![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of muscle?
|
Skeletal, smooth and cardiac
|
|
|
What does 'striated' mean?
|
Having parallel lines or grooves on the surface
|
|
|
Skeletal muscles deal with voluntary/involuntary movements? Controlled by which NS?
|
Voluntary, sympathetic NS
|
|
|
What are the two types of skeletal muscle fibres?
|
Red or White
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of red muscle fibres? (Skeletal)
|
High myoglobin and mitochondria content
Slow twitch Energy from aerobic respiration Sustained and vigorous activity |
|
|
What are the characteristics of white muscle fibres? (Skeletal)
|
Fast twitch
Greater rate of contraction than red Fatigue more easily |
|
|
What is muscle?
|
A bundle of parallel fibres
|
|
|
What is a sarcomere?
|
A unit of a myofibril
|
|
|
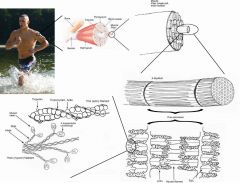
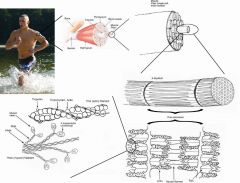
What's special about the nuclei of skeletal muscle?
|
It is multinucleated and found at the periphery of the cell
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is special about the nuclei of smooth muscles?
|
It is mononucleated and central
|
|
|
Smooth muscle is responsible for voluntary/involuntary actions? Which NS does it use?
|
Involuntary, autonomic NS
|
|
|
Where is smooth muscle located?
|
Digestive tract, bladder, uterus, blood vessel walls
|
|
|
Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle does not contain...
|
Striations
The filaments lack the organisation of skeletal sarcomeres |
|
|
What are the two filaments of muscle?
|
Actin and myosin
|
|
|
Which muscle types are myogenic?
|
Cardiac and Smooth
|
|
|
What is cardiac muscle like in relation to the other types?
|
A mixture of both - stirated in sarcomeres but autonomous
|

