![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four parts to the temporal bone?
|
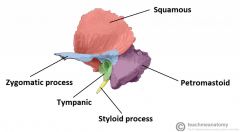
1) Squamosa
2) Mastoid 3) Petrous 4) Tympanic |
|
|
Which muscles are attached to the mastoid process?
|
1) SCM
2) Splenius capitus 3) Longissimus capitus 4) Digastric 5) Anterior, superior, posterior auricular |
|
|
What fraction of the EAC is cartilagenous?
|
1/3
|
|
|
What fraction of the eustacian tube is cartilagenous?
|
2/3
|
|
|
The skin over the cartilaginous canal has what?
|
Sebaceous glands
Ceruminous glands Hair follicules |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the external auditory canal?
Anterior: Posterior: Superior: Inferior: |
Anterior: mandibular fossa & parotid
Posterior: mastoid Superior: epitympanic recess (medially) and cranial cavity (laterally) Inferior: parotid |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the epitympanum?
Medial: Superior: Anterior: Lateral: Inferior: Posterior: |
Medial: lateral semicirc canal & VII nerve
Superior: tegmen Anterior: zygomatic arch Lateral: squamosa (scutum) Inferior: fossa incudis Posterior: aditus |
|
|
What are the following boundaries of the tympanic cavity?
Roof: Floor: Posterior: Anterior: Medial: Lateral: |
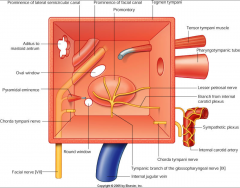
Roof: tegmen
Floor: jugular wall and styloid prominence Posterior: mastoid, stapedius, pyramidal prominence Anterior: cArotid wall, eustachian tube, tensor tympani Medial: labyrinthine wall Lateral: tympanic membrane, scutum |
|
|
This landmark is a notch on the squamosa of the TM, medial to which lies Shrapnell's membrane
|
Notch of Rivinus - a small defect in the posterior edge of the bony tympanic annual ring
|
|
|
Concavity on the superior portion of the temporal bone in which the gasserian ganglion (V) is located.
|
Mechel's cave
|
|
|
What causes gradenigo syndrome?
What is the triad? |
Secondary to perositis of CN VI where it lies in the Dorello's canal.
1) Pain behind the eye 2) Diplopia (CN 6 involvement) 3) Aural discharge |
|
|
What are the three parts to the inner ear?
|
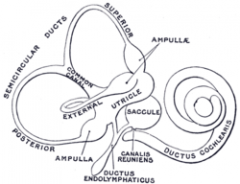
1) Pars superior: vestibular labyrinth (utricle and semicirc canals)
2) Pars inferior: coclea and saccule 3) Endolymphatic sac and duct |
|
|
What are the four openings into the temporal bone?
|
1) Internal auditory canal
2) Vestibular aqueduct 3) Cochlear aqueduct 4) Subarcuate fossa |
|
|
What percent of the population have a pneumatized petrous portion of the temporal bone?
|
1/3
|
|
|
Jacobson's nerve is a branch of which CN?
Auricular nerve is a branch of which CN? |
Jacobson's <-- CN IX
Auricular <--CN X |
|
|
Which nerves lie in the internal auditory canal?
|
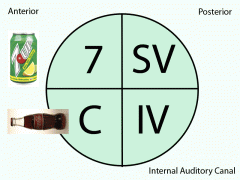
Facial, Cochlear, Superior and inferior vestibular nerves
|
|
|
Bill's Bar, a notch in the internal auditory canal, seperates which two nerves?
|
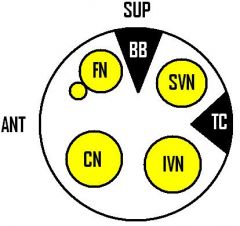
Facial and superior vestibular nerves
|
|
|
What's the length of the eustachian tube at birth? In adulthood?
|
17-18mm at birth and ~35mm in adulthood (so doubles)
|
|
|
Which two muscles help open the eustachian tube?
Which of these works in children? |
1) Tensor palati
2) Levator veli palatini In children, only the tensor palati works (because the levator palatini is separated from the eustachian tube cartilage by a considerable distance. Therefore, a cleft palate child with poor tensor palati fnct is expected to have eustachian tube problems until the levator palati starts to fnct. |
|
|
What pressure differential can "lock" the eustachian tube and prevent it from opening the tube by the tensor palati muscle?
|
90 mm Hg or greater (critical pressure difference) (if pressure differential exceeds 100, TM may rupture)
|
|
|
What do the six hillocks of His become?
|
First Arch:
1) First hillock --> tragus 2) Second hillock -->helicul crus 3) Third hillock --> helix Second Arch 4) Fourth hillock --> antihelix 5) Fifth hillock --> antitragus 6) Sixth hillock --> lobule and lower helix |
|
|
What's the incidence of congenital microtia?
|
1:20,000
|
|
|
Malformation of the auricle implies what?
Canal atresia implies what? (with normal auricle) |
Auricle defect --> auricle is formed early, so implies malformation of the middle ear, mastoid and VII nerve.
Canal atresia occurs is due to a defect @ 28weeks, so if the auricle is normal, then middle ear/ossicles and CN VII are already formed. |
|
|
Preauricular pits/sinus tracts are due to which defect?
|
Improper fusion of the first and second branchial arches
|
|
|
What is Hyrtl's fissure?
|
Provides a route of direct extension of infection from the middle ear to the subarachnoid spaces. Occurs in very young infants and closes as the infant grows. Extends just inferior and anterior to the round window.
|
|
|
What is Treacher Collins syndrome?
|
1) outward-downward slanted eyes
2) Notched lower lid 3) Short mandible 4) Bony meatal atresia 5) Malformed incus and malleus 5) Fishmouth |

