![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do cells need to transport in and out of the environment? |
Cells need to take in oxygen for aerobic respiration Need to excrete waste products such as CO2 and urea |
|
|
What does a multicellular organism need to bring and take from each and every cell? |
Every cell needs substances like glucose and oxygen as well as the removal of waste such as CO2 that can be very dangerous to the cell if left to build up |
|
|
How do single celled organisms exchange substances? |
Diffusion directly into or out of the cell across the cell surface membrane, the diffusion rate is quick because of the small distances the substances have to travel |
|
|
Why then do multicellular organisms not use diffusion as transport? |
Larger animals have a low SA:V ratio - it's difficult to exchange enough substances to supply a large volume of animal brought a relatively small outer surface They will need a large amount of oxygen rapidly but diffusion is too slow so inefficient because the diffusion pathway is too long |
|
|
Do to the SA:V issue with multicellular organisms what do they have to combat this issue? |
Exchange organs and systems like lungs |
|
|
Diagram of the lungs. (photo) |
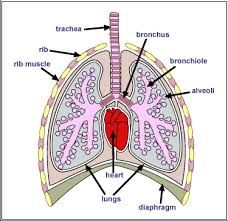
|
|
|
Explain the structure of the lungs |
Air enters the trachea Trachea splits into 2 bronchi - one bronchus leading to each lung Each bronchus then branches off into smaller tubes called bronchioles at the end of these are air sacs called alveoli The ribcage, intercostal muscles and diaphragm all work together to move air in and out |
|
|
Describe the process by which gases are exchanged in the alveolus |
-Diffusion of gas from an area of high concentration to low concentration -Oxygen is in high conc. in the lungs -Short diffusion path |
|
|
Explain why mammals have large number of alveolus in the lungs |
-Mammals are larger so need more oxygen for aerobic respiration -Increases rate of diffusion by increasing the surface area so more gas can be exchanged at any given time |
|
|
List 3 properties of lungs which make them effective in carrying out their function |
-Large Surface Area - Rich Blood Supply - Thin Walls |
|
|
Goblet Cells and ciliated epithelium |
Goblet cells produce mucus which is pushed along the trachea via the ciliated epithelium to stop pathogens invading the airways |
|
|
Elastic Fibres |
Stretch as the walls of the alveoli dilate to allow more air in |
|
|
Cartilage |
Holds the airways open to allow air to pass through smoothly |
|
|
Smooth Muscle |
Contacts allowing bronchioles to constrict and controls flow of air to the alveoli |
|
|
Squamous Epithelium |
flat and pancake-like to allow for a large surface area and rapid diffusion |
|
|
Describe how a spirometer would be used to measure tidal volume |
-Nose peg -Breathe into the mouthpiece normally -Soda lime neutralises the CO2 and the rest of the air would go through the pipes -Pin moves up and down recording the results |
|
|
Describe how you could use a spirometer trace to measure the rate of oxygen uptake |
-Measure amount of oxygen in chamber -Measure how much oxygen is in the chamber after the breathing (at the end) -Subtract the minimum amount from the maximum amount |
|
|
Suggest two factors that should be considered when carrying out a risk assessment for a spirometer |
-Mouthpiece with bacteria should be disinfected -Water levels should be checked so they don't choke |
|
|
Name the measurement represented by X (Q3ai) |
Tidal Volume |
|
|
What is happenening to the elastic fibres at point A (Q3aii) |
Stretching |
|
|
What causes the change in the volume of air between points B and C (Q3b) |
-Diaphragm relaxes and pushes back up to increases pressure -Inter coastal muscles also relax pushing the ribcage in -Air gets pushed out the trachea |
|
|
(Q3c) Calculate the breathing rate of this students breathes per minute |
5secs= 1 breathe 60secs = 12 breaths |
|
|
About 1dm3 of air cannot be expelled from the lungs. This is known as residual Volume. Suggest why it is not possible to expel all the air from the lungs |
- Lungs cannot fully flatten as the muscles and bones can not enclose that far -Stops the lungs from collapsing |
|
|
Name 4 exchange surfaces |
-Alveoli in lungs -Small Intestine -Liver -Root Hair in plants |
|
|
4 properties of efficient exchange surfaces |
-Large Surface area -Thin Wall/ Short diffusion path -Diffusion Gradient -Protected from drying out |
|
|
What happens during Exhalation |
-Ribs move down and in -Diaphragm moves up -Volume Decreases -Pressure increases |

