![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
117 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
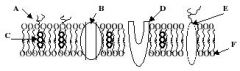
Refer to the illustration. Which molecule represents a glycoprotein that may function as a cellular ID tag, allowing cells of the immune system to recognize a cell as native to the body?
|
They are usually not particular about what types of chemicals they will allow to cross the membrane.
|
|
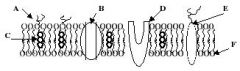
Refer to the illustration. Which molecule may function in facilitated diffusion?
|
B
|
|
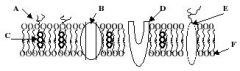
Refer to the illustration. Which molecule is a polysaccharide attached to a phospholipid?
|
A
|
|
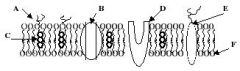
Refer to the illustration. Which molecule might serve as a binding site for a hormone, thereby eliciting a response in the cell?
|
D
|
|
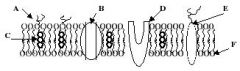
Refer to the illustration. Which molecule works to keep the membrane at optimal fluidity?
|
C
|
|
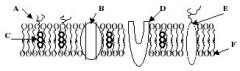
Refer to the illustration. Which molecule is both hydrophobic and hydrophilic and aggregates as a bilayer to form the "fabric" of the membrane?
|
F
|
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning membrane proteins is incorrect?
They may be receptor proteins that bind specific molecules from the surrounding solution, which triggers endocytosis (i.e., receptor-mediated endocytosis). They often require ATP to actively transport materials across the membrane against a concentration gradient. They often facilitate diffusion of molecules across the membrane that otherwise would diffuse too slowly to be of use to the cell. They are usually not particular about what types of chemicals they will allow to cross the membrane. They can act as a channel, allowing the transport of ions across the membrane. |
They are usually not particular about what types of chemicals they will allow to cross the membrane
|
|
|
What is the significance of selective permeability to biological membranes?
Selective permeability prevents toxic materials from entering the cell. Selective permeability allows cells to concentrate particular ions on either side of the membrane. Selective permeability allows the plasma membrane to control traffic into and out of the cell it surrounds. Selective permeability permits the selective uptake of nutrients and the elimination of wastes. All of the above are correct. |
All of the above are correct.
|
|
|
The movement of molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient, at the expense of ATP energy, is called ...
active transport. passive transport. facilitated diffusion. |
active transport.
Correct. Movement against a concentration gradient requires energy. It is like a ball rolling up a hill! |
|
|
Just as with most liquids, the fluid lipid bilayer can solidify and freeze at very cold temperatures. However, there are certain kinds of fish that live in very cold water. The cell membranes of these fish are likely to have more of which of the following membrane components than would a fish that occupies warmer waters?
cholesterol transport proteins glycoproteins phospholipids |
cholesterol
|
|
|
The activity of the sodium/potassium pump is critically important in maintaining proper ion concentrations across the cell membrane. Which of these steps is necessary in the pumping activity of this protein?
The pump changes shape. The pump releases its energy and changes back to its original shape. Two potassium ions in the extracellular fluid bind with the pump. The pump is energized with ATP. Three sodium ions in the cytoplasm bind with the pump. All of the above are critical steps in the activity of the pump. |
All of the above are critical steps in the activity of the pump.
|
|
|
Which of the following types of transport does NOT require the use of a transport protein?
both simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion active transport simple diffusion facilitated diffusion |
simple diffusion
|
|
|
What do you think would happen to an animal cell that was placed into a drop of 100% pure water?
The cell will be unaffected by the pure water. The cell will shrivel and shrink down. The cell will swell up and eventually burst. |
The cell will swell up and eventually burst.
|
|
|
In the process of diffusion ...
molecules move from an area of lesser concentration to an area of greater concentration. random motion of the molecules causes them to migrate toward each other. directed motion of the molecules causes them to migrate away from each other. molecules move from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. |
molecules move from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration.
|
|
|
Materials that are too large to move out of the cell through either the lipid bilayer or a transport protein must be moved out through the process of ...
receptor-mediated endocytosis. exocytosis. active transport. endocytosis. |
exocytosis.
|
|
|
Large food particles, or perhaps whole organisms, can be engulfed and pulled into the cell by the process of ...
phagocytosis. active transport. receptor-mediated endocytosis. pinocytosis. |
phagocytosis.
|
|
|
Many of the proteins that are associated with the cell membrane are said to be "integral" proteins. An integral protein is defined as a protein that is ...
always used to transport material across the membrane. always a receptor protein. bound to the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer of the membrane. not associated with the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer of the membrane. |
bound to the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer of the membrane.
Correct. They are integral because of their deep penetration into the lipid bilayer. |
|
|
Of the four primary functions of membrane proteins, which one does NOT require that the protein be in contact with the extracellular fluid?
recognition proteins transport proteins structural proteins communication proteins |
structural proteins
Correct. These proteins are concerned with maintaining contact with the cytoskeleton. |
|
|
Which of the following molecules or ions would normally need to use a membrane protein in order to move through the cell membrane?
H+ H2O CO2 O2 |
H+
|
|
|
Which of the following processes uses a difference in concentration (or concentration gradient) to transport molecules across the cell membrane?
osmosis facilitated diffusion simple diffusion all of the above |
all of the above
|
|
|
If the plasma membrane lacked a glycocalyx, the cell would have difficulty
transporting materials across the membrane keeping its fluid state adhering to other cells keeping small particles from passing easily across the membrane binding to the cytoskeleton on the inside of the membrane |
adhering to other cells
|
|
|
You eat spaghetti for dinner and digest the starch in it to glucose. The glucose is now in high concentration in the cells of your small intestine, relative to its concentration in your bloodstream.
Predictably, the glucose diffuses across the plasma membrane of your intestinal cells, into your bloodstream. False, because energy is required for diffusion. False, because molecules are too large to move across membranes. True. False, because diffusion moves materials from low concentration to high concentration. False, because molecules cannot move across membranes by diffusion. |
True
|
|
|
When a human cell is placed into water, it swells. This is said to be due to osmosis. What's happening to make the cell swell?
Water is diffusing across the plasma membrane from a region of lower solute concentration (outside the cell) to a region of higher solute concentration (inside the cell). Solutes are being drawn into the cell across the plasma membrane. The cell synthesizes new biological macromolecules as a protective response against a watery environment. Solutes are growing larger inside the cell. Water is diffusing across the plasma membrane from a region of higher solute concentration (outside the cell) to a region of lower solute concentration (inside the cell). |
Water is diffusing across the plasma membrane from a region of lower solute concentration (outside the cell) to a region of higher solute concentration (inside the cell).
|
|
|
Tyrone gave Lakeisha a rose for the anniversary of their first date. Now the rose has wilted, because
The plant's cells have insufficient water in them to push against their cell walls. The cell walls have broken down. The phospholipid bilayer has broken down. The plasma membrane has lost the proteins that keep water in. The cells have taken too much water in and burst. |
The plant's cells have insufficient water in them to push against their cell walls.
|
|
|
The protein that functions in the sodium-potassium pump is an integral protein. The word integral tells you that this protein
is connected to the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane is connected to a cholesterol molecule is connected to the glycocalyx functions on only one side of the membrane is essential to the cell |
is connected to the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane
|
|
|
You get a cut on your finger and some bacteria enter. Your immune-system cells kill off the invaders by ingesting them. This is an example of
pinocytosis active transport phagocytosis exocytosis receptor-mediated endocytosis |
phagocytosis
|
|
|
According to the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure, the membrane is made up of a
continuous base of proteins with phospholipids in it that have fairly free lateral movement bilayer of phospholipids sandwiched between two bilayers of proteins bilayer of phospholipid with layers of proteins on the outside and inside bilayer of phospholipids with proteins interspersed in it that have fairly free lateral movement bilayer of protein with layers of phospholipids on the outside and inside |
bilayer of phospholipids with proteins interspersed in it that have fairly free lateral movement
|
|
|
Calcium ions (Ca++) are present in the endoplasmic reticulum at 1000-fold higher concentrations than in the cytosol (the gel-like material of the cell outside of organelles). One protein on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane is devoted to allowing Ca++ to move from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol and another protein moves Ca++ from the cytosol to the endoplasmic reticulum. These processes are not trivial, as Ca++ released into the cytosol allows such things as muscle contraction and communication between nerve cells. In this pair of Ca++ transport proteins, you would predict that the protein moving Ca++ from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol _____ and the protein that moves Ca++ from cytosol to the endoplasmic reticulum _____.
works without ATP; requires ATP is small; is large requires ATP; works without ATP transports calcium slowly; transports calcium rapidly is large; is small |
works without ATP; requires ATP
|
|
|
Endocytosis and exocytosis are similar in that both involve the use of
vesicles that carry materials into and out of the cell diffusion to carry food and wastes across the plasma membrane starch to supply large amounts of energy the Golgi apparatus to package materials the rough ER to manufacture proteins |
vesicles that carry materials into and out of the cell
|
|
|
Osmosis refers to the net movement of _____ across a _____
water … semipermeable membrane solutes … pe rmeable membrane solutes … semipermeable membrane glucose … protein channel energy … medium |
water … semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
The hypothetical biochemical reaction A + B --> C + D requires 7.2 kcal/mole of energy to proceed. Could this reaction be coupled with the reaction ATP --> ADP + P (releases 7.2 kcal/mole of energy)?
Yes, because the reaction involving ATP yields just enough energy to drive the reaction. Yes, the reaction involving ATP produces more energy when coupled with another reaction. No, because ATP is never used when biochemical reactions are coupled. No, because some of the energy liberated in the reaction involving ATP is released as heat. |
No, because some of the energy liberated in the reaction involving ATP is released as heat.
This is the second law of thermodynamics. |
|
|
Cells probably regulate enzyme activity in all of the following ways except ...
producing two or more molecules that compete with the substrate for the active site on a given enzyme, thereby blocking or slowing down enzyme activity. denaturing an enzyme, thereby slowing down or stopping enzyme activity. utilizing the end product of the biochemical pathway in which the enzyme is involved to inactivate an enzyme. |
denaturing an enzyme, thereby slowing down or stopping enzyme activity.
Correct. Cells do not normally change their temperature or pH to the point where enzymes could be denatured. |
|
|
Which of the following is important in determining enzyme function?
its amino acid sequence temperature the chemical makeup of the active site its surface geometry All of the above are important in determining function. |
All of the above are important in determining function.
Correct. All of the above play a significant role in the functions of an enzyme. |
|
|
As biological catalysts, how do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
by changing the specific heat by bringing the reactants into proper orientation for the reaction to take place by changing an endergonic reaction to an exergonic reaction |
by bringing the reactants into proper orientation for the reaction to take place
Correct. Enzymes allow for the electron clouds of molecules to be brought together in the right orientation for them to react. |
|
|
The inhibitor of an enzyme is frequently a molecule that is produced at the end of a biochemical pathway in a cell. This inhibitor binds to the inhibitor site on an enzyme with several active sites, causing a change in the shape of the enzyme. This prevents the normal substrate from binding to all active sites. What process does this describe?
reaction coupling kinetic feedback inactive control allosteric regulation |
allosteric regulation
Correct. Allosteric regulation involves changing the shape, and therefore the activity, of an enzyme |
|
|
According to the laws of thermodynamics, which of the following is NOT possible?
the creation of a system that is 100% energy efficient the creation of a system that requires a catalyst the creation of an isolated system whose entropy decreases the creation of a system that couples an endergonic reaction to an exergonic reaction |
the creation of a system that is 100% energy efficient
The second law of thermodynamics states that energy conversions always result in the loss of heat. |
|
|
7. Which statements about ATP are correct?
I. ATP serves as a main energy shuttle inside cells. II. The reaction ATP --> ADP + P is coupled to endergonic reactions in cells. III. The reaction ATP --> ADP + P is an endergonic reaction. IV. ATP drives endergonic reactions through the transfer of a phosphate group to another molecule. I and II only III only I only I, II, and IV |
I, II, and IV
The hydrolysis of ATP (III) is energy-releasing (exergonic). |
|
|
8. In any system, what is the term for energy that is not available for doing useful work?
chemical energy Heat potential energy activation energy |
heat
Correct. Heat is random molecular motion that dissipates to the surroundings. |
|
|
The hydrolysis of ATP is probably coupled to all of the following except ...
establishing a difference in electrical charge across a membrane. active transport of amino acids across a membrane. biochemical reactions that produce polymers. osmosis. contraction of the protein microfilaments in muscle cells. |
osmosis.
Correct. Osmosis is a passive process. Review Section 5.4. |
|
|
According to the first and second laws of thermodynamics, if the entropy in the universe has increased, then what has happened?
Energy has been created. Energy has been destroyed. A transfer or transformation of energy has occurred. |
A transfer or transformation of energy has occurred.
Correct. Energy transformation always results in the loss of some energy as random molecular motion (heat). |
|
|
When energy changes from one form to another, some of the energy that can be used to do work is always lost. The loss of this energy is mostly in the form of ...
potential energy. heat energy. kinetic energy. light energy. |
heat energy.
Correct. Although heat energy can be used to do work, more often than not it is simply dissipated away. |
|
|
Many types of "perpetual motion machines" have been invented; however, none of them have ever worked. An example of a simple perpetual motion machine might be as follows: a battery is hooked up to an electrical engine, causing the engine to turn a generator, which recharges the battery. In theory, the machine could be turned on, and it would run forever; however, in reality, it will not. Why?
Eventually, the generator would wear out. Energy is being destroyed as it moves through the generator; thus, the battery will eventually run out of energy. A battery can hold a charge for only so long. Some of the energy will be lost in all of the energy transformations; thus, the battery will eventually run down. |
Some of the energy will be lost in all of the energy transformations; thus, the battery will eventually run down.
Correct. This is what the second law of thermodynamics makes clear. |
|
|
Which kind of work is exemplified by the contraction of skeletal muscles?
transport work synthetic work mechanical work all of the above |
mechanical work
Correct. Muscle contractions move objects (such as ourselves). This is mechanical work. |
|
|
Which statement concerning the following chemical reaction is NOT correct?
ADP + P + energy --> ATP The product of the reaction contains more energy than the reactants. Some of the energy used to combine ADP + P into ATP is lost as heat. This is an endergonic reaction. This is an exergonic reaction. |
Some of the energy used to combine ADP + P into ATP is lost as heat.
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT an example of potential energy?
a lump of coal water held behind a dam water turning a water wheel a high concentration of Na+ on the outside of a cell membrane |
water turning a water wheel
Correct. This is a type of kinetic energy |
|
|
Enzymes are critical to life. What is it that enzymes do that is so important?
Enzymes create energy needed for life. Enzymes cause chemical reactions to occur quickly, so that necessary products are available to living things. Enzymes alter their own molecular makeup permanently, so that chemical reactions can occur faster. All of the above are correct. |
Enzymes cause chemical reactions to occur quickly, so that necessary products are available to living things.
Correct. Without enzymes, a living organism would perish waiting for reaction products to be produced. |
|
|
Some enzymes need assistance from other molecules (such as vitamins) in order to facilitate the transformation of chemical reactants into products. These other molecules are collectively referred to as ...
substrates. coenzymes. catalysts. All of the above are correct. |
coenzymes.
Correct. Vitamins are an important kind of coenzyme; however, there are other types. |
|
|
Living things rely on a constant input of energy in order to sustain life. What is the ultimate source of energy for living things on Earth?
Lightning Volcanoes green plants the Sun |
the Sun
Correct. All of Earth's energy supplies have been, and will continue to be, supplied by the Sun. |
|
|
What is activation energy? (level 1). [Hint]
the energy lost by living things in the form of heat the energy required to initiate or begin a chemical reaction the energy gained by living things, allowing them to remain active the energy created by enzymes during exergonic reactions |
the energy required to initiate or begin a chemical reaction
Correct. Enzymes function by lowering this activation energy, thereby making reactions occur that much faster. |
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning metabolic pathways is correct?
The product of one enzyme reaction becomes the substrate of the next enzyme in the metabolic pathway. A metabolic pathway can be composed of only a single enzyme reaction. A single enzyme is usually responsible for many steps in the metabolic pathway. All of the above are correct. |
The product of one enzyme reaction becomes the substrate of the next enzyme in the metabolic pathway.
Correct. This allows for a rapid enzymatic transformation from beginning substrate to final end product. |
|
|
According to the first law of thermodynamics, energy
|
is never lost or gained, but is only transformed
|
|
|
Each time there is a chemical reaction, some energy is exchanged. According to the second law of thermodynamics, with each exchange
|
Some energy is transformed into heat.
|
|
|
Your car uses gasoline to fuel the engine. Can you explain why you need a coolant system for you car?
|
it is required to absorb the heat energy when the fuel is combusted
|
|
|
ATP stores energy in the form of
|
chemical bond energy
|
|
|
People who are lactose intolerant lack a compound called lactase in their digestive tract. You know that this compound, lactase, is probably a(n)
|
enzyme, because its name ends in -ase.
|
|
|
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that helps living things extract energy from food. From this we know that glycolysis
all of the above proceeds by means of each enzyme leaving a succeeding reaction to a different enzyme uses a number of enzymes involves the modification of a series of substrates consists of a series of chemical reactions |
all of the above
|
|
|
Each molecule of ATP stores a good deal of energy because
|
ATP’s third phosphate group exists in a highly energetic state
|
|
|
Which of the following will lower the activation energy of a reaction in a cell?
lowering the pressure lowering the temperature changing the amount of the reactants supplying ATP using an enzyme |
using an enzyme
|
|
|
The active site of enzyme A is occupied by a molecule other than its substrate. Enzyme B has had its activity reduced by means of a molecule binding to it at a site other than its active site. What is taking place in connection with enzyme A and then enzyme B?
|
competitive inhibition, allosteric regulation
|
|
|
Enzymes
are not chemically altered by binding with a substrate lower the activation energy of specific chemical reactions a and c only accelerate specific chemical reactions all of the above |
all of the above
|
|
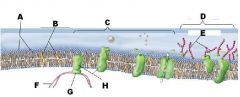
Identify A
|
A Phospholipids
|
|
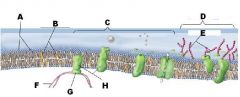
Identify B
|
B Cholesterol
|
|
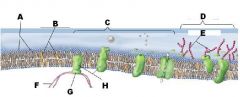
Identify C
|
C Protiens
|
|
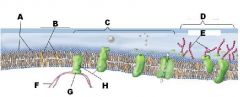
Identify D
|
D Glycoalyx
|
|
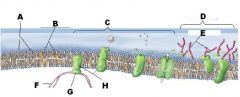
Identify E
|
E Sugar Chain
|
|
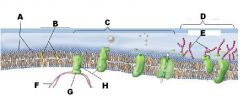
Identify F
|
F Cytoskeleton
|
|
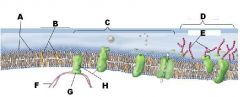
Identify H
|
H Integral Protein
|
|
|
An enzyme is a type of ________ that ___________ a chemical reaction
|
protein
accelerates |
|
|
the substance that an enzyme works on is known as its _______ . A metabolic pathway is a linked series of enzymatically controlled reaction in which the_________ of one reaction becomes the __________ for the next
|
Substrate
product substrate |
|
|
Activation energy is the energy required to _________ a chemical reaction. Enzymes work by__________ activation energy
|
initiate
lower |
|
|
The energy for most coupled reactions in the body is supplied by the molecule_______ in particular by the splitting off of this molecule's third or outter ________
|
ATP
Phosphate group |
|
|
After powering a reaction, ATP becomes the molecule_________, eith the addition of another __________, becomes ATP once more.
|
ADP
Phosphate group |
|
|
Coupled reactions combine an endergonic reaction, in which the __________ have more energy then the ___________, and an exergonic reaction in which the ___________ have more energy then the ________.
|
products
reactants reactants products |
|
|
The energy that is stored is_____ energy. while the energy is in motion is _______ energy
|
Potential
Kinetic |
|
|
the first law of thermodynamics says that energy is never________ or _______ but is only__________
|
created
destroyed transformed |
|
|
The second law of thermodynamics says that energy transfer always results in a greater amount of _________ in the universe.
|
disorder
|
|
|
when ever energy is transferred - for example from the chemical bonds in the gasoline to the movment of the car's piston-- some of the original quanity of energy is lost to _________
|
heat
|
|
|
The plasma membrane of an animal cell has four principal components these are ?
|
phospholipid bilayer
cholesterol proteins glycocalyx |
|
|
exocytosis is the movement of materials out of the cell through the fusion of a ________ with the __________.
the movment of relatively large materials into the cell takes two forms:__________ in which the entire cells or other large material may be ingested through use of plasma membrane extensions called pseudopodia; and __________, in which somewhat smaller materials are brough in through an infolding or " invagination" of the membrane to create a vesicle that then moves inside the cell. |
Transport vesicle
plasma membrane phagocytosis pinocytosis |
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning membrane proteins is true?
They always require ATP to actively transport materials across the membrane against a concentration gradient. They cause the membrane to become more solid and rigid. They are usually particular about what types of chemicals they will allow to cross the membrane. They may be receptor proteins that bind every molecule in the surrounding solution, which triggers endocytosis (i.e., receptor-mediated endocytosis). |
They are usually particular about what types of chemicals they will allow to cross the membrane.
Correct. The presence of membrane proteins makes membranes highly selective about which molecules can cross. |
|
|
What is the major constituent of the glycocalyx? (See book section:
carbohydrates cholesterol lipids protein |
carbohydrates
|
|
|
Recognition proteins are most important in _________. (See book section: 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane)
facilitated diffusion of molecules distinguishing foreign cells from "self" cells maintaining membrane fluidity maintaining membrane integrity active transport of molecules |
distinguishing foreign cells from "self" cells
|
|
|
Which word below best describes the interior portion of the phospholipid bilayer?
basic hydrophilic hydrophobic acidic |
hydrophobic
Correct. The interior portion of the bilayer is composed of the fatty acid tails. |
|
|
The main lipid component of plasma membranes is ____________.
cholesterol trans fats steroids phospholipids fats |
phospholipids
|
|
|
Many of the proteins associated with the cell membrane are said to be "integral" proteins. An integral protein is defined as a protein that is _____.
bound to the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer of the membrane always used to transport material across the membrane not associated with the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer of the membrane always a receptor protein |
bound to the hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer of the membrane
|
|
|
Of the four primary functions of membrane proteins, which one requires that the protein be in contact with the cytoskeleton of the cell?
recognition proteins communication proteins structural proteins transport proteins |
structural proteins
|
|
|
In the process of diffusion __________.
molecules move from an area of lesser concentration to an area of greater concentration random motion of the molecules causes them to migrate toward each other directed motion of the molecules causes them to migrate away from each other molecules move from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration |
molecules move from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration
|
|
|
Osmosis is defined as ___________.
movement of water down the free water gradient movement of water through a protein channel movement of ions through a protein channel movement of solute across a semipermeable membrane |
movement of water down the free water gradient
Correct. Water moves from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low solute concentration |
|
|
Which molecule is both hydrophobic and hydrophilic and aggregates as a bilayer to form the "fabric" of the membrane?
proteins cholesterol phospholipid glycocalyx |
phospholipid
|
|
|
What prevents your immune system from attacking your own cells?
inadequate enzymes receptor proteins fever cholesterol recognition proteins |
recognition proteins
|
|
|
What do you think would happen to an animal cell that was placed into a drop of 100% pure water?
The cell will swell up and eventually burst. The cell will be unaffected by the pure water. The cell will begin to concentrate salt. The cell will shrivel. The cell will dehydrate. |
The cell will swell up and eventually burst.
|
|
|
In simple diffusion, materials move _________.
via the use of energy down the concentration gradient because proteins transport them from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration |
down the concentration gradient
Correct. Salt would move from a 25% area to one of less concentration |
|
|
If a plant cell contains more solutes than its surrounding environment
water will leave the cell the cell will burst no net movement of water will occur the cell will shrivel and die water will enter the cell |
water will enter the cell
|
|
|
The movement of molecules across a membrane against their concentration gradient, at the expense of ATP energy, is called ______.
osmosis passive transport active transport simple diffusion facilitated diffusion |
active transport
|
|
|
The fluidity of a membrane refers to ________.
the ability of both the phospholipids and the proteins to move back and forth with a monolayer the ability to insert proteins within the bilayer the ability of materials to move through the membrane the hydrophobic interior of the bilayer |
the ability of both the phospholipids and the proteins to move back and forth with a monolayer
|
|
|
Materials that are too large to move out of the cell through either the lipid bilayer or a transport protein must be moved out through the process of ______.
active transport exocytosis receptor-mediated endocytosis an ATP-driven pump endocytosis |
exocytosis
|
|
|
Certain white blood cells are designed to engulf and destroy microbes such as bacteria. What is the process they use?
phagocytosis facilitated transport receptor-mediated endocytosis exocytosis pinocytosis |
phagocytosis
Correct. Phagocytosis is used to move large substances into the cell. |
|
|
A hypotonic solution has __________.
more solute than a hypertonic solution less free water than a hypertonic solution the same amount of solute as a hypertonic solution more free water than a hypertonic solution |
more free water than a hypertonic solution
Correct. A hypotonic solution contains less solute |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion requires which of the following to operate?
protein channel vesicle concentration gradient ATP a concentration gradient and a protein channel |
a concentration gradient and a protein channel
|
|
|
Living things rely on a constant input of energy for sustaining life. What is the ultimate source of energy for living things on Earth?
|
the sun
|
|
|
A "high-energy" bond in an ATP molecule is located between ______.
|
two phosphate groups
|
|
|
As biological catalysts, how do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
|
As biological catalysts, how do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
|
|
|
Enzymes are critical to life. What is it that enzymes do that is so important?
|
Enzymes cause chemical reactions to occur quickly, making necessary products available to living things.
Correct. Without enzymes, a living organism would perish waiting for reaction products to be produced. |
|
|
Enzymes are one type of ________.
|
protein
Correct. All enzymes are proteins. |
|
|
For many enzymes, the rate of product formation increases as the concentration of substrate increases. Eventually, the rate of the reaction reaches a maximum, where further increases in the concentration of substrate have no effect. Why?
|
At high concentrations of substrate, all the enzyme molecules are bound to substrate molecules.
Correct. The number of available sites on the substrate exceeds the amount of enzyme available to catalyze the reaction |
|
|
In any system, what is the term for energy that is not available for doing useful work?
|
heat
Correct. Heat is the form of energy that results from energy conversions. |
|
|
Some enzymes need assistance from other molecules (such as vitamins) to facilitate the transformation of chemical reactants into products. These other molecules are collectively referred to as _________.
|
coenzymes
|
|
|
The enzyme lactase ________.
|
facilitates the breakdown of lactose
Correct. The lactase enzymes convert lactose to glucose and galactose. |
|
|
What is activation energy?
|
the energy required to initiate or begin a chemical reaction
Correct. Enzymes lower activation energy, thereby making reactions occur faster. |
|
|
What is the best description of a coupled reaction?
|
two reactions that involve one providing energy for the other
|
|
|
When bonding a phosphate group to ADP ______.
|
Energy will be consumed.
|
|
|
Which law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can change from one form to another?
|
first law of thermodynamics
Correct. This is what the first law of thermodynamics states. |
|
|
Which of the following does not bind to the active site of an enzyme?
noncompetitive inhibitor competitive inhibitor substrate allosteric regulator |
allosteric regulator
|
|
|
Which of the following is the most critical in determining enzyme function? (See book section:
its size its overall shape its entire amino acid sequence the shape of the active site |
the shape of the active site
Correct. The shape of the active site is the most critical aspect of whether a substrate can bind or not. |
|
|
Which of the following statements about ATP is false?
It contains a nitrogenous base. It contains three phosphates. When the third phosphate group is removed from ATP, the reaction is endergonic. Energy is released when the outermost phosphate separates from ATP. |
When the third phosphate group is removed from ATP, the reaction is endergonic.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about energy is true?
Energy conversions decrease entropy. Energy cannot be created. Energy can be destroyed. Energy can be converted from one type to another with near 100% efficiency. |
Energy cannot be created
|
|
|
Which of the following statements about metabolic pathways is true?
A single enzyme is usually responsible for many steps in the metabolic pathway. A metabolic pathway can be composed of only a single enzyme reaction. The reactions in a metabolic pathway are not linked. The product of one enzyme reaction becomes the substrate of the next enzyme in the metabolic pathway. |
The product of one enzyme reaction becomes the substrate of the next enzyme in the metabolic pathway.
Correct. This allows for a rapid enzymatic transformation from beginning substrate to end product. |

