![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
describe asexual reproduction and give examples
|
-single parent creates 2 clones
-no meiosis, no gamete fuse, 1. budding- small part of parents body separates and forms new offspring (sponges & cnidarians) 2. Fragmentation- parent breaks up into separate pieces and those pieces form new offspring(sea star) 3. parthenogenesis-unfertilized egg develops into an adult animal(insects and crustaceans) |
|
|
describe the sperm
|
male parent
small motile flagellated |
|
|
describe the egg/ovum
|
female parent
large non motile has nutrients for the fetus |
|
|
what are some advantages of sexual reproduction
|
genetic variation
genetic recombination increase variation increase survival |
|
|
disadvantages of sexual reproduction
|
if offspring isn't viable
if the organism is sessil, its hard to find a mate |
|
|
describe hermaphroditism and what is special about it?
|
have both male and female repro organ
self fertilizing ** usually hermaphrodites will still look for ways to cross fertilize first before resulting to self fertilization** |
|
|
describe sequential hermaphroditism and give examples of organisms that do that
|
individuals reverse sex during lifetime.
1. protogynous- female first & then male 2. protandrous- male first then female (wrasses and harems) |
|
|
what is the function of the male reproductive system?
|
1. spermatogenesis
2. deliver sperm to the female repro track |
|
|
where in the testes does spermatogenesis occur?
|
spermatogenesis occurs in the semniferous tubules
|
|
|
what does the interstitial cells scattered between the semniferous tubules do?
|
produce testosterone and other sex hormones
|
|
|
what is the epididymis in charge of?
|
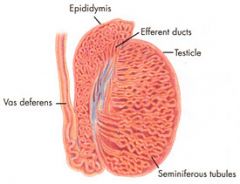
1. transport sperm -20 days
2. maturation of sperm 3. storage of sperm at the tail |
|
|
what two vital organs are found in the scrotum and why is the scrotum necessary?
|
the testes and the epydidymis are found in the scrotum
sperm needs area 1-2 degrees cooler temp. affects sperm production and longevity |
|
|
describe the mechanism of temperature regulation via the pampiniform plexus
|
the testicular artery and vein coil around each other. warm arterial blood is near the cool blood of the vein exchange heat and cool the testicular blood
|
|
|
describe muscle function in the scrotum/ testes
|
warm temperature- relaxed- testes decent
cold temperature- contract- testes closer to body |
|
|
what tube is the sperm propelled through during ejaculation?
|
vas deference
|
|
|
where can you find the vas deference(sperm ducts)
|
it externds from each epydidymis and sperm and extends from scrotum into pelvic cavity
|
|
|
where can we find the ejaculation duct
|
it passes through the prostate gland and joins with the urethra
|
|
|
what is the job of the urethra
|
carries urine and semen through penis
|
|
|
what is the job of the first of the 2 bulbourethral gland
|
deposit semen into the urethra at the time of arousal
|
|
|
what is the bulbourethral fluid?
|
mucus for lubrication
has some semen even before ejaculation |
|
|
what are the three erectile tissue
|
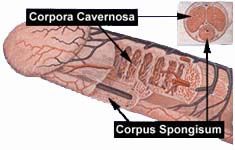
2 cavernous bodies and 1 spongy body
|
|
|
describe the process of an erection/sexual stimulation
|
parasympathetic nerves release nitric oxide which causes smooth muscles of the arterial wall to relax. Arteries dilate/ expand and compress the veins thus more blood rushes in erectile tissue faster that leaves
|
|
|
what local regulator production is stimulated by viagra
|
Nitric oxide
|
|
|
where can you find the glands penis
|
tip of penis
has sensory nerves |
|
|
where can you find the prepuce and what is it?
|
foreskin-loose fitting skin
removed during circumcision |
|
|
what are the three accessory sex glands that secrete sperm and fluid
|
1. seminal vesicles
2. prostate gland 3. bulbourethral glands |
|
|
what fluids do the seminal vesicles produce?
|
1. fructose- energy for the sperm
2. prostiglandins- stimulate contractions of female uterus and move the sperm up female repro track |
|
|
where does the seminal vesicles secrete fructose into
|
vas deference
60% of total sperm volume |
|
|
what pigment does the fructose secreted by the seminal vesicles floresce ?
|
yellow
|
|
|
what fluid is produced by the prostate gland and what is it's purpose in reproduction?
|
alkeline fluid
it neutralizes the acidic environment in the vagina so the sperm could survive |
|
|
what test has to be done to check for prostate cancer
|
PSA- prostate specific antigen test
|
|
|
what is the pathway of the sperm
|
seven up
semniferous tubules- epididymous- vas deference-ejaculation duct-urethra-release from body |

