![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Kingdom Animalia
|
multicellular
motile heterotrophic diplontic life cycle |
|
|
Phyla Porifera
|
Sponges
sessile (stay in one place), filter feeders (pore bearers), have internal framework of spicules |
|
|
Phyla Cnidaria
|
Hydra, jellyfish, portguese-man-of-war, sea anemones, coral
all examples have: cnidocytes (stinging cells), tentacles hydra have nerve tissue |
|
|
Phyla Platyhelminthes
|
Planaria, parasitic tapeworm, parasitic fluke
"flatworms" |
|
|
Phyla Nematoda
|
Human roundworm, hookworm, pork roundworm, heartworm
"roundworms" only phyla with psuedocolemate Filarial worm causes disease, Elephantiasis |
|
|
Phyla Mollusca
|
Clam, oyster, scallops, snails, slugs, squid, octopus
Second Largest Phylum All examples have: foot, mantle, and visceral mass means soft body Filter feeders: clams, oysters, and scallops |
|
|
Phyla Annelida
|
Sandworms, leeches, earthworms
|
|
|
Phyla Arthropoda
|
Crayfish, crabs, lobster, shrimp, barnacles, spiders, ticks, mites, scorpions, millipedes, centipedes, all insects
LARGEST PHYLUM All have exoskeleton means jointed appendages(feet) segmentation fused into geographic regions |
|
|
Fish body regions
|
Cephalothorax (headmost body) >>Abdomen (tail)
|
|
|
Insect body regions
|
Head>>Thorax>>Abdomen
|
|
|
Phyla Echinodermata
|
Starfish, brittle star, sandollar, sea urchins, sea cucumber
Unique watervascular system Madreporite: Opening used for water consumption Have tubed feet |
|
|
Phyla Chordata
|
Lancelets, seasquirts, lampreys, sharks, skates, rays, flounder, perch, trout, seahorse, goldfish, frogs, toads, snakes, lizards, turtles, crocodiles, alligators, all birds, all mammals
|
|
|
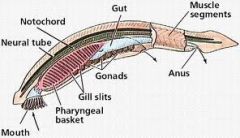
Phyla Chordata Chracteristics
|
Notochord: Stiffening rod that grows in embryonic stage (isnt there in adult stage)
Pharyngeal (gill) clefts: Slits around mouth from embryonic stage Dorsal hollow nervous system: spinal cord Post-anal tail |
|
|
Level of Organization
|
cellular- tissues- organ/organ system
|
|
|
Germ layers
|
embryonic cell layers, form in embryo
diploblastic (two germ layers) triploblastic (three germ layers) |
|
|
Symmetry
|
asymmetry (no symmetry)
radial (round) Bilateral |
|
|
Body plan
|
how the digestive tract is set up
sac plan (only one opening) tube-within-tube (two openings; mouth and anus) |
|
|
Coelem
|
body cavity with organs
acoelemate (have no coelem) pseudocoelemate (false coelem, made of mesoderm and endoderm) Coelemate (true coelem; completely lined with mesoderm) |
|
|
Invertibrate vs. Vertibrate
|
No back bone(vertebral column) vs. Has a backbone
|
|
|
Earthworms
|

Monoecious
have clitellum (thicker band) |
|
|
Cephalization
|
formation of a head
only works with bilateral symmetry |
|

Cellular- no germ layers- no symmetry- no body plan- acoelomate- nonsegmented
|
Porifera
|
|

Tissues- diploblastic- radial- sac plan- acoelomate- nonsegmented
|
Cnidaria
|
|
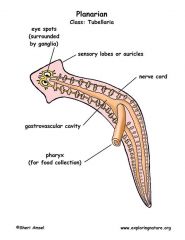
Organ system- triploblastic- bilateral- sac plan- acoelomate- nonsegmanted
|
Platyhelminthes
|
|

Organ system- triploblastic- bilateral- tube within tube- psuedocoelomate- nonsegmented
|
Nematoda
|
|
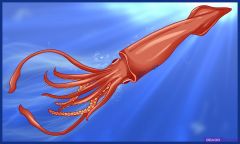
Organ system- triploblastic- bilateral- tube within tube- coelomate- nonsegmented
|
Mollusca
|
|

Organ system- triploblastic- bilateral- tube within tube- coelomate- segmented
|

Annelida, Anthropoda, or Chordata
|
|

Organ system- triploblastic- bilateral- tube within tube- coelomate- nonsegmented
|
Echinodermata
|
|
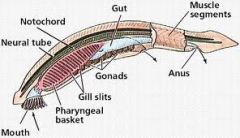
Invertebrate (proto) chordates
|
Chordates without vertebral column
early chordates sea squirts, lancelets |
|
|
Vertebrate chordates
|
chordates with a vertebral column
FISH CLASSES: "fish," aquatic, fins for locomotion, gills for respiration, 2 chambered heart, ectothermic (body temperature varies) Classes: Agnatha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, TERRESTRIAL CLASSES: mostly terrestrial, two paired limbs, lungs for respiration in adult Classes: Amphibia, Reptilia, Mammalia |
|
Class Agnatha
|
"without jaws"
lacking jaws and paired fins Example:lamprey |
|
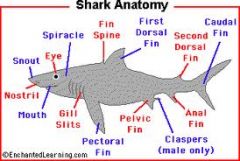
Class Chondrichthyes
|
"cartilaginous fish" --Skeleton of cartilage
have jaws and two pair of paired fins; body covered in scales; mouth is sub-terminal (under head); NO swim bladder (used to float in water) Additional sense: Electroreception 2 chambered heart; ectothermic Examples: sharks, skates, and rays |
|
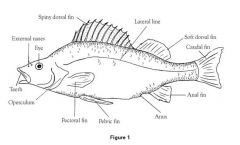
Class Osteichthyes
|
"bony fish"
skeleton of bones; mouth is terminal; usually with swim bladders; gills covered in operculum; skin with mucous glands; lateral line (picks up vibrations); ectothermic; 2 chambered heart; oviparous w/ external fertilization in water Examples: trout, perch, flounder, eel, puffer, sea horse |
|
|
Paired fins
|
Pectoral and pelvic fins
|
|

Class Amphibia
|
"both lives"
limbs without claws; no scales; metamorphosis; young aquatic with gills; adults may be terrestrial with lungs; shelless eggs laid in water; Adult : 3 chambered heart; Larva: 2 chambered heart (tadpole); Ectothermic; external fertilization; Examples: frogs, toads, newts, salamanders, and mudpuppy |
|
|
Cloaca
|
common sewer
|
|

Class Reptilia
|

All have scales, limbs, and are oviparous w/ amniotic shelled eggs
Have "true" reptiles and avian reptiles( birds) Paired limbs no metamorphosis; no gills, only lungs |
|
|
"True" Reptiles
|
Claws on limbs; ectothermic; reptiles are oviparous; internal fertilization
3 chambered heart (partial divider); 4 chambered heart (2 atrium and 2 ventricles) in alligator and crocodile Lizards have eyelids and external ear openings and snakes don't (glass snake: legless lizard) Snakes use tongues sensory structure (smell) Reptiles best known for extinct members called dinosaurs ("terrible lizard") Examples: alligators, crocodiles, lizards, snakes |
|
|
Poisonous snakes
|
Pit Vipers: rattlesnakes, copperheads, cottonmouths. have pit w/ heat sensing organ to track bitten prey; (hematoxin)
Coral Snakes and Cobras: neurotoxin (more toxic; effects nerve system) |
|
|
Why dinosaurs became extinct (3 reasons)
|
1. Dramatic climate changes following asteroids striking our planet
2. Ice ages 3. Competition w/ birds and mammals that evolved |
|

Avian Reptiles
|
Skin covered with feathers; front limbs modified into wings; toothless beak; lungs w/ air sacs (uses 100% of air taken in); oviparous; 4 chambered heart; high metabolism; Endothermic (body temperature remains constant)
Examples: owls, hawks, sparrows, jays, finches, crows |
|

Class Mammalia
|
skin w/ hair; limbs modified w/ claws, nails or hoofs; viviparous or oviparous; endothermic; specialized teeth, highly developed cerebrum, usually 2 pairs of limbs; most with placenta, w/ exception of duckbilled platypus (oviparous)
|
|
|
Parasitic tapeworm
|
Platyhelminthes
|
|
|
Human roundworm
|
Nematoda
|
|
|
Scallops
oysters squid snails |
Mollusca
|
|
|
Sponges
|
Porifera
|
|
|
earthworm
leeches |
Annelida
|
|
|
Crayfish
Any insect |
Arthropoda
|
|
|
Hydra
jellyfish |
Cnidaria
|
|
|
Sandollar
|
Echinodermata
|
|
|
lancelet
perch snake human |
Chordata
|
|
|
Amniotic Egg
|
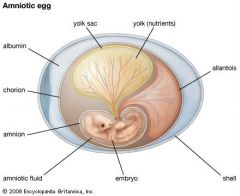
|
|
|
Blastopore
|
1st opening that forms
|
|
|
Deuterostome
|
"2nd mouth"
blastopore forms anus echinodermatas and chordata are dueterostomes |
|
|
Protosome
|
"1st mouth"
blastopore forms mouth |
|
|
Oviparous
|
"egg layers"
|
|
|
Ovoviviparous
|
"egg retainers"
can lay eggs in body cavity |
|
|
viviparous
|
"true live birth"
have umbilical cord |
|
|
Crayfish
|

|
|
|
Evolutionary tree
|
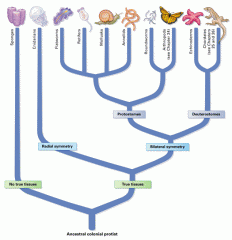
|
|
|
monoecious
|
having both female and male reproductive organs
|
|
|
diecious
|
reproductive organs in separate individuals
|

