![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a Chromosome? |
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and proteins in the nucleus |
|
|
What information does a chromosome contain? |
Genetic information |
|
|
From where do you get your chromosomes? |
Half from mother and half from father |
|
|
What is a gene? |
Physical and functional unit of hereditary |
|
|
What is an allele? |
Alternative forms of a gene |
|
|
What is a dominant trait? |
A trait that will appear in the offspring if one parent contributes it |
|
|
What is a recessive trait? |
Carried in a person's genes without appearing in that person |
|
|
What is a genotype? |
Alleles individual receives at fertilization |
|
|
What is a phenotype? |
Physical appearance of individual |
|
|
What did Watson and Crick contribute to our knowledge of DNA? |
Built a DNA model and suggested how replication works, won the Nobel Prize |
|
|
What is the structure of DNA? |
A double helix, like a twisted ladder |
|
|
How are the sides held together in DNA? |
Deoxyribose sugar and phosphate molecules are bonded |
|
|
How are the "rungs" of the ladder held together in DNA? |
By the bases |
|
|
What is DNA replication? |
Process of copying DNA before cell division |
|
|
Why is DNA replication known as a semiconservative process? |
Each new DNA molecule is made of one parent strand and one new strand |
|
|
Why does DNA replication in eukaryotes start at multiple points along the DNA strand? |
To form "replication bubbles" |
|
|
What are three differences between DNA and RNA? |
1- DNA contains thymine while RNA contains uracil 2- DNA is usually double stranded and RNA is usually single stranded 3- In DNA the pentose sugar is deoxyribose and RNA is ribose |
|
|
Messenger RNA (mRNA) |
Carries genetic message to ribosomes |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
Transfers amino acids to ribosomes, only 1 each |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
Joins with proteins to form ribosomes |
|
|
Generally, what is transcription? |
DNA serves as a template to make mRNA |
|
|
Where does transcription occur? |
The nucleus |
|
|
What is the template in transcription? |
DNA |
|
|
What is being transcribed in transcription? |
DNA to RNA |
|
|
Generally, what is translation? |
mRNA directs sequence of amino acids in the protein |
|
|
Where does translation occur? |
Protein synthesis |
|
|
What is the template in translation? |
mRNA |
|
|
What is being translated in translation? |
Amino acids brought in by tRNA |
|
|
What is a codon? |
3 nucleotide sequence in mRNA |
|
|
Where is the anticodon found? |
On molecules of tRNA |
|
|
What is the function of tRNA? |
Helps decode mRNA sequence into a protein |
|
|
What is a mutation? |
Change in the sequence of the bases in a gene |
|
|
How would a mutation affect the DNA, RNA, and protein formation? |
-sickle cell disease -extra or missing nucleotides -all downstream codons affected |
|
|
What is a transgenic organism? |
An organism that have altered genomes, "genetic engineering" |
|
|
What are the two major functions of meiosis? |
1- reducing chromosome number 2- shuffling chromosomes in the cell to produce genetically different combinations |
|
|
What are homologous chromosomes? |
Members of a pair of chromosomes |
|
|
What are sister chromatids? |
One half of the duplicated chromosome |
|
|
What are diploid cells? |
Complete set of necessary chromosomes, 46 |
|
|
What are haploid cells? |
One complete set of chromosomes, 23 |
|
|
When does DNA replication occur? |
During prophase I |
|
|
What is crossing over? |
The exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes |
|
|
Prophase I |
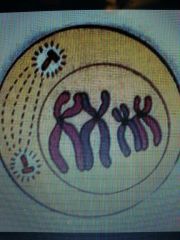
Chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down, crossing-over occurs |
|
|
Metaphase I |
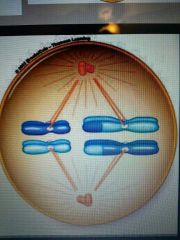
Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell |
|
|
Anaphase I |
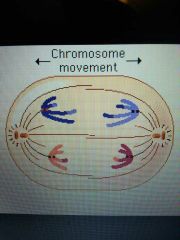
Homologous chromosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell |
|
|
Telophase I |
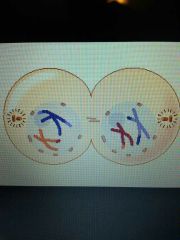
Chromosomes gather at the poles of the cell, the cytoplasm divides |
|
|
Prophase II |
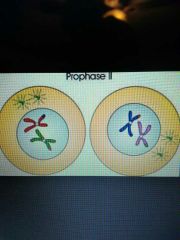
A new spindle forms around the chromosomes |
|
|
Metaphase II |
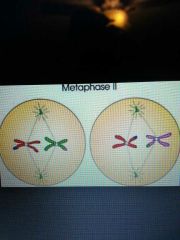
Chromosomes line up at the equator |
|
|
Anaphase II |
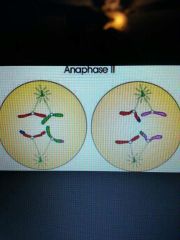
Centromeres divides, chromatids move to the opposite poles of the cells |
|
|
Telophase II |
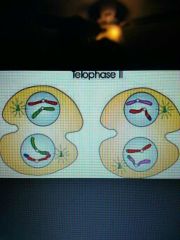
A nuclear envolpes forms around each set of chromosomes, the cytoplasm divides |
|
|
What is the end result of meiosis? |
4 daughter cells are produced |
|
|
What is nondisjunction? |
Meiosis I- when both members of a pair go into the same daughter cell Meiosis II- when sister chromatids fail to separate |
|
|
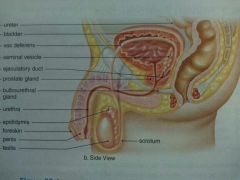
Male Reproductive System |
|
|
|
Ureter Function |
A tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder |
|
|
Vas Deferens Function |
Transports mature sperm to the urethra |
|
|
Seminal Vesicle Function |
Secrets a thick, viscous fluid containing nutrients for sperm |
|
|
Ejaculatory Duct Function |
Combines stored sperm with seminal fluids and then transports them to the prostate |
|
|
Prostate Glad Function |
Secretes milky alkaline fluid believed to activate sperm, may become enlarged in older men |
|
|
Bulbourethral Gland Function |
Mucous secretions with a lubricating effect |
|
|
Urethra Function |
Tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body and ejaculates sperm when the man reaches orgasm |
|
|
Epididymis Function |
Stores and transports sperm from the testes |
|
|
Foreskin Function |
Covers the elongated shaft during erection, other times protects the sensitive glans penis |
|
|
Penis Function |
Sex organ, acts as conduit for urine to leave the body |
|
|
Testes Function |
To produce sperm and adrogens, mostly testosterone |
|
|
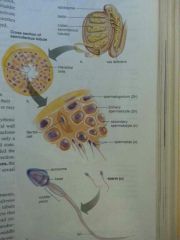
What are the testes composed of? |
Lobules each containing 1-3 seminiferous tubules |
|
|
Which cells undergo spermatogenous? |
Cells in seminiferous tubules |
|
|
What hormone is responsible for sperm production? |
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) |
|
|
Seminiferous Tubules |
|
|
|
What are secondary sex characteristics? |
Features that appear at sexual maturity Ex: height; broad shoulders; long legs; deep voice; pattern of hair on face, chest, and other regions; muscle development |
|
|
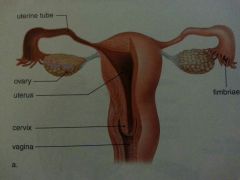
Female Reproductive System |
|
|
|
Oviduct (Fallopian Tubes) Function |
Links the ovary to the uterus which the ovulated oocyte travels down to become fertilised by sperm |
|
|
Ovary Function |
1- produce oocytes (eggs) for fertilisation 2- produce reproductive hormones, oestrogen and progesterone |
|
|
Uterus Function |
Nurturing the fertilized ovum that develops into the fetus and holding it till the baby is mature enough for birth |
|
|
Fimbriae Function |
Catch the released egg and help move it down into the fallopian tube |
|
|
Cervix Function |
To allow flow of menstrual blood from the uterus into the vagina and direct the sperm into the uterus during intercourse |
|
|
Vagina Function |
Receives the penis during sexual intercourse and also serves as a conduit for menstrual blood flow from the uterus, baby also passes through it during childbirth |
|
|
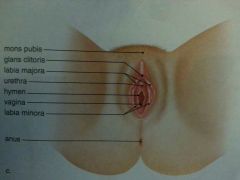
Vulva Parts |
|
|
|
What is the primary follicle? |
An immature follicle consisting of an oocyte surrounded by a single layer of tall, supporting granulosa cells |
|
|
What is ovulation? |
Release of secondary oocyte surrounded by follicle cells |
|
|
What is the corpus luteum? |
Follicle that has ovulated and lost its oocyte |
|
|
Ovarian Cycle and Oogenesis |
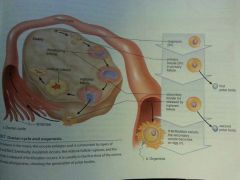
|
|
|
What happens during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle? |
FSH promotes development of follicles, follicle secretes estrogen, blood estrogen levels rise, estrogen inhibits FSH, ovulation ends the follicular phase |
|
|
What happens during the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle? |
LH promotes development of corpus luteum, corpus luteum secretes progesterone, as progesterone levels rise LH levels drop, corpus luteum degenerates if fertilization does not occur |
|
|
FSH Function |
it stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles in the ovary before the release of an egg from one follicle at ovulation |
|
|
LH Function |
Female- it triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum Male- it stimulates production of testosterone |
|
|
Estrogen Function |
Female- development of female secondary sexual characteristics Male- helps in maturation of the sperm and maintenance of a healthy libido |
|
|
Ovarian and Menstrual Cycles |
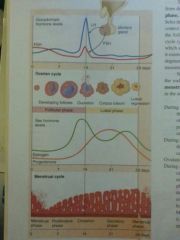
|
|
|
Hormone Pill |
combination of estrogen and progesterone shuts down production of LH and FSH so no follicles develop |
|
|
Hormone Implant |
synthetic progesterone prevents ovulation by disrupting ovarian cycle |
|
|
NuvaRing |
small flexible piece of plastic that is inserted into the vagina once a month |
|
|
IUD |
fertilization will likely not occur and implantation cannot take place |
|
|
Condom |
Female fits into cervix Male- better when combined with spermicide |
|
|
Diaphragm |
Latex cup covering cervix |
|
|
Sterilization |
a procedure that closes or blocks your fallopian tubes so you can't get pregnant |
|
|
Abstinence |
Very reliable and prevents sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) |
|
|
Genital Warts |
Caused by human papillomaviruses (HPVs), most common |
|
|
Genital Herpes |
Painful genital blisters that rupture leaving ulcers |
|
|
Hepatitis |
Infection of liver A- usually drinking contaminated water, but can be sexually transmitted B- spread same way as AIDS C- contact of blood from inected person |
|
|
Chlamydia |
Causes cervical ulcerations, risk of pelvic inflammatory disease |
|
|
Gonorrhea |
Thick, greenish-yellow urethral discharge Tubes may be blocked by scar tissue |
|
|
Syphilis |
3 stages seperated by latent periods Last stage can affect cardiovascular and/or nervous systems |
|
|
Trichanomiasis |
Caused by flagellated protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis |
|
|
Yeast Infection |
Normally found in vagina, caused by candida |
|
|
How does HIV cause AIDS? |
It attacks the immune system destroying CD4 positive T cells, a white blood cell that fights off infection |
|
|
What are the 3 stages of AIDS? |
A- about 1 year; no symptoms but can spread B- 6-8 years; weight loss, fatigue, fever, diarrhea; thrush and herpes recur C- full-blown AIDS; nervous disorder, opportunistic infections; without intensive treatment, patient dies in 7-9 years |
|
|
What are two big reasons for getting annual STD checks? |
1- to stop or cure it at an early stage 2- to make sure you are safe just in case |
|
|
What is in-virto fertilization? |
-Immature eggs taken to maturity in lab dish -sperm added for fertilization -embryos transferred to woman in secretory phase of menstrual cycle -excess embryos my be frozen |
|
|
Extraembryonic Membranes |
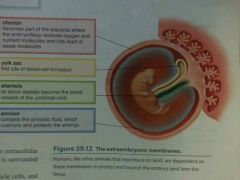
|
|
|
What is fertilization? |
Results in a zygote, requires sperm and secondary oocyte to interact |
|
|
How do the sperm penetrate the zona pellucida? |
Acrosomal enzymes from sperm digest through zona pellucida |
|
|
During which time in pregnancy does early embryonic development occur? |
First 2 months |
|
|
Where does the early embryonic development occur? |
6 days of development occur in the oviduct before embryo implants in the uterus |
|
|
What is cleavage? |
Cell division without growth |
|
|
What is an early blastocyst? |
-Fluid- filled cavity -Inner will be embryo -Outer will be part of the placenta |
|
|
What is secreted after the blastocyst implants? |
Human chorionuc growth hormone (hCG) |
|
|
What is gastrulation? |
3 layers of cells develop- embryonic germ layers |
|
|
What are the three embryonic layers? |
-Ectoderm- outer layer -Mesoderm -Endoderm- inner layer |
|
|
What do the the three embryonic layers become in adults? |

|
|
|
From what layer does the nervous system arise? |
Ectoderm (outer layer) |
|
|
What happens to the embryo at 5 weeks? |
Has limb buds |
|
|
What happens to the embryo at 6-8 weeks? |
-remarkable external appearance change -recognizable human -reflex reaction |
|
|
At what time during pregnancy does the embryo develop into the fetus? |
3rd to 9th month |
|
|
Generally, what happens during fetal development? |
-extreme increase in size -geneitalia appear -hair and nails appear |
|
|
What is the function of the placenta? |
-Carbon dioxide and waste move from fetal side to maternal side -nutrients and oxygen move from maternal to fetal side |
|
|
What causes the uterus to contract during labor and birth? |
The hypothalamus cause the pituitary to stimulate the adrenal cortex to secrete androgens |
|
|
Three stages of birth |
1- cervix dilates and amnion bursts 2- baby is born and umbilical cord is cut 3- placenta is delivered |

