![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the two functions of the ear
|
balance and hearing
|
|
|
where is the center for balance and equilibrium
|
the inner ear
|
|
|
what are the organs of equilibrium
|
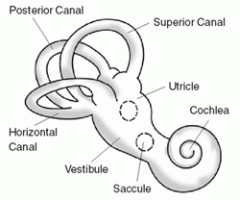
interconnected canals and sacs--> labyrinth
|
|
|
what are the two components of the vestibular apparatus?
|
1. sacule and utricle
2. three semicircular canals |
|
|
where do i find the hair cells and what are their function?
|
inner ear->labyrinth->sacule and utricle
1. sensory receptors 2. mechanoreceptors (pressure) 3. awareness of position relative to the ground |
|
|
where do i find the otolithes and what do they do?
|
labbyrinth->sacule and utricle-> otoliths
Ear stones-they are grains of calcium carbonate 1. gavity reception 2. when head tilts, otoliths bend hairs |
|
|
what fills the semicircular canal?
|
filled with endolymth fluid
|
|
|
what is the ampulla?
|
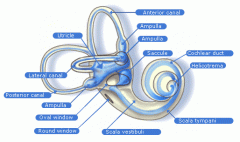
1. enlargements at the base of each canal
-head moves-->fluid moves in canal-->hairs im ampulla bend--> action potential happens |
|
|
what is the orientation of the ear canals and why is it important?
|
each canal is at right angle to each other and it allows detection of turning in any direction
|
|
|
frequency of wave
|
# of pressure waves that occur in a second
slow fequency-low pitch fast frequency- high pitch |
|
|
what is the significance of amplitude of a wave
|
it is proportional to the loudness of a sound
|
|
|
what are the three chambers of the ear?
|
outer ear-pinna
middle ear-auditory bones inner ear-cochlea |
|
|
how does the ear hear?
|
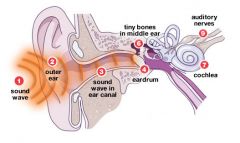
1. sound enters outer ear
2. pinna leads to ear canal 3. ear canal collects waves and channels it to the tympanic membrane 4. tympanic membrane vibrates 5. vibration is transmitted to the middle ear 6. vibrations amplifies sound from the middle ear into the inner ear 7. oval window transmits info into inner ear 8. waves vibrate the basilar membrane 9. stereocilia(tips of hair cells) rub against tectorial membrane 10. action potential |
|
|
describe the structures of the middle ear
|
1. air filled cavity
2. connects to the through via Eustachian tube 3. equalizes pressure btw middle ear and atmosphere 4. ossicles |
|
|
what are the 3 ossicles and what do they do?
|
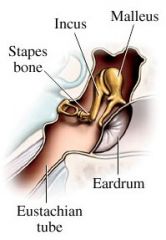
malleus- hammer
incus- anvil stapes-stirrup |
|
|
what are the 3 chambers of the cochlear in the inner ear
|
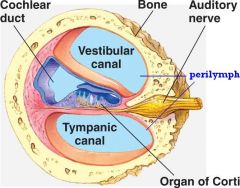
3 structures filled with fluid
1. vestibular canal 2. cochlear duct 3. tympanic canal *basilar membrane separates cochlear duct from temp. canal |
|
|
how does the oval window transmit info
|
1. bows in and out
2. pressure waves transmitted to fluid in the vestibular and tympanic canals 3. causes round windew to bow in and out 4. vibrates vasilar membrane |
|
|
what is the organ of corti and where is it located?
|
ear->inner ear->cochlear duct->organ of corti
1. auditory organ 2. 18000 receptor cells 3. detects changes in pressure and waves 4. located between 2 membranes 5. hairs rest of basilar membrene 6. tectorial membran is stiff and doesnt vibrate much |
|
|
how is the auditory nerve formed?
|
axons joined to form cochlear nerves which join to form the auditory nerve to the brain
|
|
|
what does the basilar membrane do?
|
allows the brain to interprate different sound sound pitches.
1. stiff and narrow end- high pitches 2. wide and flexible end- low pitches |

