![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ecology
|
The study of how organisms interact with one another and with their environment.
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
Places where organisms interact like deserts, ponds, mountains, oceans, and tropical forests.
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
All the ecosystems of the earth-interconnected
|
|
|
Florida ecosystems
|
Beaches, alt marshes, fresh water streams, wet prairie, pine forests
|
|
|
Populations
|
Members of a single species living together and interbreeding. ex. bullfrogs in a Mississippii pond.
|
|
|
Community
|
All the populations living together and interacting.
|
|
|
5 types of symbiosis
|
1. Mutualism- Both organisms benefit
2. Commensalism- One species benefits while the other is unaffected 3. Parasite/Host: One species is positively affected while the other is negatively affected 4. Competition: Both species are negatively affected 5. Predator/Pray: One species benefits while the other is negatively affected |
|
|
Ectoparasite
|
Lives on the outside
|
|
|
Endoparasite
|
Lives on the inside
|
|
|
Ecological Niche
|
It is a unique role that a critter plays in its ecosystem. Address and occupation. It is the sum of all of a species ecological interactions.
|
|
|
Food Chains
|
Energy passes through trophic levels. The sun is the energy source for most ecosystems. Only ten percent of the energy moves from one trophic level to another.
|
|
|
Tophic Levels
|
1. Sun
2. Autotrophs- They feed themselves and are producers. 3. Heterotroph- primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers |
|
|
Food webs
|
Recognizes organisms feed from a complex menu.
|
|
|
Bio geochemical cycles
|
Exchanges of important chemical compounds between critters and the abiotic ecosystem.
|
|
|
Ecological succession
|
The changes that occur on a landscape as one community replaces another as the ecosystem matures.
|
|
|
Early stages of Ecological succession
|
Low biomass
Low diversity Higher growth-rate less nutrient cycling more autotrophs less stable |
|
|
Late stages of ecological succession
|
High biomass
High diversity Low growth-rates More nutrient cycling More heterotrophs More stable |
|
|
Biomes
|
Large geographic areas characterized by similar climates, similar latitudes, and vegetation types.
|
|
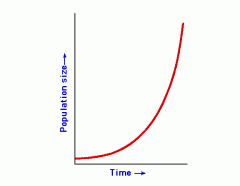
Exponential Growth
|
- Population grows at its biotic potential
|
|
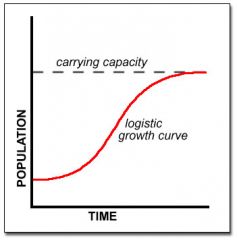
Logistic growth Curve
|
Actual growth and is constrained by environment conditions
|
|
|
Limiting factors that restrict population growth.
|
Density dependent factors- Disease, famine, poor water quality, predation, competition
Density Independent factors- Natural disasters like fire, freeze, and storms |
|
|
Controlled Experiment
|
Control groups: companion experiment without a variable and allows comparison to measure the effect of the variable.
Experiment Variable: Some condition that is tested for its effect- ex. light, temp., drug |
|
|
Metric System
|
International system of measurements and has standardized units.
|
|
|
King Henry Died Unusually Drinking Chocolate Milk
|
K= Kilo 1000/1
H= Hecto 100/1 D= Deca 10/1 U= Basic unit like meters, liters, or grams 1/1 D= Deci 1/10 C= Centi 1/100 M= Milli 1/1000 |
|
|
Density
|
Is the mass over the volume (m/v) of an object
grams/cm 3 or grams/ml |
|
|
Atoms
|
Building blocks of matter
|
|
|
Periodic table
|
Predictable chemical behaviors of elements. Shows an element's atomic number and atomic mass number
|
|
|
Ion
|
When the total number of electrons in an atom is different from the number of protons
|
|
|
Atomic number
|
The number of protons in an atom
|
|
|
Atomic mass number
|
The average number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus
|
|
|
Isotopes
|
Most elements have some atoms with different numbers of neutrons
|
|
|
Valence Electrons
|
Inner electrons are more stable and have less energy
Outer electrons are less stable and have more energy |
|
|
Covalent bonds
|
2 atoms share unpaired valence electrons. The atom becomes more stable as the valence level satisfies the octet rule
|
|
|
Ionic bonds
|
Unstable atom transfers an electron to another atom so that each becomes more stable
|
|
|
Solvent
|
A substance tin which another substance is dissolved
|
|
|
Solute
|
A substance that is dissolved in the solvent
|
|
|
Water as a solvent
|
Water forms hydrogen bonds to polar solutes and puts them in the solution
|

