![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a chromosome? |
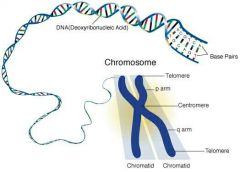
-DNA in a coiled form -Formed during interphase of cell division in animals and plants - Made of 2 identical sister chromatids joined by a centromere -Carries 2 copies of the same DNA molecule |
|
|
What is cell division? |
-The formation of new cells in multicellular organisms -There are two methods. Mitosis and Meiosis
|
|
|
What is Mitosis |
The production of genetically identical cells for growth and repair of tissues |
|
|
What is Meiosis? |
The production of genetically different haploid cells as gametes for sexual reproduction |
|
|
What are the stages of Mitosis? |
Interphase/Mitosis/Cytokinesis |
|
|
What are the stages of interphase? |
G1: Protein synthesis S: DNA replication ( Doubles set of DNA) G2: Organelle synthesis |
|
|
What are the stages of Mitosis? PMAT |
Prophase: DNA coils to form chromosomes, nucleus breaks down, spindle fibres form Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and attach to spindle fibre via the centromere Anaphase: spindle fibres pull, centromere splits, sister chromatids move to opposite ends Telophase: chromatids uncoil, nucleus reforms ( left with two genetically identical nuclei |
|
|
What is Cytokinesis? |
Separation of the cell into two cells Each receives a nucleus and organelles and cytoplasm |
|
|
What is cancer? |
Uncontrolled cell division( Mitosis) Caused by almost no time spent in interphase |
|
|
How do bacteria do cell division? |
Binary Fission They copy their DNA ( Single loop and plasmids) and then separate into new genetically identical bacteria ( Asexual reproduction) |
|
|
What are the two types of microscopes? |
Light and electron (Transmission and Scanning) |
|
|
How to judge a microscope? |
By Magnification and Resolution |
|
|
What is Magnification? |
How much larger the image size is compared to the actual size |
|
|
What is the order of highest to lowest Magnification microscopes? |
TEM>SEM>LM |
|
|
Formula for Magnification? |
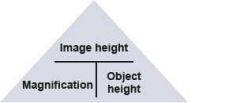
|
|
|
What are the conversion of units? mm micrometers and nanometers? |
1 mm = 1000 micrometers 1 micrometers = 1000 nanometers |
|
|
Why do electron microscopes have a higher resolution? |
Electron microscopes use electrons which have a shorter wavelength ( light microscopes use light which have a larger wavelength) |
|
|
What is the difference between a TEM and a SEM |
In transmission the electrons pass through the specimen In scanning the elections bounce off the specimens surface |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a TEM? |
Advantage = highest Magnification and highest resolutions Disadvantage = Only works in vacuum so specimen has to be dead, specimen needs to be thin, 2D image in black and white |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a SEM |
Advantage= produces a 3D image Disadvantage = works in a vacuum, black and white,. Artefacts produced |
|
|
What is the definition of resolution? |
The minimum distance that two very close objects can be distinguished |
|
|
What are the main steps of Cell Fractionation? |
1:Breaking down the tissue into cells 2: add cold/Isotonic/Buffer solution 3: Homogenate to break open cells and release the organelles 4: filter to reduce the large debris and intact cells 5:centrifuge. Spin at low speed which results in the largest organelle being at the bottom ( nucleus) and leaves the rest as a supernatant. Spin at a higher speed means the next heaviest is the pellet |
|
|
Organelles by size? |
Nucleus Chloroplast Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Lysosomes Ribosomes |

