![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Somatic-voluntary |
I.e skeletal muscle |
|
|
Autonomic-involuntary uncontrol |
Inside our internal organ i.e cardiac muscle and smooth muscle produce a response via sympathetic fight or flight action for instance when you almost get run by a tiger your internal organ such as blood vessels (effector) increases this is called autonomic things you can't control |
|
|
Descending |
Gradually going from higher to lower-top of hill to the bottom |
|
|
Plexus |
Each of the cervical plexus in the neck, brachial plexus in the shoulder,lumbar plexus lower abdomen,sacral plexus, lower parts I.e leg and foot. Each plexus consist of specific names for specific job they do. Each nerve plexus shape like nerve branches out to their specific job |
|
|
Somatic motor neuron |
ACh is short for acetylcholine and this is the neurotransmitter chemical at the synapse |
|
|
SNS |
provides Conscious and subconscious controls over the skeletal muscle of the body lower motor neurons maybe controlled by reflexes at the spinal cord I.e the somatic motor neuron send ACh acetylcholine neurotransmitter chemical at the synapse to the effector such as skeletal muscle and the result is contraction of the leg |
|
|
Preganglion neuron |
The cell bodies of the preganglionic neuron lie in the brain stem and spinal cord |
|
|
Autonomic ganglia |
Here, the axon endings of preganglionic neurons synapse with the dendrites or cell bodies of postganglionic neurons the second motor neuron in the pathway |
|
|
Sympathetic-fight or flight |
Branch of ANS controlling response to. The sympathetic division activate the body during extreme situations such as fear, exercise or rage |
|
|
Parasympathetic |
Branch of ANS controlling which response to. The parasympathetic is active when the body is at rest allowing us to conserve body energy. |
|
|
Sympathetic division is the action division. It. C |
H h /txzeE |
|
|
Afferent neurons |
Incoming information to the CNS |
|
|
Efferent neurons |
Incoming information away from the CNS |
|
|
Ascending and descending |
|
|
|
Limbic system |
Thalamus and hypothalamus regions |
|
|
Glands |
Glands are cells that produce exocrine or endocrine secretions. Ducts are a passageway that delivers exocrine secretions to an epithelial surface |
|
|
Exocrine exo outside crying |
Exocrine glands cry through tubes called ducts to the outside I.e anywhere that is connected to the outside e.g tear ducts are exocrine crying to the outside of the eye, salivary glands cry into the mouth other glands cry into the digestive system |
|
|
Endocrine glands |
Cry to the inside I.e into the bloodstream |
|
|
(Exocrine glands) (into ducts) Non hormonal secretions - chemicals |
Sweat glands produce a watery secretion that empties onto the surface of the skin, salivary glands secrete saliva that flows into the mouth |
|
|
Endocrine system (diffuses) (ductless glands) |
Secrete their chemical product known as hormones into the intercellular spaces surrounding the gland. From these space the hormones diffuses directly into the blood and are carried through out the body |
|
|
Follicle cells & parafollicular cells |
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells- connective tissue between are parafollicular cells which produces hormone called calcitonin |
|
|
Stimulating |
Encouraging |
|
|
Neurotransmitter |
is a chemical within the axon terminal that is released into the synaptic cleft in response to a nerve impulse and that binds specifically to a receptor in the postsynaptic neuron to affect changes in the postsynaptic neurons membrane permeability. |
|
|
Endocrine system |
Conveys information by chemical signals hormones which travel distances in the bloodstream |
|
|
Inhibit |
Stop |
|
|
Hyperglycaemic effect-high blood glucose stimulate beta cells to secrete |
Many hormones can raise blood glucose levels in the body (hyperglycaemic effect) only insulin can lower it. |
|
|
Stimulate |
Encourage, motivate, inspire |
|
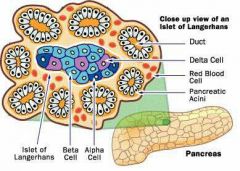
Beta cell and alpha cell of pancreas |
Vuvivufuv |
|
|
Regulate |
Internal control over internal environment |
|
|
Glucose oxidation |
Chemical reaction requires oxygen refers to any reaction where oxygen is combined with another molecule which is then said to be oxidised |
|
|
Internal respiration |
The exchange of gases between the blood I.e red blood cells a and body cells |
|
|
External respiration |
exchange of gases i.e oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli and bloodstream |
|
|
Gas exchange |
The main function of the respiratory system |
|
|
Conducting portion of the respiratory system are the |
Trachea, bronchiole NOT alveoli |
|
|
Residual volume |
The air that never leaves the lungs-if it did they would collapse |
|
|
Inspiratory reserve volume |
Inspiratory is referring to inspired air |
|
|
Expiratory reserve volume |
Volume of air that can be exhaled after normal exhalation |
|
|
Primary chemical stimulus for breathing is the concentration of |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
Dilate |
Open |
|
|
Constrict |
Narrow or tignten |

