![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

what is the main actin filament found in the large cells
|
spectrin
|
|

what is the main function of this cell?
|
phagocytosis
|
|

what is the immediate precursor of the smaller cells?
|
megakaryocytes. platelet demarcation channels mark the boundaries of where the platelets bleb off.
|
|

what is the major enzyme found in the large cell and what is its function?
|
carbonic anhydrase. it catalyzes the following reaction: H20 + CO2->H + HCO3
|
|

what is the major protein associated with anion transport in the large cell?
|
band 3. aka coupled anion transporter
|
|

what portion of hemoglobin is responsible for oxygen transport? what is the maximum number of oxygen molecules it can transport?
|
Heme (iron). 4 is the max
|
|

the large cell does not have MHC molecules to allow for self recognition. What are the two alternative sets of self recognition proteins it uses?
|
A, B and Rh
|
|

what is the immediate precursor of the large cell?
|
reticulocyte
|
|

where is the place of origin of the large cell?
|
red bone marrow
|
|

what is the major place of storage of the smaller cell?
|
spleen
|
|
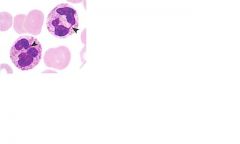
what are some of the major enzymes associated with this cell and what are their functions?
|
Collagenase-degrades ECM of bacteria
Defensins- act like antibodies Myeloperoxidases-reacts with hydrogen peroxide to generate potent bacteria killing oxidants (bleach) Lactoferrin-actively binds iron (essential to bacterial nutrition) Lysozyme-breaks down the cell wall of some gram positive bacteria |
|

what is the major function of this cell?
|
phagocytosis, specifically of antigen/antibody complexes
|
|

what is a major cell surface specialization found on these cells?
|
IgE receptors
|
|

how do these cells affect inflammation?
|
by inactivating the leukotrienes and himstamine produced by other cells
|
|

what are 2 major proteins associated with the function of these cells and how do they perform this function?
|
MBP and eosiniophilic cationic proteins form transmembrane pores in parasites
|
|

what is a major cell surface specialization found on these cells?
|
IgE receptors
|
|

what are the azurophilic granules located in these cells?
|
lysosomes
|
|

what is the function of this cells?
|
differentiate into macrophages. phagocytosis
|
|

what is the origin of this cell?
|
MPS
|
|

what is the immediate precursor of this cell?
|
promonocyte
|
|

is this cell capable of mitosis
|
no
|
|
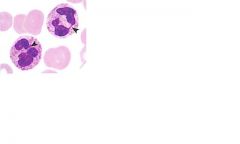
what is the immediate precursor of this cell?
|
neutrophilic band
|
|
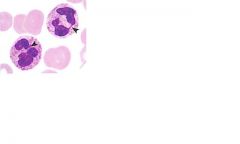
is this cell capable of mitosis?
|
no
|
|
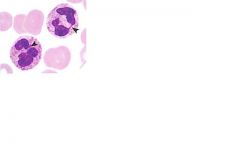
what is the origin of this cell?
|
red bone marrow
|
|
what type of intermediate filament is found specifically in this cell?
|
vimentin
|
|

what is the immediate precursor?
|
eosinophilic band
|
|

what is the origin of this cell?
|
bone marrow
|
|

is this cell capable of mitosis?
|
no
|
|

what is the process of production of the large cell called? what is the name of the growth that initiates this process? where is the growth factor made?
|
erythropoiesis, erythropoietin, KIDNEY!
|
|

what is the process of making the smaller cells called? what is the growth factor associated with it? where is the growth factor manufactured?
|
thrombopoiesis, thrombopoietin, bone marrow and LIVER
|
|

what is the CFU for the production of the large cells?
|
BFU-E for fast spurts; CFU-E for constant production
|
|

what is the CFU for the smaler cells?
|
CFU-Meg
|

