![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Name of this particular device |
Brightfield Microscope
|
|
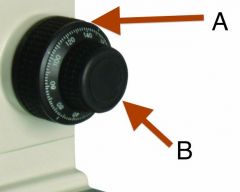
Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |
A: Coarse adjustment knob - moves stage up and down at larger intervals
B: Fine adjustment knob - moves the stage up and down at fine, almost invisible levels. |
|

Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |
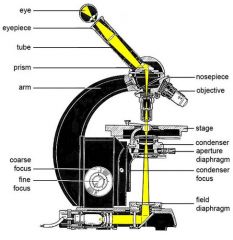
Illuminator
Source of white light source - controlled by dimmer |
|

Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |
Ocular lens - NOT the objective lens. Think ocular = related to eyes or vision. Definitely not objective.
Lens through which specimens are observed. Our microscopes have 10x magnification. |
|

Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |
Nosepiece - used to rotate the objective lenses into position. |
|

Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |
Objective lens - provides various powers of magnification. Ours are 10x, 20x, 40x, and 100x) |
|

Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |
Mechanical stage - where the slide is clipped. Controlled by the fine and coarse adjustment knobs (move up and down), as well a mechanical mechanism to the side that moves it horizontally. |
|
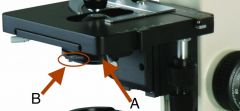
Name and Function on Brightfield Microscope |

A. Condenser (right) system of lenses that collects the light coming from below and directs it up onto the slide. B. Iris (aperture) Diaphram (left) Opens and closes to control the amount of light that reaches slide - provides contrast. |
|
|
Why do we use oil at the 100x magnification level? |
Due to the focal point being so small, any light lost from the different refractions between glass and air means a significant loss of resolution. Since oil has the same light refraction as glass, it provides a channel for the light to continue up into the objective lens without loss. |
|
|
Does the condenser do anything to help magnify the slide? |
No! The condenser only condenses the light coming up from the illuminator onto the slide above. |
|
|
Total Magnification |
The ocular magnification multiplied by the objective magnification. Think: you have regular vision and when viewed through a 10x lens you have 10x vision (1x10). If you have 10x vision and you're viewing it through a 10x lens, you have 100x vision (10x10). |
|
|
Resolution (definition and resolution limit for our microscopes) |
The ability to distinguish fine detail. Specifically, to see two objects as individual objects without them blending together. Limit for our microscopes: 0.2 micrometers (human limit 200 micrometers or 0.2mm) |
|
|
Resolving Power (formula and need light intensity?) |
Represented by R which predicts how easy it will be to distinguish two close points from one another. The higher d is, the further away two things need to be for you to distinguish them. You can cheat and use shorter wavelengths (blue light) to lower d without changing the NA.
d(distance of resolving power)= .5 lambda(wavelength of light) / NA(numerical aperture of the lens - should be written on the side where the magnification is written)
Good light intensity is a must for greater resolving power!! Especially with stained specimens |
|
|
Contrast (definition) |
Allows one object to be distinguished from another. Done with different light differences between image and background (can be done with iris diaphragm). Also achieved via staining |
|
|
Field of View (FOV) |
circular field seen through ocular lens. |
|
|
Starting position with Brightfield Microscope (prepared to begin examining specimen) |
Microscope light on, glass slide clipped into stage, specimen centered over the light, 10x lens set, stage at its highest point.
Stained specimen? Open iris diaphragm and make sure condenser is raised as high as it goes. Need lots of light for best resolution (contrast not as much of an issue here) |
|
|
Bringing specimen into focus using Brightfield Microscope |
After starting position, use coarse adjustment knob to lower the stage until specimen is in view. Once in focus, turn the nose (parfocal) to increase the magnification of the specimen, fine tuning with the fine adjustment knob as necessary. Before using the 100x objective lens, put a drop of oil over the center of the slide so when you click it over, the lens is immersed in it. |
|
|
Parfocal (definition Brightfield Microscope) |
The Brightfield microscope objective lenses do not require large amounts of refocusing to go from one magnification level to another due to their design. You can switch between them and fine focus as necessary |
|
|
Why calibrate the ocular micrometer on a Brightfield Microscope? |
To make sure the objective lens is properly calibrated. At 100x the ocular micrometer should have 100 notches in 0.1mm of the stage micrometer when it's in focus. If it's not, final measurements need to be adjusted proportionately. |
|
|
How do you calibrate the ocular micrometer at 100x on the Brightfield Microscope |
Clip on the stage micrometer and bring it into focus like you would any other specimen. Match up the starting line of the ocular micrometer to whatever line makes sense on the in-focus stage micrometer. If you're at 100x, then 100 lines on the ocular micrometer should fit in .1millimeter |
|
|
millimeter to micrometer |
1 mm = 1000 micrometers .1 mm = 100 micrometers
|
|
|
Putting the Brightfield Microscope away |
(if applicable) Wipe away any oil from the slide and objective lens using alcohol. Set up the observation lens 10x and raise the stage all the way. Turn off the light and cover the machine. |

