![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The specific immune response can target a specific pathogen, although it's slower to act than the non specific response. It futures two main types of response to pathogens. What are they called? |
Cellular and humoral |
|
|
What does cellular response involve? |
Highly specialized cells that target pathogens inside cells |
|
|
What does humoral response involve? |
Targets pathogens in body fluids with antibodies |
|
|
What are lymphocytes? Where is it found? |
Type of white blood cell found in blood and lymph nodes |
|
|
What are the two main types or lymphocytes? |
T and b cells |
|
|
What are the t and b cells produced by? |
Stem cells |
|
|
T cells are produced by stem cells where and mature where? |
Bone marrow then mature in thymus |
|
|
B cells are produced where by stem cells and mature where? |
Bone marrow |
|
|
What is the role of helper t cell? |
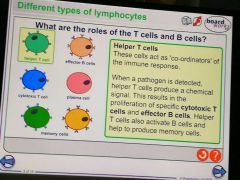
|
|
|
What is the role of effector b cell? |

|
|
|
What is the role of killer t cells? |

|
|
|
What are the roles of plasma cell? |

|
|
|
What is the role of memory cell? |

|
|
|
What is the process of cellular immune response? |
Once a macrophage destroys pathogen by phagocytosis, the macrophage attached the pathogens antigen on it's surface of membrane. It becomes antigen presenting cell (apc).
It interacts with helper t cell releasing a chemical called interleukin -1 which is cytokine (a chemical involved in cell signaling) Interleukin-1 then stimulates helpter t cell to also produce cytokine aka interleukin -2 which causes growth and development of antigen specific killer t cells. The killer t cell detect the antigen on the surface of infected cell and so release perforin. This protein forms pores in the membrane of the infected cell so water and ions and go in and flood it causing membrane walls to rupture and then lysis to occur
Memory t cells are then produced to remember this type of pathogen for future attacks from this pathogen |
|
|
What is the process humoral immune response? |
When macrophage destroys pathogen by phagocytosis, the macrophage displays the pathogens antigen on it's cell surface. This is now an antigen presenting cell (apc)
The apc interacts with a specific helper t cell and releases interleukin -1 which is a cytokine (involves chemical in cell signalling)
The helper t cell is then stimulates by interleukin -1 to produce cytokine as well aka interleukin-2 which stimulates effector b cell to convert into plasma cells
The plasma cell divide and produce a lot of antigen specific antibodies which attach to pathogens and destroy them by neutralization or agglutination Memory b cells then form in order to prepared for future if same pathogen enters |
|
|
Antibodies kill pathogens by neutralization or agglutination. Explain neutralization |

|
|
|
Antibodies kill pathogens by neutralization or agglutination. Explain agglutination |

|
|
|
Tip |
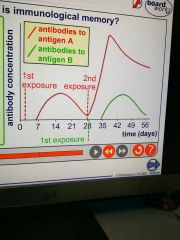
|
|
|
Polyclonal antibodies are produced how? |
Naturally produced in an immune response. |
|
|
How are antibodies in polyclonal antibody type different from each other? |
Differently plasma cells secrete antibodies resulting in variety of different antibodies against a specific antigen |
|
|
How are monoclonal antibodies produced? |
Produced from clones of a single plasma cell and are therefore all identical |
|
|
What are the uses of monoclonal antibodies? |
- treat cancer - home pregnancy kit - drug screening - scientific research |
|
|
Large quantities of monoclonal antibodies can be produced using what? |
Rabbits or mice |
|
|
Remember |

|
|
|
Problem with producing monoclonal antibodies using mice? |
Chance of our body rejecting it and recognise it as a foreign cell and attack it |
|
|
How to overcome the problem with producing monoclonal antibodies with mice? |
Use genetic engineering to produce them with only the antigen binding site coming from mice |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
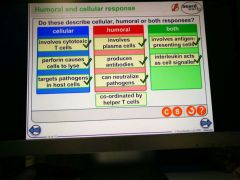
|

|
|
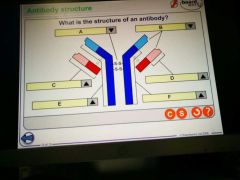
|

|

