanoma |
Like killing brain mass |
|
|
Oligodendroglioma mutations |
IDH and 1P19Q |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter of the nucleus accumbens |
GABA |
|
|
|
Input neurotransmitter nucleus accumbens |
Dopamine |
|
|
|
Nucleus accumbens cell type |
Medium spiny neuron |
|
|
|
Afferent input Thalamus to Cortex, which cortical layer? |
Internal granular layer IV |
|
|
|
Glioblastoma multiforme |
Pseudo palisading necrosis |
|
|
|
Rosenthal fibers |
Pilocytic astrocytoma WHO Grade I Posterior fossa |
|
|
|
Homer Wright rosettes |
Medulloblastoma |
|
|
|
Perivascular pseudorosettes |
Ependymoma |
|
|
|
Entacapone |
Comt inhibitor increase on-time of levodopa, side effect is hepatotoxicity |
|
|
|
Treatment of paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia |
Carbamazepine |
|
|
|
Repetitive stimulation frequency in MG/LEMS |
3-5 Hz MG 30-50 Hz LEMS |
|
|
|
Paramyotonia congenita |
Sodium channels Almost the same thing as hyperkalemic periodic paralysis autosomal dominant Worse with exercise |
|
|
|
Myotonia congenita |
Chloride channels |
|
|
|
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis |
Calcium channels |
|
|
|
Localization of Hemiachromatopsia |
Inability to perceive color Infracalcarine occipital cortex |
|
|
|
Rett syndrome genetics |
X linked dominant, MECP-2 gene |
|
|
|
Common peroneal neuropathy vs. L5 radiculopathy |
Cannot invert in L5 radiculopathy |
|
|
|
Substantia nigra pars compacta gives _______ neurons to striatum |
Dopaminergic |
|
|
|
Gerstmann-straussler-scheinker |
PRP mutation on codon 102 |
|
|
|
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 |
Chromosome 19 Autosomal dominant CTG repeats |
|
|
|
Fabry disease |
X-linked, alpha gal, globotriasoylceramide |
|
|
|
Drugs to avoid absence epilepsy |
Carbamazepine, vigabatrin |
|
|
|
What is the claustrum |
The thin gray matter layer between the extreme capsule and the external capsule |
|
|
|
Type of headache associated with REM sleep |
Cluster headache |
|
|
|
Common presentation of Legionnaires disease |
Delirium |
|
|
|
Action potential: sodium |
Sodium enters cell |
|
|
|
Action potential potassium |
Potassium exits the cell |
|
|
|
Glycogen store in brain |
Astrocyte glycogen is degraded to lactate during intense neural activity |
|
|
|
Wernicke's area |
Superior temporal gyrus posterior to the Sylvian fissure |
|
|
|
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 - balding, cardiac conduction, infertility, cataracts |
CTG on DMPK Gene Autosomal dominant |
|
|
|
Myotonic dystrophy type 2 Gene |
Znf9 on chromosome 3, CCTG repeat |
|
|
|
Intracranial aneurysms occur in what percentage of patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
10 to 30% |
|
|
|
Neurofibromatosis genes |
Chromosome 17 for NF1 chromosome 22 for nf2 |
|
|
|
Meningiomas have been associated with what mutation |
Monosomy 22 |
|
|
|
Contents of the cavernous sinus |
CN 3, 4, V1, V2, 6 ICA with sympathetics |
|
|
|
When does the caudal (posterior) neuropore close |
Day 25 of embryogenesis |
|
|
|
Directly innervated by the C5 root |
Rhomboid |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters at the anterior horn cells |
Excitatory is glutamate, inhibitory is Gaba and glycine |
|
|
|
Deficient enzyme in stiff person syndrome |
Glutamate decarboxylase, resulting in glutamate (excitatory) not being broken down into Gaba (inhibitory) |
|
|
|
Lambert Eaton pre or post |
Presynaptic |
|
|
|
Myasthenia gravis pre or post |
Postsynaptic, blocks acetylcholine receptor |
|
|
|
Autosomal recessive disorder associated with night blindness and phytanic acid |
Refsum's disease |
|
|
|
Charcot-marie-tooth type 1A |
Pmp22 duplication on chromosome 17, autosomal dominant |
|
|
|
Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsies |
Autosomal dominant, this one is the deletion. Sausage appearance |
|
|
|
Antibodies associated with multifocal motor neuropathy |
Gm1 |
|
|
|
Conduction block, normal CSF, normal snap, cmap is demyelinating |
Multifocal motor neuropathy |
|
|
|
Conduction block |
Multifocal motor neuropathy |
|
|
|
DADS |
anti-MAG, poor response to IVIg/steroids |
|
|
|
Very elevated CSF protein, polyneuropathy |
POEMS |
|
|
|
Like Guillain-Barre but with altered mental status |
Porphyria |
|
|
|
Miller Fisher antibody |
Gq1b |
|
|
|
Guillain-Barre but with elevated WBC in CSF |
Sarcoidosis, polio, Lyme, HIV |
|
|
|
Conduction block means |
It's an acquired demyelinating disorder |
|
|
|
Second Wind phenomenon |
Mcardle's myophosphorylase deficiency. Forearm exercise Test shows no rise in lactate |
|
|
|
Amyloidosis |
Onset 50 in males. Fatigue, weight loss, associated with heart failure, autonomic neuropathy and orthostatic hypotension. Treatment is stem cell transplant |
|
|
|
Very prolonged distal latency |
DADS-M and anti-MAG neuropathy. Distal acquired demyelinating syndrome. Slow gait imbalance and sensory loss |
|
|
|
Vitamin e deficiency |
Fatty stools, posterior column dysfunction |
|
|
|
CMT1a duplication or HNPP deletion |
PMP22 |
|
|
|
Most common intra medullary spinal cord tumor |
Ependymoma |
|
|
|
Caudate head atrophy |
Huntington's disease |
|
|
|
Machado Joseph genetics |
SCA3, autosomal dominant, CAG trinucleotide repeat in ATXN3 |
|
|
|
Conversion rate of MCI to Alzheimer's |
15% per year |
|
|
|
Alexia without agraphia localization |
Left PCA; left occipital and splenium of corpus callosum. Cannot read, and cannot transfer visual to language input due to corpus callosum |
|
|
|
Neonatal seizures in the first 24 hours |
Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy |
|
|
|
Neonatal seizures, 24 to 72 hours. Days 1 until 3 |
Intracranial bleed (IVH, SAH) |
|
|
|
Neonatal seizures after day 3 |
Inborn errors of metabolism, they have begun to feed |
|
|
|
Gramophone speech |
Pick's disease, subset of frontotemporal dementia |
|
|
|
Congenital Myasthenia pathogenesis |
ACHR epsilon (not alpha)subunit |
|
|
|
Auditory pathway |
Cochlear nerve to the superior Olive in the Pons. To the lateral lemniscus still in the pons. Inferior colliculus and then medial geniculate nucleus in the midbrain. Then to the auditory cortex |
|
|
|
Only thalamic nucleus that does not project to the cerebral cortex |
Reticular nucleus |
|
|
|
Zellweger syndrome symptoms |
Polymicrogyria and pachygyria, hypotonia, hepatomegaly |
|
|
|
Trace alternans timeline |
40 until 44 weeks |
|
|
|
Composition of BBB |
Endothelial cells (tight junctions) Endfeet of astrocytes Pericytes |
|
|
|
Pes cavus, scoliosis, ataxia, upgoing toes |
Friedreich's ataxia, GAA repeat |
|
|
|
Superior orbital fissure syndrome |
CN 3, 4, V1, 6, ocular sympathetics (Horners). No V2 |
|
|
|
PKAN/Hallervorden-Spatz |
NBIA-1, PANK2 mutation, AR on chromosome 20 Parkinsonism, dystonia, dementia |
|
|
|
Wakefulness, while scanning complex picture causes this |
Lambda waves |
|
|
|
Central activity, attenuated by movement |
Mu activity |
|
|
|
Vacuolation of myelin along the intraperiod line |
Tri-ethyl Tin (neurotoxin) |
|
|
|
Foramen Lacerum |
ICA |
|
|
|
Jugular Foramen |
CN 9, 10, 11 |
|
|
|
Foramen spinosum |
Middle meningeal artery |
|
|
|
Cluster B |
Dramatic, unpredictable. Borderline Antisocial Histrionic Narcissistic |
|
|
|
Cluster A: Odd |
Paranoid, schizoid, schizotypal |
|
|
|
Cluster C: anxious |
Dependent OCD Avoidant |
|
|
|
Nucleus accumbens |
Pleasure Center, ventral tegmental area sends dopaminergic neurons |
|
|
|
Pleasure center/substance addiction |
Nucleus ac-cum-bens |
|
|
|
Motor nucleus for 9, 10, 11 |
Nucleus ambiguus |
|
|
|
C1-C7 exit above |
C8 to T1 exit below vertebrae |
|
|
|
Phenytoin and Warfarin interaction |
Increase the plasma availability of each other, mechanism unknown |
|
|
|
Eye of the Tiger sign, bilateral Globus pallidus hyperintensities |
PKAN, Hallervorden-Spatz, AR chr 20 |
|
|
|
Topiramate metabolism |
Hepatic |
|
|
|
Felbamate |
Blocks NMDA, potentiates GABA Aplastic anemia, liver failure |
|
|
|
Best for Rapid Cycling Mania/Depression |
Valproic acid |
|
|
|
Best for euphoric Mania |
Lithium |
|
|
|
Igg4 monoclonal antibody that inhibits leukocyte extravasation into the CNS |
Natalizumab |
|
|
|
H reflex |
Like a DTR |
|
|
|
AIDS dementia complex affects which brain cells |
Microglia |
|
|
|
Brainstem nucleus involved in salivation and gustatory function |
Nucleus solitarius (medulla) |
|
|
|
Central scotoma localization |
Anterior to the optic chiasm |
|
|
|
Layers of the meninges |
Dura (periosteal/meningeal) Arachnoid Pia |
|
|
|
Hartnup disease |
Autosomal recessive, niacin supplementation required |
|
|
|
Rimmed vacuoles |
Inclusion body myositis |
|
|
|
DiGeorge syndrome |
Catch 22 Cardiac defects Abnl Face Thymic hyoplasia Cleft palate Hypocalcemia Chromosome 22 |
|
|
|
OIRDA |
Associated with childhood absence epilepsy |
|
|
|
Medication which worsens atonic seizures |
Carbamazepine |
|
|
|
Origin of the anterior spinal artery |
Vertebral arteries |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter secreted by the climbing fibers of the cerebellum |
Aspartate - excitatory input |
|
|
|
Pre-eclampsia HTN |
>140mmHg |
|
|
|
Retrograde transport per day |
100 - 250 millimeters per day |
|
|
|
Prosody localization |
Non dominant hemisphere |
|
|
|
Mechanism of Statin induced myopathy |
Inhibition of synthesis of coenzyme Q10 |
|
|
|
SSRI and sleep |
SSRI cause REM suppression |
|
|
|
Benign familial neonatal epilepsy |
Kcnq2 mutation |
|
|
|
Sudden Awakening with dystonic movement or posture in a child |
Autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy |
|
|
|
Myoclonic - astatic epilepsy. Doose syndrome |
Myoclonic jerks of head or body, followed by loss of tone |
|
|
|
Landau-kleffner |
Acquired epileptic aphasia |
|
|
|
Panayiotopoulos syndrome |
Autonomic seizures. Mostly nocturnal. |
|
|
|
Antidepressant sedating at lower doses |
Mirtazapine. At higher doses its less sedating |
|
|
|
Weakness of wrist flexors and finger flexors more than extensors |
Inclusion body myositis |
|
|
|
A - beta protein aggregates |
Inclusion body myositis |
|
|
|
Serotonin syndrome vs. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome |
Serotonin syndrome has myoclonus |
|
|
|
Bilateral ptosis, contractures, weak cry and difficulty feeding and seizures |
Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy, autosomal recessive, FKTN |
|
|
|
SFEMG is highly sensitive or highly specific |
Highly sensitive for myasthenia gravis |
|
|
|
Seizure with olfactory aura |
Uncus of the temporal lobe |
|
|
|
Source of intraventricular hemorrhage in preterm infant |
Germinal Matrix |
|
|
|
Source of intraventricular hemorrhage in term infant |
Choroid plexus |
|
|
|
Outflow tract of the amygdala |
Stria terminalis |
|
|
|
Early Progressive muscular dystrophy with elbow contracture |
Emery dreifuss |
|
|
|
Deletion of DMD on Chr X |
Dystrophin is absent, onset by 5, wheelchair by 12. Duchennes |
|
|
|
Autosomal dominant muscular dystrophy with facial weakness and scapular winging |
Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy dystrophy |
|
|
|
Muscular dystrophy with ptosis dysphonia |
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, CGG mutation in French Canadians. AD, PABPN1 |
|
|
|
Only neurons in the cerebellum to provide an excitatory input |
Granule cells |
|
|
|
Muscles innervated by the trigeminal |
Tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini, anterior belly of digastric, mylohyoid |
|
|
|
Perifascicular atrophy with CD4 predominance |
Dermatomyositis. D is Fourth letter of alphabet, Fascicular |
|
|
|
Painless, endomysial inflammation, CD8. Very high CK |
Polymyositis |
|
|
|
Myoglobinuria after a forced March the military or a fasted state |
CPT deficiency |
|
|
|
Like Myasthenia without ptosis |
Progressive external opthalmoplegia |
|
|
|
Eye movement issues, retinitis, heart block, myopathy |
Kearns-Sayre |
|
|
|
Negri bodies |
Rabies |
|
|
|
Benign familial neonatal convulsion Channel abnormality |
Potassium Channel |
|
|
|
Ataxia, pulmonary infections, dilated conjunctival vessels |
Ataxia telangiectasia. Associated with leukemia |
|
|
|
Structural components of a Lewy Body |
Alpha-synuclein |
|
|
|
Periodic alternating nystagmus |
Phenytoin causes it, baclofen treats it |
|
|
|
Gluteus medius and Minimus innervated by |
Ipsilateral Superior gluteal nerve, responsible for abducting hip |
|
|
|
Inferior gluteal nerve innervates |
Gluteus maximus, which causes hip extension |
|
|
|
Vincristine side effect |
Loss of reflexes, followed by sensorimotor axonal polyneuropathy |
|
|
|
Most common location for neurosarcoidosis |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter of dorsal raphe nucleus |
Serotonin |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter of locus coeruleus |
Norepinephrine |
|
|
|
Myoclonus and night blindness |
Sialidosis type 1, also known as cherry red spot myoclonus syndrome |
|
|
|
Riluzole mechanism of action |
Effects sodium channels and reduces glutamate release |
|
|
|
Slowly Progressive but painless weakness and atrophy of one arm |
Hirayama disease, AKA monomelic amyotrophy |
|
|
|
Motor neuron disease with white blood cells elevated in CSF |
Polio, not GBS |
|
|
|
Encephalitis, high fever with nuchal rigidity, and acute flaccid paralysis |
West Nile |
|
|
|
Perioral fasciculations, sensory loss, gynecomastia |
Kennedy's, AKA spino bulbar muscular atrophy. CAG repeat |
|
|
|
Neuropathy involving face and hands first, non length dependent, with ataxia |
Sensory neuronopathy, dorsal root ganglion involvement leads to loss of peripheral sensory input leading to ataxia |
|
|
|
Sensory ataxia, with upgoing toes and nystagmus |
Friedreich's Ataxia, GAA repeat. Autosomal recessive |
|
|
|
Hamartin and tuberin |
Tuberous sclerosis proteins |
|
|
|
Post stroke depression |
Left orbitofrontal |
|
|
|
Innervation of gluteus medius, Minimus and tensor fascia Lata |
Superior gluteal nerve |
|
|
|
Roots of sciatic nerve |
L4, L5, S1, S2, S3 |
|
|
|
Gastrocnemius and Soleus |
Tibial nerve, S1 S2, plantar flexion |
|
|
|
Biceps femoris, it's in the upper leg |
Long head is tibial, short head is peroneal. Both are S1 S2 knee flexion |
|
|
|
Neurocysticercosis |
Albendazole, if calcified then symptomatic treatment only anti-seizure meds and steroids |
|
|
|
Low CSF chloride levels |
Tuberculosis meningitis |
|
|
|
Spinal ganglia, autonomic ganglia, ganglia of CN 5, 7, 9, 10, peripheral nerve sheath, meninges embryology |
Neural crest |
|
|
|
HCQ toxicity |
Skeletal muscle myopathy |
|
|
|
GD1A |
AMAN |
|
|
|
Niemann-pick type c |
Vertical gaze palsy, cholesterol accumulation liver and spleen, always fatal |
|
|
|
Decorticate above midbrain such as thalamus |
Decerebrate below the midbrain |
|
|
|
Marfanoid habitus, lens dislocation, long and thin fingers |
Homocystinuria, supplement with B6 and B12 |
|
|
|
Inflammatory infiltrates in the endomysium |
IBM |
|
|
|
Mesial temporal sclerosis prognostic/diagnostic value |
FDG-PET, not SPECT |
|
|
|
NREM arousals |
Confusional arousals, sleepwalking, sleep terrors |
|
|
|
Medication that will not exacerbate absence or myoclonic seizures |
Topiramate |
|
|
|
Automatisms and dystonia seizure |
Temporal lobe, ipsilateral to the side with automatisms |
|
|
|
Hypocretin: lateral hypothalamus |
Narcolepsy with cataplexy, CSF hypocretin is reduced, if no cataplexy then hypocretin is normal |
|
|
|
Benzo = GABA-A = opens Cl channels |
Baclofen = GABA-B |
|
|
|
TCA MoA |
SNRI but so muscarinic, histamine receptors (not selective) |
|
|
|
Atypical antipsychotics: Quetiapine, olanzapine, ziprasidone mechanism of action |
5-ht 2A mainly and D2 receptors |
|
|
|
Side effects of lithium |
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus leading to hypernatremia, Tremor, acne |
|
|
|
Reduced complement levels, constitutional symptoms, arthralgias |
Cryoglobulinemia |
|
|
|
Erb's palsy |
Upper trunk lesion |
|
|
|
Myotonia worsens with exercise |
Paramyotonia (SCN4A - sodium channel) |
|
|
|
Becker and duchenne inheritance |
X-linked recessive |
|
|
|
Central core myopathy |
Autosomal dominant, RYR1, malignant hyperthermia |
|
|
|
Distal myopathy, posterior leg compartment |
Miyoshi myopathy |
|
|
|
Pure autonomic failure is a gradual time course |
Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy occurs over weeks |
|
|
|
LGMD AD are 1 (myotilin, lamin, caveolin) |
AR are 2 (Calpain, fukutin) |
|
|
|
Gastroenteritis, followed by myalgias edema of eyelids, diplopia, limb weakness |
Trichinosis,, which has elevated eosinophils and is also called a leptospirosis |
|
|
|
Autosomal recessive condition caused by a deficiency of acid maltase also known as alpha 1 4 glucosidase |
Glycogenosis type 2, acid maltase deficiency |
|
|
|
Lamin (AD) and emerin (X-linked) |
Emery dreifuss, elbow contractures |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic nervous system is cranial and sacral |
Cranial portion is CN 3, 7, 9, 10 Sacral is S2 to S4 |
|
|
|
T1 to L2 |
Preganglionic neurons of sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
|
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers release |
Norepinephrine. Preganglionic sympathetic release acetylcholine, and all parasympathetic release acetylcholine |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic neurotransmitter |
Acetylcholine is both pre and post. Also pre ganglionic sympathetic |
|
|
|
Horner's syndrome anhidrosis |
Lesions in the ICA will not have anhidrosis. Pancoast tumor, medullary infarct will |
|
|
|
Horner syndrome anisocoria worse in the |
Dark |
|
|
|
Myotonia congenita, Thomsen's is childhood-onset |
Becker's is adult onset and more severe |
|
|
|
GCG repeat, PAPB2 gene |
Oculopharyngeal dystrophy |
|
|
|
Non paraneoplastic stiff person syndrome |
Anti Gad |
|
|
|
Paraneoplastic stiff person syndrome |
Anti-amphiphysin |
|
|
|
Tongue protrusion dystonia |
Neuroacanthocytosis |
|
|
|
Dermatomyositis cancer |
Ovarian, lung, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, non-hodgkin *Dermato is more associated with cancer |
|
|
|
Polymyositis cancer |
Non-hodgkin lymphoma, lung and bladder |
|
|
|
Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis or sensory neuropathy |
Anti-hu |
|
|
|
Verocay bodies |
Schwannoma |
|
|
|
Radiation myelopathy time course |
Transient develops at three months Delayed develops at 6 months and remains |
|
|
|
Fever, lethargy, flaccid quadriparesis |
West Nile which is a flavivirus |
|
|
|
Adrenomyeloneuropathy |
Form of adrenal leukodystrophy, x-linked inheritance, abcd1 Gene on chromosome X. Men in their twenties with spastic paraparesis, neuropathy and cognitive impairment due to accumulation of a very long chain fatty acids |
|
|
|
Horners syndrome localization |
Spinal cord lesions above t1 |
|
|
|
Neurosyphilis treatment |
Intravenous penicillin G, 24 million units daily for 14 days |
|
|
|
Conus medullaris is symmetric sensory deficits |
Cauda equina is asymmetric with radicular pain. Both LMN |
|
|
|
Spinal canal anatomy |
Anterior longitudinal ligament is anterior to vertebral bodies than posterior longitudinal ligament is posterior to them then spinal cord and then ligamentum flavum is behind that |
|
|
|
SMAs, 1 most severe, 4 least |
EMG shows large polyphasic motor units, biopsy shows atrophy |
|
|
|
Active denervation |
Sponataneous activity |
|
|
|
Chronic denervation |
Reduced recruitment, large MUPs |
|
|
|
Neonatal lactic acidosis, ataxia, nystagmus, dysarthria and lethargy |
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency |
|
|
|
Low CSF glucose with normal serum glucose and seizures |
Glucose transporter type 1 deficiency |
|
|
|
Anterior neuropore Fusion deficits are anencephaly and encephalocele |
Posterior neuropore Fusion deficits are spina bifida and myelomeningocele |
|
|
|
Cells of origin of central nervous system |
Ectoderm, neural tube (brain and spinal cord is a tube) |
|
|
|
Cell of origin of peripheral nervous system |
Ectoderm, neural crest cells |
|
|
|
Reduced visual acuity, panhypopituitarism, absent septum pellucidum |
Septo-optic dysplasia |
|
|
|
Akinetic mutism localization |
Anterior cingulate gyrus |
|
|
|
Risk factor for permanent visual loss in GCA |
Elevated PLT |
|
|
|
Palatal myoclonus lesion |
Mollaret's triangle = Dentate nucleus, Red nucleus, Inferior olive |
|
|
|
Vitamin K is depleted by PHB |
Supplement in labor |
|
|
|
Locus ceruleus localization |
Pons |
|
|
|
Newborn with ketoacidosis, pancytopenia, bleeding disorders, elevated propionic acid levels |
Propionic acidemia, autosomal recessive |
|
|
|
Filipin test (ability of cultured fibroblasts to esterify cholesterol) |
Abnormal in niemann-pick type c, NPC1 gene |
|
|
|
Demyelination of Central and peripheral nervous system, accumulation of sulfatide |
Metachromatic leukodystrophy, autosomal recessive, deficiency in arylsulfatase A |
|
|
|
Very long chain fatty acids |
Zellweger also known as cerebrohepatorenal syndrome |
|
|
|
Aggressiveness, spasticity, incoordination. T2 hyperintensities |
Adrenoleukodystrophy, x-linked recessive, abcd1 Gene |
|
|
|
Four-layer lissencephaly with intractable seizures |
Miller-dieker syndrome |
|
|
|
Mad Sam or lewis-sumner syndrome |
Upper Limb predominant asymmetric CIDP |
|
|
|
Distal, symmetric CIDP |
DADS, IgM |
|
|
|
Chronic Miller Fisher |
CANOMAD, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia |
|
|
|
CGG repeat, mental retardation |
CGG = child with giant gonads Fragile X |
|
|
|
Betz cells |
Upper motor neurons of the nervous system, found in primary motor cortex, layer 5 |
|
|
|
Molecular layer External granular layer External pyramidal layer |
Internal granular layer Internal pyramidal layer Multiform layer Subcortical white-matter |
|
|
|
Encephalo trigeminal angiomatosis, gyral calcifications |
Sturge-weber syndrome. Thought to be due to persistence of embryonal blood vessels |
|
|
|
Opisthotonos with hypersensitivity to stimuli and death by Age 2 |
Krabbe disease infantile form |
|
|
|
Macrocephaly, psychomotor developmental delay, spasticity, seizures, GFAP |
Alexander's disease |
|
|
|
Tigroid MRI in a kid |
Pelizaeus-merzbacher disease. This is a hypomyelinating leukodystrophy that is x-linked recessive |
|
|
|
Intra medullary spinal cord tumor |
Ependymoma |
|
|
|
Alzheimer's genes |
Chr 14 Chr 1 |
|
|
|
Anterior nucleus of the thalamus |
Memory formation |
|
|
|
Dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus |
Abulia, anterograde Amnesia, social disinhibition |
|
|
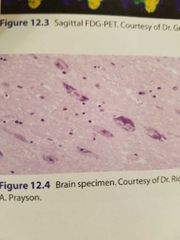
|
Lewy body |
|
|
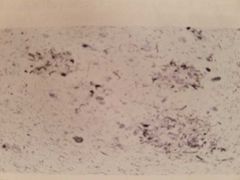
|
Amyloid neuritic plaques, Alzheimer's disease |
|
|
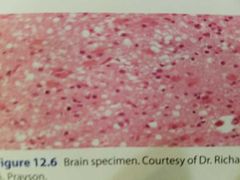
|
CJD, Chr 20 |
|
|
|
Hypometabolism of the posterior temporal and parietal lobes |
Alzheimer's |
|
|
|
Bunina bodies |
ALS |
|
|
|
Prosopagnosia localization |
Inability to recognize faces, lesions of the bilateral fusiform gyri which is the temporal occipital region as can be seen in a bilateral PCA infarct |
|
|
|
Prefrontal cortex with social disinhibition and utilisation behavior |
Orbitofrontal |
|
|
|
Prefrontal cortex with the motivation, lesions lead to abulia |
Dorsomedial prefrontal cortex |
|
|
|
Prefrontal cortex involved judgement and problem solving |
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex |
|
|
|
Leber's |
Mitochondrial, associated with WPW. Painless vision loss only in males |
|
|
|
Like AION but no disc swelling and associated with spine surgeries |
PION |
|
|
|
Ipsi CN3, contralateral hemiplegia |
Weber, base of the midbrain |
|
|
|
Ipsi CN3, contra ataxia and tremor |
Claude, tegmentum of midbrain |
|
|
|
Ipsi CN3, contra hemiplegia and tremor |
Benedikt |
|
|
|
Meningitis affecting the base of the brain, such as multiple cranial neuropathies |
Tuberculosis meningitis |
|
|
|
First branch of the internal carotid artery |
Ophthalmic artery supplies cranial nerve 2 |
|
|
|
DT time period |
48 to 96 hours |
|
|
|
Caffeine MoA |
Adenosine |
|
|
|
PCP and ketamine mechanism of action |
Nmda receptor antagonist |
|
|
|
Garlic breath, diffuse rash, nausea, vomiting |
Arsenic poisoning |
|
|
|
Nucleus solitarius is sensation and taste |
Nucleus ambiguus is motor to pharynx and larynx |
|

