![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
antigen
|
any substance, that causes the production of antibody-mostly proteins but can include some carbohydrates and nucleoproteins
- foreign or non-self |
|
|
antibody
|
protein made in response to an antigen and binds specifically to the antigen that caused its production
|
|
|
Bacterial Antigens (immunogens)
|
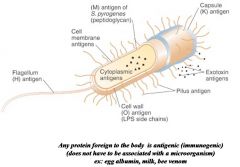
|
|
|
Antigenic Determinants (Epitopes)
|
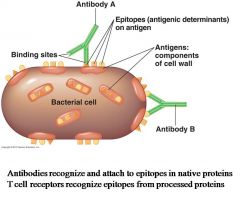
Epitope : sequence of amino acids within a protein recognized as foreign
AMI : specific antibodies made in response to each epitope and attach to epitope. |
|
|
Antibody Monomeric Structure
|
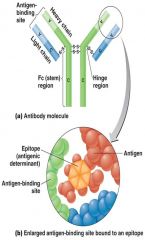
|
|
|
Immunoglobulin Classes
|
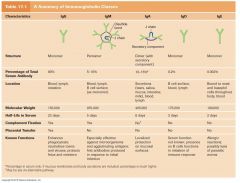
|
|
|
Why do plasma cells secrete different isotypes of antibody with same idiotype?
|
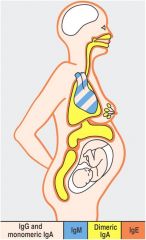
Different isotypes access different body compartments
blood (IgM, IgG, IgA) tissue fluid (IgG, IgA) secretions (dimeric IgA) fetus (IgG) skin and membranes (IgE) |
|
|
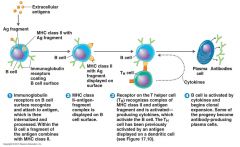
Activation of B Cells
|
|
|
|
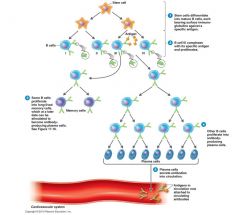
Clonal Selection and Differentiation of B Cells
|
|
|
|
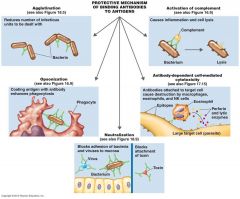
Results of Antigen-Antibody Binding
|
|
|
|
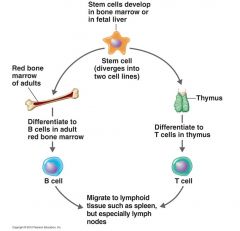
Differentiation of T and B Cells
|
|
|
|
Differentiation of T and B Cells
|
|
|
|
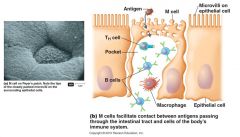
M Cells
|
|
|
|
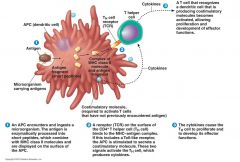
Activation of CD4 T Helper Cells
|
|
|
|
Activation of CD4 T Helper Cells
|
|
|
|
CTL's Destroys Virus Infected Cells
|
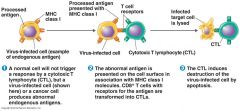
TCR on CTL recognizes viral epitopes displayed by MHC I molecules on surface of infected cells
Tc destroys target cells with perforin and granzymes Cell induce to apoptosis (programmed cell death) Only target cell is destroyed |
|
|
Cell Mediated Immunity (Chart)
|
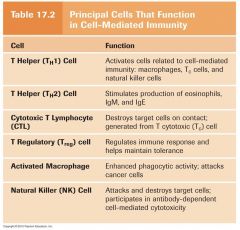
|
|
|
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
|
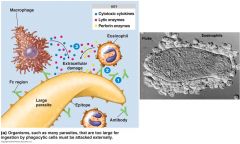
|
|
|
Antibody Response
|
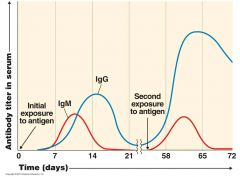
|
|
|
Types of Adaptive Immunity
|
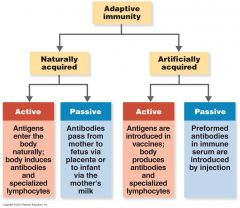
|
|
|
Serum Proteins
|
|
|
|
Serum Proteins
|

|
|
|
Humoral and Cellular Immuntity
|
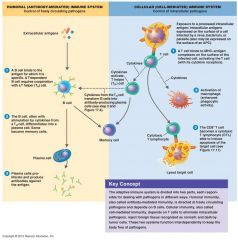
|

