![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an enzyme? |
A biological catalyst made from globular proteins that interact with substrate molecules to facilitate chemical reactions |
|
|
What are anabolic and catabolic reactions? |
A- build up molecules C- break down moleculea |
|
|
What is metabolism? |
The sum of all reactions in a cell or organism |
|
|
What is a cofactor and give an example |
Organic non-protein component. Temporary binding. Enables a reaction to happen. Eg, vitamins |
|
|
What is a coenzyme and give an example |
Inorganic non protein component. Eg, chlorine ions for amylase |
|
|
What is a prosthetic group and give an example |
Inorganic non protein component, permentantly bound. Eg zinc ions |
|
|
What is apoenzyme precursor activation |
An enzyme in an inactive form (apoenzyme) is made to work with a cofactor |
|
|
Zymogen precursor activation |
Something is taken away from the enzyme structure in order to fit substrate |
|

Fill the gaps |
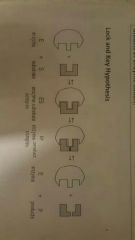
|
|
|
What is induced fit hypothesis? |

|
|
|
Competitive and non-competetive inhibitors |
Competitive inhibitors bind onto active site changing the shape of the active site meaning it is no longer complimentary to the substrate Non-competetive inhibitors bind onto allosteric site and change the shape of the active site that way |
|
|
What is a biochemical pathway? |
Series of stages which change substrates into final products |
|
|
What are irreversible inhibitors and give examples and what they do |
Inhibitor binds permentantly. Poisons and drugs, cyanide- inhibits enzyme involved in respiration and prevents ATP synthesis Heavy metals- block metabolic reactions |

