![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleic acids are polymers. True or false? |
True |
|
|
What are nucleic acids made up of? |
Many repeating units called nucleotides |
|
|
What are nucleotides made up of? |
Three components: One of more phosphate groups A Pentose sugar An organic nitrogenous base |
|
|
How are the three components of nucleotides combined? |
Condensation reaction |
|
|
What does organic nitrogenous base contain? |
Nitrogen |
|
|
What are the three main nucleotides? |
DNA, RNA and ATP |
|
|
What is ATP? |
ATP is a nucleotide |
|
|
What does the symbolic form of a nucleotide look like? |
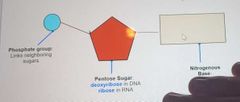
|
|
|
What are the bases in DNA? |
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine |
|
|
What are the bases in RNA? |
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Uracil |
|
|
What are the difference between the bases in DNA and RNA? |
DNA has thymine and not uracil RNA has uracil and not thymine |
|
|
Describe the structure of ATP? |
It has an extra phosphate added to it (aswell as the components of nucleotides) so we say it has been phosphorylated |
|
|
What does ATP stand for? |
Adenosine triphosphate |
|
|
What is the function of ATP? |
ATP is the universal energy currency do the cell - it supplies energy for all reactions in all cells in all organisms |
|
|
Describe what ATP looks like |
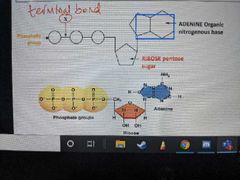
|
|
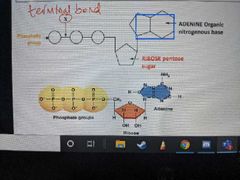
What does W represent? |
The phosphate group |
|
|
How many phosphate groups does ATP contain? |
3 |
|
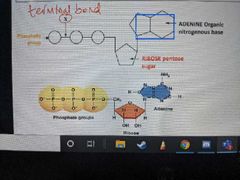
What does Y represent? |
The Pentose sugar |
|
|
What is the Pentose sugar in ATP called? |
Ribose |
|
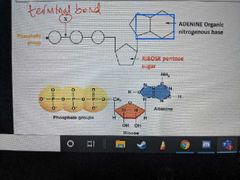
What does Z represent? |
An organic nitrogenous base |
|
|
What is the organic nitrogenous base in ATP called? |
Adenine |
|
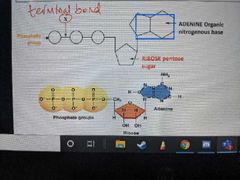
How is bond C formed? |
Condensation reaction |
|
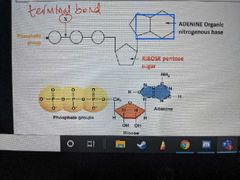
How is bond X broken? |
Hydrolysis |
|
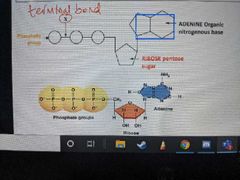
How much energy so released when bond X is broken? |
30.6kJ/mol |
|
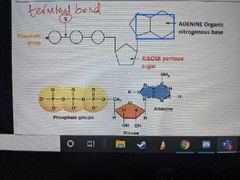
What enzyme catalyses the hydrolysis of bond X? |
ATPase |
|
|
Draw ATP |
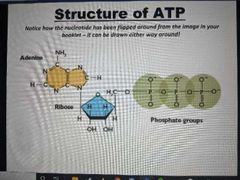
|
|
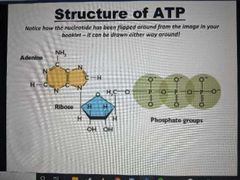
What portion of this is adenosine? |
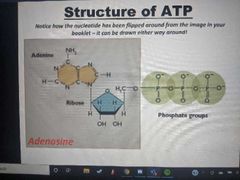
|
|
|
What is the SIMPLE structure of ATP |
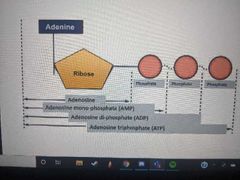
|
|
|
What type of bond is present between the phosphate groups in ATP? |
Covalent bonds |
|
|
Are covalent bonds stable or unstable? |
Unstable |
|
|
What does the instability of covalent bonds result in? |
They are easily broken by hydrolysis |
|
|
What does the hydrolysis reaction of ATP involve? |
The addition of a water molecule and the removal of the terminal phosphate group |
|
|
What is produced on the hydrolysis reaction of ATP? |
ADP Pi |
|
|
What type of reaction is the hydrolysis reaction of ATP, and why? |
Exergonic react It releases 30.6kJ/mol of energy |
|
|
What is the equation for the hydrolysis of ATP? |

|
|
|
What is the equation for the hydrolysis reaction of ATP, including pictures? |

|
|
|
How do you reform ATP after it has been hydrolysed? |
Condensation |
|
|
How is energy transferred by ATP |
The energy-releasing exergonic reactions and the enrgy-requiring endogonic reactions are always coupled together so that energy is transferred. This is the inter-conversion of ATP |
|
|
Draw a diagram of the inter-conversion of ATP |
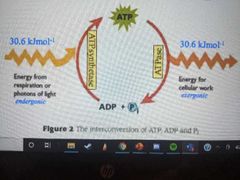
|
|
|
What are the uses of ATP |
Metabolic processes (synthesis of organic molecules) Active transport Movement Nerve transmission Secretion |
|
|
Describe the use of ATP in metabolic processes (synthesis of organic molecules) |
To build large, complex molecules from smaller, simpler molecules. E.g. the synthesis of DNA from nucleotides, polypeptides from amino acids |
|
|
Describe the use of ATP in active transport |
To change the shape of carrier proteins in cell membranes to allow molecules and ions to be transported against a concentration gradient |
|
|
Describe the use of ATP in movement |
For muscle contraction |
|
|
Describe the use of ATP in nerve transmission |
Sodium-potassium pumps actively transport sodium and potassium ions across the axon cell membrane |
|
|
Describe the use of ATP in secretion |
The packaging and transport of secretory products into vesicles in cells |
|
|
What are the advantages of using ATP? |
The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP involves a single reaction that releases immediate energy. The breakdown of glucose involves a number of intermediates and it takes much longer for the energy to be released. Only one enzyme (ATPase) is needed to release energy from ATP, while many are needed in the case of glucose. ATP releases energy in small useable amounts when and where needed, whereas glucose contains large amounts of energy that may not be needed immediately. ATP is soluble and easily transpired e.g. from companion cell to die e element in phloem. ATP provides a common source of energy for many different chemical reactions, increasing efficiency and control by the cell. ATP is the universal intermediary molecule between energy-yielding and enrgy-requiring reactions in the cell. |
|
|
What does the law of conservation of energy state? |
Energy cannot be created or destroyed It can only be converted from one form to another |
|
|
What are the two types of nucleic acid? And what are they built up of? |
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Repeating nucleotides |
|
|
What are the two groups of nitrogenous bases? |
Pyrimidines Purines |
|
|
What are the two groups of nitrogenous bases? |
Pyrimidines Purines |
|
|
What does pyrimidine always pair up with? How? |
Purine Hydrogen bonding |
|
|
What is in the pyrimidines group? |
Cytosine Uracil Thymine (CUT) |
|
|
What is the the purine group? |
Adenine Guanine (AG) |
|
|
Describe the structure of pyrimidines |
Single ringed structures |
|
|
Describe the structure of purines |
Double ringed structures |
|
|
What does cytosine look like? |
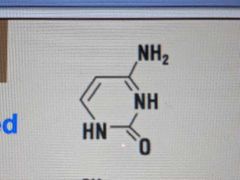
|
|
|
What does uracil and thymine look like? |
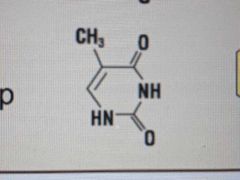
|
|
|
What does adenine look like? |
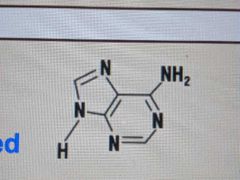
|
|
|
What does Guanine look like? |
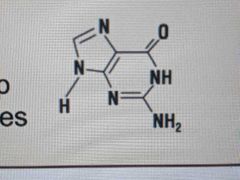
|
|
|
How many bonds is used for adenine to bond with thymine or uracil |
2 |
|
|
How many bonds is used for cytosine to bone with Guanine? |
3 |
|
|
What are the functions of DNA? |
Replication in dividing cells and protein synthesis |
|
|
What is a gene? |
A gene is a short sequence of the DNA |
|
|
What does the sequence of bases on the DNA form? |
The genetic code |
|
|
What does the genetic code code for? |
Amino acids |
|
|
What do genes code for? |
Proteins and functional RNA products |
|
|
What is the Pentose sugar in DNA? |
Deoxyribose |
|
|
What is DNA? |
A nucleic acid |
|
|
What is DNA made up of? |
Two chains of nucleotides bonded together by hydrogen bonding. |
|
|
What is DNA made up of? |
Two chains of nucleotides bonded together by hydrogen bonding. |
|
|
Describe the structure of the sugar phosphate backbone of the polynucleotide |
Alternating phosphate groups and Pentose sugars |
|
|
Describe an individual chain of DNA |
Each chain is a polymer of nucleotides or polynucleotide |
|
|
Describe an individual chain of DNA |
Each chain is a polymer of nucleotides or polynucleotide |
|
|
How to the nucleotides in one chain of DNA join together? |
Condensation reactions between their phosphate groups and deoxyribose sugars. The sugars of one nucleotide joins to the phosphate group of another at position 3' and a molecule of water is released. A phosphodiester bond is formed. This forma a sugar phosphate backbone |
|
|
What position is each polynucleotide chain in, in reference to one another? |
The polynucleotide chains are antiparallel to each other, with a different carbon atom 'leading' in each ribose sugar. The directions are 5'->3' and 3'->5' |
|
|
What do the two directions on the polynucleotide chains look like? |
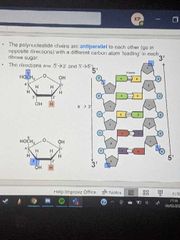
|
|
|
What is the shape of a DNA molecule? |
Twisted to form a double helix. |
|
|
How is the shape of a double helix maintained? |
Hydrogen bonding |
|
|
Where is DNA found? |
In the nucleus |
|
|
What does RNA stand for? |
Ribonucleic acid |
|
|
What is RNA? |
A single stranded polymer of nucleotides |
|
|
What are the three types of RNA? |
mRNA tRNA rRNA |
|
|
Describe the structure of mRNA |
A long single stranded molecule |
|
|
How is mRNA synthesised? |
It is synthesised in the nucleus by a process called transcription and carries the genetic code from the DNA to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm |
|
|
What does each stand of mRNA contain? |
The genetic code for one gene |
|
|
What is every 3 bases on mRNA called? |
a codon |
|
|
What does each codon code for? |
One amino acid |
|
|
What does a codon ensure? |
The correct tRNA binds, bringing the correct amino acid into the ribosome |
|
|
What does ensuring the correct tRNA binds, bringing the correct amino acid into the ribosome ensure? |
The primary structure of the polypeptide is correct |
|
|
Where is rRNA found? |
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
What is rRNA a component part of? |
Ribosomes |
|
|
What are ribosomes made of? |
rRNA and protein |
|
|
Describe the synthesis of ribosomes |
They are synthesised in the nucleolus if the nucleus (they leave the nucleus via the nuclear pores). |
|
|
What is the function of ribosomes? |
Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis by a process called translation. |
|
|
Describe the shape of tRNA |
A small single stranded molecule folded into the shape of a clover leaf |
|
|
Describe the structure of tRNA molecules |
An amino acid binding cite CCA. At the opposite end of the tRNA molecule there is a triplet of bases called an anticodon. |
|
|
What is the function of tRNA |
To transport amino acids to the ribosomes |
|
|
What do anticodon bases form with complimentary bases? |
Codon-anticodon-complex |
|
|
What does the formation of codon-anticodon-complexes allow? |
Allows translation to take place |
|
|
What are the differences between DNA and RNA? |
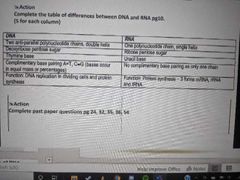
|

