![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
living organisms all... |
need nutrition |
|
|
plants
|
multicellular
chloroplasts photosynthesize cellulose cell walls store carbohydrates as starch or sucrose |
|
|
animals
|
multicellular |
|
|
fungi
|
made from hyphae
hyphae have many nuclei chitin cell walls feed using saprotrophic nutrition store carbohydrate as glycogen |
|
|
bacteria
|
single celled
have a cell wall and plasmids no nucleus some carry out photosynthesis some feed off dead organisms have a circular chromosome of DNA |
|
|
protoctists
|
single celled
microscopic |
|
|
viruses
|
smaller than bacteria
parasitic no cellular structure have a protein coat contain nucleic acid |
|
|
what is a pathogen?
|
pathogens are things that cause diseases and can be fungi, bacteria, protoctists and viruses.
|
|
|
what are carbohydrates and lipids made of?
|
carbon
hydrogen oxygen |
|
|
what are proteins made of?
|
carbon
hydrogen oxygen sulphur phosphorus nitrogen |
|
|
what is the test for glucose?
|
add benedict's solution then heat gently
change from blue to orange indicates glucose is present |
|
|
what is the test for starch?
|
add iodine and swirl
change from red to black/blue indicates starch is present |
|
|
What does amylase do? Where's it produced?
|
breaks down of starch into maltose
is found in the mouth and small intestine produced in the salivary glands, pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
What does maltase do? Where's it produced? |
breaks down maltose into glucose
found in the stomach produced in the pancreas |
|
|
What do proteases do? Where are they produced?
|
breaks down proteins into amino acids
found in the stomach and small intestine produced in the pancreas |
|
|
What do lipases do? Where are they produced?
|
breaks down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
found in the small intestine produced in the pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
what factors affect enzymes?
|
temperature
pH |
|
|
what is diffusion?
|
the movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
|
|
|
what is active transport?
|
the movement of substances against a concentration gradient from low concentration to high concentration. this requires energy from respiration.
|
|
|
what is osmosis?
|
the movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential along a concentration gradient.
|
|
|
what are turgid cells?
|
cells which are swollen with water making them rigid
|
|
|
what are the factors that affect the rate of movement in and out of cells.
|
concentration gradient
temperature surface area |
|
|
What are the equations for photosynthesis
|
carbon dioxide +water = glucose + oxygen
CO2 + H2O = C6H12O6 + O2 chlorophyll and sunlight are necessary |
|
|
what factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
|
carbon dioxide concentration
temperature light intensity |
|
|
nitrogen deficiency
|
making leaves and amino acids
yellow leaves, weak stem |
|
|
magnesium deficiency
|
making chlorophyll
upper leaves normal, lower leaves yellow |
|
|
phosphorus deficiency
|
making roots
poor root growth, purple leaves |
|
|
potassium deficiency
|
making flowers and fruit
yellow leaves with dead spots, poor fruit and flower growth |
|
|
carbohydrate
|
immediate energy
bananas, brown rice, potatoes |
|
|
protein
|
growth and repair
meat, sea food, spinach |
|
|
lipids
|
long term energy
milk, cakes |
|
|
vitamin A
|
vision and skin
yellow-orange fruit and vegetables, eggs, milk |
|
|
vitamin C
|
aiding the absorption of iron and copper, helps fight infection
fruits, oranges, blackcurrants |
|
|
vitamin D
|
absorption of calcium, skin
sunlight, some fish, eggs |
|
|
calcium
|
bones and teeth
dairy products |
|
|
iron
|
haemoglobin, myoglobin
red meats |
|
|
dietary fibre
|
bowel function
cereals, bread |
|
|
water
|
respiration
water |
|
|
what is digestion?
|
process in which large insoluble molecules of food are broken down into smaller ones.
|
|
|
what is absorption?
|
the process by which soluble molecules produced by digestion are taken from the gut.
|
|
|
what is assimilation?
|
the cells of the tissues absorb the molecules for use
|
|
|
what is excretion?
|
the removal of metabolic waste products that have been in the body mainly through sweating, urine and exhaling.
|
|
|
what is egestion?
|
the removal of waste undigested products such as faeces.
|
|
|
how is the small intestine adapted for absorption?
|
villi and micro-villi give it a large surface area
there is a continuous blood supply keeping the concentration gradient high the surface of the intestine is only one cell thick so that diffusion is quick and easy |
|
|
aerobic respiration
|
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy
C6H12O6 + O2 = CO2 + H2O + energy |
|
|
anaerobic respiration
|
glucose = lactic acid + energy
|
|
|
What happens when you inhale
|
Intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract
Thorax volume increases, decreasing pressure, allowing air in |
|
|
What happens when you exhale |
Intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax Thorax volume decreases, forcing air out |
|
|
how are alveoli adapted?
|
large surface area
thin walls large capillary network |
|
|
what are the effects of smoking?
|
cause cancerous mutations
removes cilia hardens the arteries causing coronary disease carbon monoxide hinder oxygen absorption |
|
|
what does the phloem do?
|
transports amino acids and sucrose round the plant.
the tube like cells are alive and substances can flow both ways. |
|
|
what does the xylem do?
|
transports water and dissolved minerals.
it is made up of a dead hollow column of cells. |
|
|
what affects transpiration?
|
humidity
temperature wind speed light intensity |
|
|
what role do phagocytes play in the blood?
|
ingest pathogens by encircling them and then breaking them down and releasing the broken down waste products.
|
|
|
what role do lymphocytes play in the blood?
|
release antibodies which are specific to each pathogen. the body remembers past pathogens using memory cells and can then quickly reproduce that antibody this is how vaccinations work.
|
|
|
what role does plasma play in the blood?
|
transports carbon dioxide, digested food, urea, hormones and heat energy. these substances are dissolved in water as plasma is 90% water.
|
|
|
what role do red blood cells play in the blood?
|
they transport oxygen for respiration.
haemoglobin enucleate bi-conclave |
|
|
what role do platelets play in the blood?
|
cause blood clotting if there is any damage thereby preventing loss of blood. fibrin then covers the platelets in a mesh.
|
|
|
arteries
|
have a small hole in the centre and thick bands of muscle and tissue.
carry blood away from the heart |
|
|
veins
|
have a large hole in the centre and thin bands of muscle and tissue.
carry blood towards the heart valves along the vein stop blood flowing backwards |
|
|
capillaries
|
walls only one cell thick
carry blood through tissues |
|
|
what does urine contain?
|
water, salts and urea
|
|
|
what is homeostasis?
|
the maintenance of a constant internal environment despite external changes.
|
|
|
what is geo-tropism?
|
growth in response to gravity
in roots and shoots |
|
|
what is photo-tropism?
|
growth in response to light
in the tips of shoots and in drought conditions |
|
|
nervous communication is...
|
fast, electrical, uses nerves, short, local
|
|
|
hormonal communication is...
|
slow, chemical, uses blood, long, widespread
|
|
|
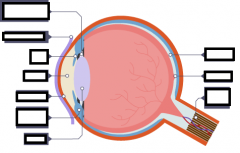
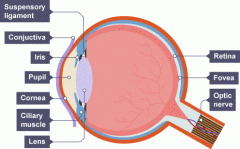
What happens to the eye in bright light?
|
radial muscles relax
circular muscles contract the pupil is small |
|
|
What happens to the eye in dim light?
|
radial muscles contract
circular muscles relax the pupil is big |
|
|
What does the eye do to focus on things close up?
|
contracts the ciliary muscles
lengthens/slackens the suspensory ligaments the lens is more convex |
|
|
What does the eye do to focus on things far away?
|
relaxes the ciliary muscles
ahortens/tightens the suspensory ligaments the lens is less convex |
|
|
What does ADH do?
|
It makes the kidney reabsorb more water (osmoregulation)
|
|
|
what does adrenaline do?
|
adrenal glands
prepares body for physical activity increases HR |
|
|
what does insulin do?
|
pancreas
glucose regulation liver and muscles store glucose as glycogen |
|
|
what does testosterone do?
|
testes
regulates development secondary male characteristic and maturing of sperm |
|
|
what does progesterone do?
|
ovaries
regulates the menstrual cycle maintains the uterus during pregnancy |
|
|
what does oestrogen do?
|
ovaries
regulates the menstrual cycle and development controls female secondary sexual characteristics causes the egg to be released |
|
|
What are the characteristics of sexual reproduction?
|
two parents
full number of chromosomes in the offspring half of their chromosomes from each parent there is variation from the parents produced through meiosis |
|
|
what are the characteristics of asexual reproduction?
|
one parent
offspring have the full number of chromosomes all the chromosomes come from the one parent there is no variation from the parent genetically produced through mitosis |
|
|
what are the adaptations of insect pollinated plants?
|
brightly coloured large petals
sweetly scented contain nectar moderate quantity of pollen pollen is sticky/spiky anthers inside the flower and firm stigma inside the flower stigma is sticky |
|
|
what are the adaptations of wind pollinated plants?
|
small dull petals
no scent no nectar lots of pollen produced pollen light and smooth anthers loosely attached and dangle out stigma hangs out stigma is feathery or net-like |
|
|
what happens during plant pollination?
|
pollen sticks to stigma
pollen grows a pollen tube downwards towards the ovary of the flower pollen tube carries the nucleus of the pollen into the ovary pollen fuses with an ovule (fertilisation) petals die and fall off ovule turns into a seed the ovary may then produce sugars to form a fruit |
|
|
conditions necessary for seed germination...
|
moisture
warm temperature oxygen |
|
|
what methods do plants use to produce asexually?
|
runners
tubers cuttings |
|
|
what does adenine pair with?
|
thymine
|
|
|
what does cytosine pair with?
|
guanine
|
|
|
what is meiosis?
|
four cells produced
each has half the number of chromosomes haploid gametes chromosomes switch genes before the cell switches |
|
|
what is mitosis?
|
two cells produced
each has a full number of chromosomes diploid gametes both genetically identical to each other and the parent |
|
|
what factors increase the likelihood of a mutation occurring?
|
ionising radiation
chemical mutagens chemicals in tobacco |
|
|
how much energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next?
|
10% |
|
|
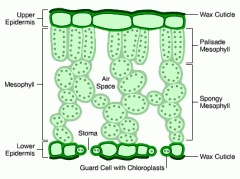
How is the leaf adapted for photosynthesis? |
Thin- so light can get in
Lots of chlorophyll to trap light Stomata for efficient gas exchange |
|
|
What factors affect the rate of movement of substances into and out of cells? |
SA:Volume ratio- more SA:Volume = faster diffusion Temp- higher temp= faster moving particles = faster diffusion Concentration gradient- steeper gradient = faster diffusion |
|
|
What value is very important when calculating energy content in a food sample? |
4.2J of energy are needed to raise 1ml of water by 1 degree C |
|
|
How do we investigate the effect of light on net gas exchange from a leaf? |
Use BIS indicator. High CO2- Yellow Medium- Red Low- Purple |
|
|
Describe the journey of water through a plant
|
Soil --> Root Hairs --> Xylem --> Leaves --> Stomata --> Air |
|
|
How does the immune system respond to disease? |
Phagocytosis --> Antigen presentation to T helper cells --> T helper cells activate --> B helper cells make antibodies --> antibodies kill pathogens |
|
|
How does vaccination work? |
It results in the manufacture of memory cells, which stay alive to fight the disease if you get re-infected (these cells have specific antibodies). |
|
|
What organs excrete? |
Lungs excrete carbon dioxide Kidneys excrete urea and excess water Skin excretes some urea and plenty of water/salt |
|
|
What is happening when a mouse jumps in the air in surprise? |
The sound is the stimulus. The receptor (the ear) transduces the sound into a signal. The signal is carried up the sensory neurone to the spinal cord (the coordinator) which links to a motor neurone, via a relay neurone. The motor neurone carries the signal to the muscles of the legs (the effectors). The contracting muscles make the mouse jump- this is the response. |
|
|
What do we do when we are too hot and too cold? |
Too hot: Lots of sweat is produced (transfers heat away from body when evaporates) Blood vessels close to surface of the skin vasodilate to allow more heat to radiate away Hairs lie flat Too cold: No sweat Blood vessels near surface of skin vasoconstrict You shiver Hairs stand on end to create insulating layer of air |
|
|
What is fertilisation? |
The fusion of a male and female gamete to produce a zygote that undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo |
|
|
What are genes and chromosomes? |
Genes are recipes for proteins Chromosomes are long chains of genes |
|
|
What does mRNA use instead of Thymine? |
Uracil |
|
|
What are recessive alleles? |
Alleles that are only expressed when no other alleles are present |
|
|
What is codominance? |
Where both alleles are expressed in the same phenotype |
|
|
In human cells, what is the diploid number of chromosomes and the haploid number of chromosomes? |
Diploid- 46 Haploid- 23, gametes have this |
|
|
What is MRSA? |
It is a bacteria that is resistant to most antibiotics (and is therefore very dangerous) |
|
Fill in the gaps |
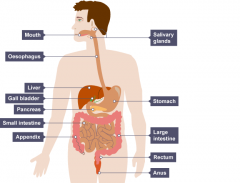
Ask for definitions on p16 (RG) |
|
Fill in the gaps |
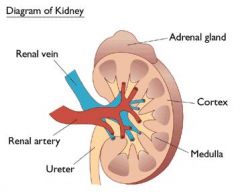
|
|
Fill in the gaps |
Ask for definitions on p45 (RG) |
|
Fill in the gaps |
|
|
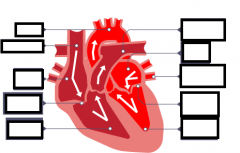
Fill in the gaps |
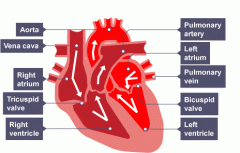
Ask for definitions on p38 (RG) |
|
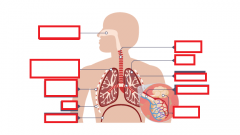
Fill in the gaps |
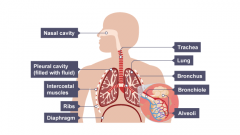
|
|
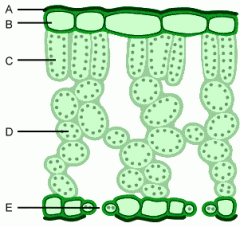
Fill in the gaps |
Ask for definitions on p19 (RG) |
|
|
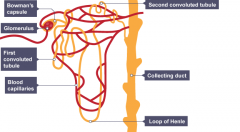
Describe what happens in ultrafiltration |
Blood from the renal artery flows through the glomerulus. A high pressure is built up which squeezes the water, urea, salts and glucose out of the blood and into the Bowman's Capsule. The membranes b/w the blood vessels in the glomerulus and the Bowman's capsule act like filters (big molecules like proteins and blood cells aren't squeezed out). The filtered liquid in the Bowman's capsule is known as glomerular filtrate. |
|
|
Describe what happens in reabsorption |
As the filtrate flows along the nephron, useful substances are selectively reabsorbed back into the blood. Glucose is reabsorbed at the proximal convoluted tubule Sufficient salt is reabsorbed Sufficient water is reabsorbed from the collecting duct into the bloodstream |
|
|
What do pulmonary, hepatic, and renal mean? |
Pullmonary- to do with lungs Hepatic- to do with liver Renal- to do with kidneys |
|
|
Where is bile produced, stored and what does it do? |
Produced in liver, stored in gall bladder, secreted into small intestine where it emulsifies fats (it is alkaline) |

