![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
119 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell membrane |
Keeps the cell together while allowing certain organism through |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Used as tubes to move material such as proteins through the cell |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Create protein which is used to fix damage and direct chemical process |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Collect and process materials to be removed from the cell |
|
|
Vacuole |
A storage and contorts turgid pressure |
|
|
Micro tubules |
Act as a conveyor belt that moves substances from place to place |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Converts energy into a useable form and stores energy |
|
|
Nucleus |
A rough spherical object in the center containing DNA or coded instructions for the function of the cell |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Used to digest and break down protein |
|
|
Centrioles |
Help with the division of the cell as they copy the DNA |
|
|
What two things are found only in a animal cell |
Cell wall and chloroplasts |
|
|
How does a plant cell differ from an animal cell structure wise |
Plant cells are mostly rectangular and have ridged corners |
|
|
Function of the chloroplasts |
Do photosynthesis |
|
|
What is the magnification of the ocular lens of a microscope |
10x |
|
|
What is the magnification of the three objective lenses |
4x 10x 40x |
|
|
What are the three main points of the cell theory |
Made, basic, pre-existing |
|
|
What are the two main categories of cells |
Prokaryotes Eukaryotes |
|
|
Why are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different |
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus but an eukaryotes is usually larger and can be a multicellular organism and has a nucleus |
|
|
Reasons for cell division |
Repair Reproduction Growth |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of chemicals from high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion but only with water |
|
|
What are the two types of reproduction |
Asexual Sexual |
|
|
What type of organism can do an asexual reproduction |
Unicellular organism |
|
|
Sexual reproduction |
A cell from one parent (gamete) meets with another parent and form together to have a full set of DNA as both have half. The offspring will have a different DNA |
|
|
Stages of the cell cycle |
Interphase Mitosis Cytokinesis |
|
|
Stages of mitosis |
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
(Pmat) |
|
|
How long does a cell usually take to reproduce |
24 hours but skin is faster and neuron never |
|
|
When will the cell cycle not occur |
Receives a signal not to Malnutrition DNA not duplicated DNA damaged |
|
|
What happens in the interphase |
New organelle is formed Spends most time in this stage DNA is copied as chromatids |
|
|
What happens in the prophase |
DNA become shorter and thicker Nuclear membrane dissolves Each chromosome is made of two chromatids |
|
|
Metaphase |
The chromosome line up in the center Spindle fibers are visible |
|
|
Anaphase |
The spindle fibers pull the chromosomes apart and they split |
|
|
Telophase |
The daughter chromosomes reach opposite ends of the cell and a new nuclear membrane is formed |
|
|
What happens in the cytokinesis |
Cytoplasm divides and organelles move In animal cells its pinched closes and in animal cells a new wall is formed |
|
|
Embryonic stem cells |
When the egg and sperm meet 200 cells are created and are called embryonic stem cells through a process called cellular differentiation |
|
|
Adult stem cells |
Exist within special tissues such a bone marrow and umbilical cord. And can be used to create certain things such as rdc or wbc. Used to treat leukemia |
|
|
Meristematic stem cells |
Active for the plants whole life on the roots and stems |
|
|
What is tissue engineering |
Some animals can regrow body parts
Research is trying to grow human organs |
|
|
Cancer cells |
Cells that divide despite message not to |
|
|
Types of Tumors |
Two types
Benign and maligned |
|
|
Benign Tumors |
Not active and can be surgically removed |
|
|
Malignant Tumors |
Interferes with the function of other cells and can break away and spread. This is called metastasis |
|
|
What causes Tumors |
Mutations that make it constantly divide or not stop.
Canligents: environment factors like cigarette smoke and uv light
Genetics
Proto-oncogenes( genes that tell cells to divide normally) become oncogenes via mutations and divide continuously.
Tumor suppressor genes become inactive |
|
|
What is cancer screening |
Testing and looking for irregular, asymmetric, border, colour and the diameter of the cells |
|
|
Treatment options |
Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Biophotonic |
|
|
How does surgery treat cancer |
Removes tumor Have a ____ectomy |
|
|
How does chemotherapy treat cancer |
Use drugs to kill dividing cells |
|
|
Radiation |
To destroy DNA of the cell Use lasers |
|
|
How does biophotonics |
Use beams of light to target certain cancers |
|
|
Hierarchy of structures |
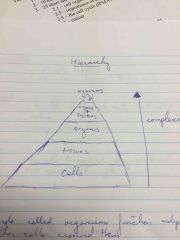
Organisms Organs + systems Organs Tissues Cells |
|
|
Male plant parts |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Plant organ systems |
Shoot Root |
|
|
Shoot system |
Everything above ground And does photosynthesis and reproduction |
|
|
Organs in the shoot systems |
Leafs Flower Stem |
|
|
What does the leaf do in the shoot system |
Photosynthesis Are edible and used for meds and wax
|
|
|
Guard cell |
Controls the amount of oxygen water and Carbon dioxide can leave and enter the plant |
|
|
What does the flower do in the shoot system |
Used for reproduction Have both male and female reproductive parts After pollination the plant becomes the fruit |
|
|
What does the stem do in the shoot system |
Supports branches leaves and flowers Transports materials Provides with sugar cane, potatoes, wood, linen, many medicines |
|
|
Root system |
Everything underground |
|
|
Functions of the root system |
Anchors plants Prevents erosion Absorbs water Stores food |
|
|
Tissues |
Specialized cells that work together |
|
|
Types of root systems |
Tap root system Fibrous root system |
|
|
Tap root system |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Fibrous root system |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Main roles of the digestive system |
Take in food Break down and absorb material Extract waste |
|
|
2 types of digestion |
Mechanical Chemical |
|
|
Mechanical digestion |
Break down into small pieces
Ie teeth |
|
|
Chemical digestion |
Chemicals and enzymes that break down food |
|
|
Digestive tract |
Pathway for the food to travel
Mouth. Esophagus. Stomach. Small intestine. Large intestine. Rectum. Anus |
|
|
Accessory organs |
Chemical formulas to break down food. ie liver pancreas |
|
|
Villa |
Long squiggly substance to increase surface area if a tissue |
|
|
Main types of tissues |
Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve |
|
|
Function of the mouth |
Food us taken in |
|
|
Function of the salivary glands |
To provide saliva that helps with chemical digestion |
|
|
Function of the esophagus |
A tube from the mouth to stomach that pushes food down
Lots of muscles |
|
|
Function of the epiglottis |
Is like a switch that opens and closed to allows food and air down different pathways |
|
|
Function of the stomach |
Holds food and churns its Chemical and mechanical |
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Thin layers that covers the surface of the body (ie skin intestines) |
|
|
Connective tissues |
Provide support ( bones, ligaments, tendons) |
|
|
Muscle tissues |
Bundles of muscle cells that that contract and relax |
|
|
Nerve tissues |
Long cells that carry electric signals |
|
|
Organs |
A group of tissues working together to do a function and form a structure |
|
|
Organ systems |
A group of organs performing a complex function together |
|
|
Female plant parts |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Hierarchy of structures |
Organisms Organs + systems Organs Tissues Cells |
|
|
Male plant parts |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Plant organ systems |
Shoot Root |
|
|
Shoot system |
Everything above ground And does photosynthesis and reproduction |
|
|
Organs in the shoot systems |
Leafs Flower Stem |
|
|
What does the leaf do in the shoot system |
Photosynthesis Are edible and used for meds and wax
|
|
|
Guard cell |
Controls the amount of oxygen water and Carbon dioxide can leave and enter the plant |
|
|
What does the flower do in the shoot system |
Used for reproduction Have both male and female reproductive parts After pollination the plant becomes the fruit |
|
|
What does the stem do in the shoot system |
Supports branches leaves and flowers Transports materials Provides with sugar cane, potatoes, wood, linen, many medicines |
|
|
Root system |
Everything underground |
|
|
Functions of the root system |
Anchors plants Prevents erosion Absorbs water Stores food |
|
|
Tissues |
Specialized cells that work together |
|
|
Types of root systems |
Tap root system Fibrous root system |
|
|
Tap root system |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Fibrous root system |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Main roles of the digestive system |
Take in food Break down and absorb material Extract waste |
|
|
2 types of digestion |
Mechanical Chemical |
|
|
Mechanical digestion |
Break down into small pieces
Ie teeth |
|
|
Chemical digestion |
Chemicals and enzymes that break down food |
|
|
Digestive tract |
Pathway for the food to travel
Mouth. Esophagus. Stomach. Small intestine. Large intestine. Rectum. Anus |
|
|
Accessory organs |
Chemical formulas to break down food. ie liver pancreas |
|
|
Villa |
Long squiggly substance to increase surface area if a tissue |
|
|
Main types of tissues |
Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve |
|
|
Function of the mouth |
Food us taken in |
|
|
Function of the salivary glands |
To provide saliva that helps with chemical digestion |
|
|
Function of the esophagus |
A tube from the mouth to stomach that pushes food down
Lots of muscles |
|
|
Function of the epiglottis |
Is like a switch that opens and closed to allows food and air down different pathways |
|
|
Function of the stomach |
Holds food and churns its Chemical and mechanical |
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Thin layers that covers the surface of the body (ie skin intestines) |
|
|
Connective tissues |
Provide support ( bones, ligaments, tendons) |
|
|
Muscle tissues |
Bundles of muscle cells that that contract and relax |
|
|
Nerve tissues |
Long cells that carry electric signals |
|
|
Organs |
A group of tissues working together to do a function and form a structure |
|
|
Organ systems |
A group of organs performing a complex function together |
|
|
Female plant parts |
Back (Definition) |

