![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chloroplasts are concentrated in the cells of the _______, the green tissue in the interior of the leaf
|
mesophyll
|
|
|
Tiny pores in a plant where carbon dioxide enters the leaf and oxygen exits
|
stomata
|
|
|
_____ is a thick fluid found in the second compartment of the chloroplast. What happens here?
|
stroma, sugars are made from co2.
|
|
|
thylakoids
|
a system of disklike membranous sacs which contain the third chloroplast compartment.
|
|
|
thylakoids are concentrated in stacks called _____
|
grana
|
|
|
Where are chloroplasts located?
|
thylakoid membranes
|
|
|
Photosynthesis formula
|
6 CO2+ 12 H20+ light> C6H12O6+ 6 H2O+ 6O2
|
|
|
Where does 6O2 released in photosynthesis come from?
|
12H2O
|
|
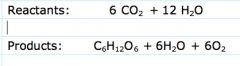
Where does each molecule end up?
|
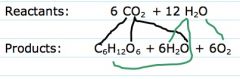
here
|
|
|
Redox reaction
|
oxidation-reduction process
|
|
|
oxidation
|
the loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction.
|
|
|
reduction
|
the gain of electrons by a substance involved in a redox reaction.
|
|
|
When water molecules are split apart, they are ______.
|
oxidized
|
|
|
CO2 is _____ when it's turned to sugar.
|
reduced
|
|
|
What are the two stages of Photosynthesis?
|
Light reactions and Calvin Cycle (or dark reactions)
|
|
|
Which reactions convert light energy to chemical energy and produce O2 gas as a waste product?
|
light reactions
|
|
|
Summary of the Calvin cycle
|
a cyclical series of reactions that assemble sugar molecules using Co2 and the energy-containing products of light reactions.
|
|
|
What is ATP made from?
|
ADP and phosphate.
|
|
|
The incorporation of carbon from Co2 into organic compounds
|
carbon fixation
|
|
|
Electromagnetic Spectrum
|
Gamma, X-Ray, UV, Visible, Infrared, Microwave, Radio
|
|
|
Which kinds of light are absorbed mainly by pigments in the granum?
|
blue-violet and red-orange
|
|
|
Which pigment participates directly in light reactions? What color light does it absorb?
|
Chlorophyll a
|
|
|
What pigment broadens the range of light that a plant can use by conveying absorved energy to chlorophyll a?
|
chlorophyll b
|
|
|
Which pigment passes some light to chlorophyll a but mostly dissipates excessive light energy? What color does it absorb the most?
|
carotenoids, blue-green
|
|
|
The molecule which excited electrons pass their electron too.
|
primary electron acceptor
|
|
|
Reaction center (in photosynthesis)
|
the donating chlorophyll molecule which gives an electron to the primary electron acceptor and the primary electron acceptor.
|
|
|
Photosystem
|
antenna molecules, reaction center, primary electron acceptor
|
|
|
the chlorophyll A molecule in photosystem I
|
P700
|
|
|
the chlorophyll A molecule in photosystem II
|
P680
|
|
|
Which is first, photosystem 1 or photosystem II?
|
photosystem II
|
|
|
What is added to NADP+ to create NADPH?
|
two high-energy electrons and a H+.
|
|
|
What is the process which gives photosystem II needed electrons?
|
H2O is split into 2 H+, O, and two electrons. The two electrons are used in photosystem 2. 2H+ is in the chloroplast and is used later for reduction of NADP+. O molecules combine and are released through stoma.
|
|
|
Products of light reactions
|
ATP, O2, and NADPH
|
|
|
the protein complex which is flask shaped and creates energy through chemiosmosis
|
ATP synthase
|
|
|
In photosynthesis, the chemiosmotic production of ATP is called _____________.
|
photophosphorylation
|
|
|
An electron transport chain is between ________ and _______. The energy released pumps ___ ions from the ________ into the _____
|
photosystem II and photosystem I. H+. stroma. thylakoid compartment.
|
|
|
What molecule is constructed from the Calvin cycle which is used to make glucose or other organic molecules as needed?
|
G3P
|
|
|
First step of Calvin cycle, enzyme, and product, and sugars involved.
|
(3) CO2 molecules are catalyzed by Rubisco, which combines each CO2 with a five-carbon sugar called RuBP. Six molecules of 3-PGA result, 2 from each CO2 molecule.
|
|
|
how many GP3s are needed to make one glucose?
|
2
|
|
|
What is the net gain of one calivn cycle spin?
|
1 G3P
|
|
|
in one turn of the calvin cycle, __ CO2 molecules are used, ___ ATP molecules are used, and ___ NADPH molecules are used.
|
3,9,6
|
|
|
Where do the Calvin cycles take place?
|
the stroma
|
|
|
a type of reproduction used by prokaryotes meaning "dividing in half".
|
binary fission
|
|
|
sexual reproduction
|
the reproductive process that involves the union of a sperm and an egg.
|
|
|
The scientist who stated that all cells come from cells
|
Rudolf Virchow
|
|
|
chromosomes
|
the structure that contains most of the organism's DNA.
|
|
|
Cell theory
|
all cells come form preexisting cells
|
|
|
What are the sections of Interphase in Mitosis?
|
GI, S, G2
|
|
|
What percent of the cell cycle is interphase?
|
90%
|
|
|
What happens in G1?
|
-cell increases supply of proteins
-increases number of organelles -grows in size |
|
|
What happens in the S phase?
|
DNA synthesis occurs
|
|
|
What happens in G2?
|
-metabolic activity
-protein synthesis |
|
|
What does the mitotic phase consist of?
|
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
|
|
|
What happens in mitosis vs cytokinesis?
|
Mitosis- nucleus and contents divide and are evenly distributed in two daughter cells
Cytokinesis- cytoplasm divides. |
|
|
Four stages of mitosis
|
prophase metaphase anaphase telophase
|
|
|
Prophase (5 things, but in no particular order)
|
1.Chromatin coils
2.Nucleoli disappears 3. Late in prophase, nuclear envelope breaks up 4. Mitotic spindle begins to form 5. kinetochore forms at the centromere region where microtubules attach. |
|
|
Metaphase (2, in no order)
|
1. Mitotic spindle fully formed
2. Chromosomes convene on metaphase plate. |
|
|
Anaphase (2, in no order)
|
1. Two centromeres come apart from each chromosome and sister chromatids separate.
2. Motor proteins of the kinetochores powered by ATP walk the daughter chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. |
|
|
Telophase (4, in no order)
|
reverse of prophase
1. Daughter nuclei appear 2. nucleoli reappear 3. chromatin forms 4. mitotic spindle disappears |
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
Cleavage furrow in animals cells, cell plate in plants. Cytoplasm divides.
|
|

What stage?
|
Anaphase
|
|

WHat stage?
|
prophase
|
|

What stage?
|
metaphase
|
|
what phase?
|
interphase
|
|

what phase?
|
telophase/cytokinesis
|
|
|
Forms in animal cells during cytokinesis
|
cleavage furrow
|
|
|
Forms in plant cells during cytokinesis
|
cell plate
|
|
|
typical body cell
|
somatic cell
|
|
|
How many chromosomes does the typical somatic cell have?
|
46
|
|
|
homologous chromosomes
|
two chromosomes which both carry genes controlling the same inherited characteristics
|
|
|
Autosomes
|
non-sex chromosomes
|
|
|
how many pairs of homologous chromosomes do humans have?
|
23
|
|
|
diploid cells
|
cells whose nuclei contains two homologous sets of chromosomes
|
|
|
diploid number? in humans?
|
total number of chromosomes. In humans, 46
|
|
|
gametes
|
A sex cell. a haploid egg or sperm.
|
|
|
haploid cell
|
a cell with a single chromosome set (23 in humans)
|
|
|
haploid number in humans
|
23
|
|
|
location for a gene on the chromosome
|
locus
|
|
|
goal of meiosis
|
reduce the chromosome number from diploid to haploid
|
|
|
Prophase I (7)
|
1. Chromatin coils so that each chromosome becomes visible.
2. synapsis/ creation of tetrad 3. Crossing over 4. Nucleoli disappears 5. Spindle forms 6. Nuclear envolope breaks 7. Tetrads move towards center of cell |
|
|
synapsis
|
homologous chromosomes come together as pairs
|
|
|
four chromatids, 2 homologous chromosomes. all together as a pair.
|
tetrad
|
|
|
Metaphase I
|
Tetrads are aligned int he center of the cell
|
|
|
How are homologous chromosomes held together in Metaphase I?
|
at sites of crossing over
|
|
|
Anaphase I
|
Duplicated chromosomes move to either end of the cell, breaking from the tetrad.
|
|
|
Telophase I and Cytokinesis 1
|
1. Chromosomes arrive at the ends of the poles
2. Two daughter haploid cells are born 3. In some cells, chromosomes uncoil and nuclear envelope reappears. There is a interphase. Sometimes this doesn't happen. |
|
|
In Meiosis, when does each cell become a haploid cell?
|
Telophase I
|
|
|
Meiosis II
|
Basically Mitosis with a haploid cell.
|
|
|
Crossing over? when?
|
the exchange of corresponding segments between two homologous chromosomes during prophase 1 of meiosis.
|
|
|
chiasma
|
site of crossing over which appears as x-shaped regions.
|
|
|
karyotype
|
an orderly display of magnified images of the individual's chromosomes
|
|
|
nondisjunction
|
one of the members of a chromosome pair fail to separate. Can occur in meiosis one or two.
|
|
|
disorder with XXY, XXXY, XXXXY.
Who does it occur in? Results? |
Klinefelter's Syndrome. Men only. Small testes, breast development, sterile.
|
|
|
XYY disorder. Who does it occur in? Results?
|
Normal Male. Taller than average.
|
|
|
XXX disorder.Who does it occur in? Results?
|
Metafemale. limited fertility
|
|
|
XO. Who does it occur in? Results?
|
Turner's syndrome, female.
-Short stature. -web of skin between neck and shoulders. -not fully developed sex organs -sterile |
|
|
Trisomy 21
|
Also known as Down syndrome. Round face, flattened nose bridge, small, irregular teeth, heart defects, susceptibility to respiratory infection, leukemia, Alzheimer's disease. 50% chance of giving down syndrome to the child of one who has down syndrome.
|
|
|
hybrids
|
the offspring of two different varieties
|
|
|
monohybrid cross
|
parents differ in only one characteristic
|
|
|
dihybrid cross
|
mating of parental varieties differing in two characteristics
|
|
|
principle of segregation. Who's principle?
|
pairs of genes segregate (separate) during gamete formation. the fusion of gametes at fertilization pairs genes once again.
Mendel's |
|
|
principle of independent assortment, who?
|
each pair of alleles segregates independently during gamete formation
|
|
|
testcross
|
a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual.
|
|
|
recessive genetic disorders
|
1.albinism
2.cystic fibrosis 3.galactosemia 4. PKU 5. Sickle cell 6. Tay-Sachs |
|
|
dominant disorders
|
1. dwarfism
2. alzheimer's disease 3. huntington's disease 4. hypercholesterolemia |
|
|
Aminocentesis
|
a physician carefully inserts a needle through the mother's uterus, extracting amniotic fluid
|
|
|
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
|
the physician inserts a flexible tube through the mother's vagina and cervix into the uterus and suctions off a small amount of fetal tissue from the placenta. Faster than aminocentesis.
|
|
|
Which is less risky? amniocentesis or CVS?
|
aminocentesis
|
|
|
A, B, O, or AB refers to
|
the type of carbohydrates covering a person's red blood cells.
|
|
|
incomplete dominance
|
red+white=pink
|
|
|
codominance
|
both alleles expressed
|
|
|
polygenic inheritance
|
the additive effects of two or more genes on a single phenotypic characteristic
|
|
|
dna has a _________ backbone
|
sugar-phosphate
|
|
|
Thymine and cytosine are ___-ring structures called ______.
|
single, pyrimidines.
|
|
|
Adenine and guanine are _____-ring structures called _____.
|
double, purines
|
|
|
Says #A=#T and #c=#g
|
Chargaff Rule
|

