![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Thrombocytes (platelets)
|
Forms clot to stop bleeding
|
|
|
|
erythrocytes (RBCs)
|
oxygen carrying cell
|
|
|
|
leukocytes (WBCs)
|
general name for white blood cells
|
|
|
|
neutrophils
|
60% - 70% of all WBCs
|
|
|
|
anemia
|
a deficiency of erthrocytes
|
|
|
|
monocyte and lymphocyte
|
two types of agranulocytes
|
|
|
|
basophils
|
0.5 - 1% of all WBCs
|
|
|
|
lymphocytes
|
20 - 25% of all WBCs
|
percentage of WBCs
|
|
|
eosinophils
|
WBC with red-stained granules
|
|
|
|
monocyte
|
largest WBC
|
|
|
|
lymphocyte
|
The nucleus of this WBC is 90% cell size
|
nucleus size
|
|
|
38-45
|
normal hematocrit range in female
|
|
|
|
neutrophils/lymphocytes
|
elevated numbers of this WBC in bacterial infections
|
|
|
|
eosinophils
|
elevated numbers of this WBC seen in parasitic infections
|
|
|
|
lymphocytes
|
elevated numbers of this WBC seen in viral infections and leukemia
|
elevated numbers
|
|
|
Lindsay had a differential WBC count that showed elevated eosinophils
|
parasitic infection or allergic reaction
|
|
|
|
fatigued with a hematocrit of 36%
|
anemia
|
|
|
|
platelet count of 100,000
|
Thrombocytopenia (hemophilia)/blood clotting
|
|
|
|
AB+ what type of blood can she receive in a transfusion
|
A, B, AB, O (+)
|
|
|
|
Has O- blood received O+ blood. will he have a transfusion reaction
|
no not after first exposure
|
|
|
|
Stacy has antibody A in her blood with no Rh antigen. What is her red blood cell type ?
|
A-
|
|
|
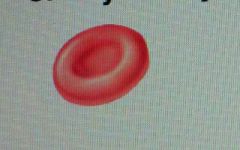
|
red blood cell or erythrocytes
|
|
|
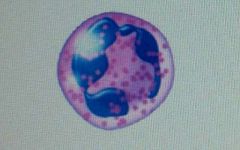
|
neutrophils (granular leukocytes)
|
|
|
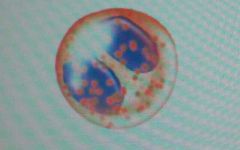
|
eosinophils (granular leukocytes)
|
|
|
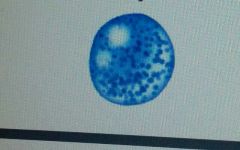
|
basophils (granular leukocytes)
|
|
|
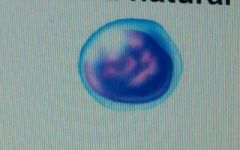
|
lymphocytes (agranular leukocytes)
|
|
|
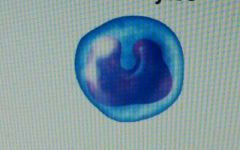
|
monocyte (agranular leukocytes)
|
|
|

|
platelets
|
|

