![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
80 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atom
|
Smallest unit of mater
|
|
|
Element
|
A pure substance made of only one type of atom
|
|
|
Compound
|
A substance made by combining 2 or more different elements
|
|
|
Molecule
|
2 or more atoms held together in a bond where electrons are shared (covalent bond0
|
|
|
Ion
|
An atom that has gained or lost electrons
|
|
|
Matter
|
Anything that occupies space, has mass (weight) and is composed of atoms
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Organic compound made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; the key source of energy found in most foods.
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Building block of carbs (single sugar) Ex: Glucose
|
|
|
Disaccharides
|
Double sugar formed when monosaccharides join Ex: Sucrose ( combined glucose and fructose)
|
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
chains of 3 or more monosaccharides Ex: starch (in plants) glycogen (in humans)
|
|
|
Macromolecule
|
Large molecule formed by many smaller molecules
|
|
|
Cellulose
|
Polysaccharide that provides plants with structural support; found in the cell wall
|
|
|
Lipids
|
Nonpolar molecules that aren't soluble in water Ex: Fats, phosholipids, steroids and waxes
|
|
|
Fats
|
Store energy, 3 fatty acids (long chain of carbon and hydrogen bonds) joined to glycerol, 3 carbon molecule, can be saturated or unsaturated
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Large molecules formed by linked smaller molecules (amino acids)
|
|
|
Amino Acid
|
Building block of proteins. There are 20 different ones, some polar/nonpolar, can act as enzymes
|
|
|
Nucleic Acids
|
A long chain of smaller molecules (nucleotides)
|
|
|
Nucleotides
|
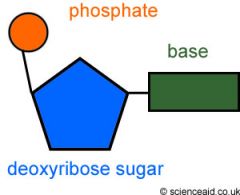
|
|
|
DNA
|
Deoxyribonucleic Acid, double helix structure, contained in chomosomes, blueprint to the body, made of nucleotides
|
|
|
RNA
|
Ribonucleic Acid, single strand of nucleotides, can act as an enzyme
|
|
|
ATP
|
Adenosine TRIphosphate, single nucleotide wtih 2 extra energy storing phosphate groups, stores energy temporally, steady supply is needed for cells to function.
|
|
|
Energy
|
Ability to move/ change matter. Needed for: Metabolism, Building cell structures, Creating proteins, Transforming material in/out of cells
|
|
|
Chemical Reaction
|
A+B-C (A&b are reactants, while C is a product). When bonds can be broken (energy required) or formed (energy released)
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
Sum of all chemical reactions that occur in a n organism to generate energy. Need energy to begin, energy comes form converting food energy to cell energy
|
|
|
Activation Energy
|
Energy needed to start a chemical reaction.
|
|
|
Enzyme
|
Substance that increases the speed of a chemical reaction by reducing amount of activation energy (Protein)
|
|
|
Substrate
|
Substance that an enzyme acts on in a reaction, action determined by shape
|
|
|
Active Site
|
Folds on an enzyme that only certain substrates fit in to.
|
|
|
Bases
|
Have a Ph from 8-14, form hydroxide ions when dissolved in water, neutralize acids
|
|
|
Acid
|
Have a Ph from 0-6, forms hydrogen bonds when dissolved in water, neutralize bases
|
|
|
Cohesion
|
Attraction between two of the same substances
|
|
|
Adhesion
|
Attraction between two different substances
|
|
|
Nonpolar
|
Covalent bonds that share equally, have no charge, and don't dissolve in water
|
|
|
Polar
|
Covalent bonds that share, but one has more than the other, soluble in water
|
|
|
Solution
|
Mixture of evenly distributed substances
|
|
|
Biology
|
The study of life
|
|
|
Cell
|
Highly organized, tiny structure with thing coverings called membranes, smallest unit capable of all life functions.
|
|
|
Reproduction
|
Process by which organisms make more of their own kind.
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
Sum of all chemical reactions carried out in an organism (how it converts everything to energy)
|
|
|
Homeostasis
|
Maintenance of internal stable conditions inspite of changes in the external environment.
|
|
|
Gene
|
Basic unit of heredity in a DNA molecule.
|
|
|
Heredity
|
Passing of traits from parent to offspring.
|
|
|
Ecology
|
Branch of biology that studies interaction between organisms and environment.
|
|
|
Observation
|
Perception of an object or event using the senses
|
|
|
Hypothesis
|
Statement that can be tested, accepted or rejected.
|
|
|
Prediction
|
Expected outcome of an expirement.
|
|
|
Experiment
|
Planned procedure used to test a hypothesis.
|
|
|
Control Group
|
Receives no experimental treatment.
|
|
|
Independent Variable
|
The factor that CHANGES.
|
|
|
Dependent Variable
|
Factor that is measured or DOESN'T CHANGE.
|
|
|
Theory
|
Set of related hypotheses that have been confirmed.
|
|
|
Prokaryotic
|
A small cell w/o a nucleus and internal components (bacteria).
|
|
|
Eukaryotic
|
A larger, more complex cell with a nucleus and organelles (plant, animal, protist, or fungi
|
|
|
Organelle
|
Internal components of a cell that carry out specific functions.
|
|
|
Robert Hooke
|
The first man to look/ name cells under a very simple microscope.
|
|
|
Cell theory
|
1. All cells come from existing cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms 3. All living things are made up of one or more cells |
|
|
Nucleus
|
Boss of the cell and holds the cell's DNA.
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
Cell's interior (gel like)
|
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Takes energy from organic compounds to make ATP.
|
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
Moves proteins made by ribosomes.
|
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
Lacks ribosomes, makes lipids, and breaks down toxic substances.
|
|
|
Gogli Appartaus
|
Processes proteins then packages them into new vesicles.
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
Make proteins.
|
|
|
Cell Membrane
|
Cell's boundary, selectively permeable, made up of a lipid bilayer- polar phosphate groups and 2 fatty acids.
|
|
|
Chromosomes
|
DNA and proteins associated with DNA
|
|
|
Cillia
|
Tail like things on the outside of a eukaryotic cell that are used to move/ direct the cell
|
|
|
Flagella
|
One long tail on a prokaryotic cell that is used to direct and move a cell.
|
|
|
Chloroplast
|
Organelle found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll (stuff that makes cell green) and produces carbs (food) for the cell through photosynthesis.
|
|
|
Central Vacuole
|
Plant cell organelle that stores the cell's nutrients and waste. When full makes the cell rigid and allows it to stand upright.
|
|
|
Cell Wall
|
Found on plant cells, thick outer wall that provides additional shape and protection.`
|
|
|
Passive Transport
|
Movement across a cell membrane that doesn't require energy.
(Goes down the concentration gradient- goes from high conc. to low conc.) |
|
|
Active Transport
|
Movement across a cell membrane that requires energy (Moves against concentration gradient- goes from low conc. to high conc.)
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
Random motion of substances from high to low concentration. (Passive Transport)
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. (Passive Transport)
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion
|
Use of carrier proteins to move large molecules across the membrane down the conc. gradient (Passive Transport)
|
|
|
Sodium- Potassium
|
Uses a carrier protein that transports 3 NaCl+ out of a cell and 2 K+ into the cell. (Active Transport)
|
|
|
Endocytosis
|
Movement of a larger substance into a cell by a vesicle. (Active Transport)
|
|
|
Phagocytosis
|
Bringing in another cell/organism to the cell. (endocytosis)
|
|
|
Pinocytosis
|
Bringing in a liquid that contains dissolved particles to the cell. (endocytosis)
|
|
|
Exocytosis
|
Movement out of the cell by a vesicle. (passive Transport)
|

