![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plasma Membrane |
Regulates traffic of molecules btw the cell membrane and its surroundings; a filter |
|
|
Nucleus |
Houses DNA Genetic control of Eukaryotic cells Control center; tells other organelles what to do |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Produces proteins |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Produce lipids Break down toxins
NO ribosomes on it
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Package & transport materials from E.R. thru-out the cell Stores things Make lysosomes |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Produces ATP (energy) site of cellular respiration --> energy |
|
|
Ribosome |
Builds proteins according to instructions from the genes Made up of protein and RNA, made by nucleoli |
|
|
Cystoskeleton |
Network of Fibers keeps cell structure and shape |
|
|
Animals and Plants have what cell structures? |
All 8: Golgi Ribosome Mucleus Rough ER Smooth ER Mitochondria Cell membrane Cytoskeleton |
|
|
Bacteria have what 2 cell structures |
Membrane and Ribosomes |
|
|
Prokaryote |
a single celled organism No nucleus: DNA floatin around in clumps No organelles (ribosomes not considered oranelle Small cell |
|
|
Eukaryote |
Have many organelles Organized nucleus; membrane bound Large cell |
|
|
What kingdoms are Prokaryotic? |
Archaebacteria - unicellular, in harsh conditions
Eubacteria - unicellular, like bacteria or germs |
|
|
What kindoms are Eukaryotic? |
Protista - anything eukaryotic that isn't fungus, plants, or animals/uni and multi cellular/ don't specialize in functions
Fungi - mostly multicellular, decomposers
Animalia - multicellular, fully functional organelles
Plantae - organelles help w/ photosynthesis |
|
|
Nucleotide |
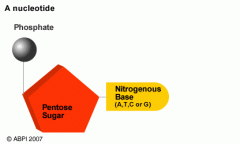
|
|
|
Nitrogenous bases are connected by what bond? |
Hydrogen (weaker so it can break off and DNA/RNA can translate and replicate, etc) |
|
|
What kind of bond connects parts of the nucleotide? |
Covalent (stronger) |
|
|
3 nitrogen bases make up? |
RNA Codon |
|
|
RNA Codons make up? |
Amino acids |
|
|
Who discovered DNA double helix |
Watson and Crick |
|
|
Who provided XRay images of molecular structure of double helix |
Rosalind Franklin |
|
|
What did the helix make them realize? |
DNA copies itself immediately |
|
|
What are the 4 nitrogenous bases in DNA? |
Adenine - Thymine Guanine - Cytosine |
|
|
What nitrogenous base goes with RNA? |
Uracil (replace Thymine) |
|
|
Why is DNA twisted up? |
So it fits in the cell |
|
|
A unit of heredity transferred to the next generation? |
Gene |
|
|
2 types of Genes? |
Structural: code for particular enzyme Regulatory: tells structural what to do/when |
|
|
Who made breakthrough in genetics? |
Mendel |
|
|
How chromosomes got their name? |
Scientists stained them w/COLOR to see and distinguish them |
|
|
What did Mendel grow for genetic experiments? |
Pea Plants because they were easy to grow and manipulate/cross bread
|
|
|
When one trait has NOTHING to do with another, not linked?(like height and eye color) |
Law of Independent Inheritance |
|
|
Diagram used to predict outcome of cross breeding genes/traits |
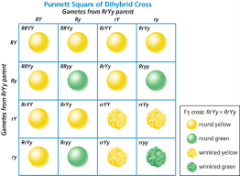
Punnet Square |
|
|
Which chromosome makes someone male? |
Y |
|
|
What is genetic makeup or an organism? |
genotype |
|
|
What are the observable characteristics or an organism? |
Phenotype |
|
|
When a hybrid falls between phenotypes, almost like a mix of the 2, not completely one or the other is? |
Incomplete dominance |
|
|
When both alleles are expressed in heterozygous person? |
Codominant (mostly with blood types like AB) |
|
|
When inheritance of one character has no effect on the inheritance of another |
Law of Independent Assortment |
|
|
How to tell if something is homo or hetero dominant |
Test Cross -if it breeds a recessive gene when mated w/ a homo recessive then its hetero |
|
|
What cells have long hemoglobin proteins that crystaize?
|
Sickle Cells - genetic disease
-cause clots -lead to weak body and pain in heart, kidney, brain |
|
|
when genes are located at specific positions on chromosomes (loci) --> inheritance patterns |
Chromosome theory of Inheritance |
|
|
genes that are close together on a chromosome, tend to be inherited as a set (DON'T follow law of indep assort.) |
Linked Genes |

