![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Q. Basal Metabolic Rate |
(BMR) is the amount of energy per unit time that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. |
|
|
|
Thiamine (Vitamin B1) |
· Beriberi (result from a diet of carbohydrate rich and thiamine deficiency). · Wernicke-Korsaskoff syndrome (thiamine related disease mostly found in chronic alcoholic’s due to their poor dietary lifestyle). |
|
|
|
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) |
Riboflavin decomposes when exposed to visible light (photolabile). This characteristic can lead to riboflavin deficiencies in newborns treated for hyperblirubinemia by phototherapy. |
Deficiency. It is often seen in chronic alcoholic’s due to their poor dietetic habits. |
|
|
Niacin (Vitamin B3) |
· Niacin is NOT a true vitamin in the strictest definition since it can be derived from amino acid tryptophan. Deficiency: . Severe symptoms. Depression, dermatitis and diarrhea, are associated with the condition known as PELLAGRA. |
|
|
|
Pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) |
· It is formed from b-alanine and pantoic acid. · Source. Whole grain cereals, legumes, and meat. · Deficiency. Extremely rare for it is readily available food sources. |
|
|
|
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine, Pyridoxal, and Pyridoxamine): |
Q. Drugs (↓) pyridoxal isoniazid for tuberculosis, and penicillamine (for rheumatoid arthritis and cystinurias). Q. Diclectin (vitamin B6 R10 mg+ doxylamine 10 mg) is used for the treatment of nausea & vomiting in pregnancy (morning sickness). Up to 4 tabs daily (2 bedtime, 1 in morning and 1 afternoon). |
Avoid vitamin B6 with levodopa because, vitamin B6 increases the peripheral conversion of levodopa to dopamine thereby it gives nausea and vomiting. Q. Deficiency (<10nmol/L): Peripheral neuropathy, convulsions, sideroblastic anemia, and hyperirritability. |
|
|
Biotin (Vitamin B7) |
Deficiency. Excessive consumption of raw eggs due to affinity of egg white protein, AVIDIN, for biotin preventing |
|
|
|
Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) |
- is deficient in elderly - It is only nutrient require gastric secretion (intrinsic factor) to be absorbed from GIT - vitamin that is deficient in vigan diet (NO dairy and No meat) - Vegetarians have deficiency of vitamins - Deficiency: Megaloblastic anemia. |
Deficiency: Q. Megaloblastic anemia. |
|
|
Folic Acid (vitamin B9) |
- Chemical ring structure in folic acid that binds to para aminobenzoic acid is; pteridine ring Folic acid structure consist of? Pteridyl- PABA -glutamate - Deficiency: Folic acid deficiency in pregnancy can cause neural tubule defect. - Deficiency of folic acid can cause megaloblastic anemia. |
• Q. Drugs that ↓ folic acid: Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, phenytoin), oral contraceptives, methotrexate, 5-flurouracil, sulfonamides, trimethoprim, sulfasalazine and dapsone. |
|
|
Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) |
1) What vitamin is deficient in smokers? Smoking severely decreases vitamin C in blood. 2) Women have more vitamin C then men. 3) Essential for the synthesis of “collagen” in connective tissues. |
Deficiency: Q. Scurvy. |
|
|
Vitamin A |
- Beta carotene is a precursor of vitamin A. - Rhodopsin is active form of vitamin A in vision. (11-cis retinal to 11-trans retinal). - Vitamin A overdose can cause? Toxicity - Deficiency. Xerophthalmia. Night blindness (11 cis retinoic acid) in rhodopsin pigment. |
|
|
|
Vitamin D |
- It is a steroid hormone. Active form is 1, 25-dihydroxy cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) Ergocalciferol (D2) - Chronic renal failure can cause deficiency of vitamin D3 - Deficiency: Rickets (weak bones and decaying teeth) in children and osteomalacia in adult |
1) Vitamin D3 is steroidal hormone 2)What vitamin is deficiency in chronic renal failure? 3) What is dose of vitamin D for > 50y ? 800 U 4) Infants on breast-feeding have deficiency of? Vitamin D drops 5) Active vitamin D is? D3 (1,25 dihydroxy cholecalciferol) 6) Deficiency of Vitamin D? Osteomalacia, osteoporosis, rickets. |
|
|
a-Tocopherol (vitamin E) |
Storage site of vitamin E is in adipose tissue (fatty tissues). Alpha tocopherol is the strongest antioxidant among all tocopherols. Occurs only with fat malabsorption. Symptoms Q. Increase in red blood cell fragility (increase cell integrity) |
|
|
|
Vitamin K |
- Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone) is derived from green vegetables - Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone) is produced by intestinal bacteria. - Vitamin K3 is a synthetic menadione. When vitamin K3 is administered. It will be alkylated to one of the vitamin K2 forms of menaquinone. |
Q. Vitamin K is antidote of warfarin. |
|
|
deficiency |
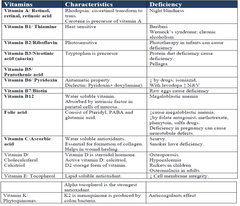
Vitamin A Night blindness Vitamin B1 Beriberi (nervousness, paralysis of muscles) - Vitamin B2 Ariboflavinosis - Vitamin B3 Pellagra - Vitamin B5 Paresthesia - Vitamin B6 Sideroblastic anemia - Vitamin B12 Megaloblastic anemia - Vitamin C Scurvy, swelling gum - Vitamin D Rickets & osteomalacia - Vitamin K Non-clotting of blood or bleeding |
|
|
|
diet |
DASH diet: Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension focuses on more vegetable, fruit and low-fat dairy, fish, nuts, poultry and whole grain. Keto diet: Low carbs, high fat and high proteins. May reduce frequency of seizure. Q. Functional Foods: also known as nutraceuticals are food ingredients that offer health benefits in addition nutrition value. Examples fortified with vitamins, minerals. Probiotics or fiber. Some fruits and vegetable with high antioxidants. |
|
|
|
Infants nutrition |
· Formula milk ( cow milk-based formula, lactose free cow milk based formula, soy protein isolate based formula, hydrolyzed protein formula, amino acid based formula, pre-thickened formulas). · Iron fortified formula milk (birth to 6 months). |
|
|
|
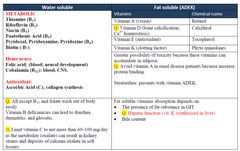
water and fat soluble vit |
|
|

