![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cell division |
The process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells |
|
|
|
Mitosis |
Part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides |
First stage |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division |
|
|
|
Chromatids |
One of two identical sister parts of a duplicated chromasome |
|
|
|
Centromeres |
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached |
|
|
|
Interphase |
Period of the cell cycle between cell division |
|
|
|
Replication |
Copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA |
|
|
|
Cell cycle |
Series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide |
|
|
|
4 stages of mitosis |
Prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase |
|
|
|
DNA polymerase |
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule |
|
|
|
Prophase |
The first and longest stage of mitosis |
|
|
|
Centrioles |
One of two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope |
|
|
|
Messenger RNA (mRNA) |
RNA molecule that carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell |
|
|
|
Spindle |
A fan like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes |
|
|
|
Metaphase |
During this stage the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell and microtubules connect the centromere of each chromosome to the two poles of the spindle |
Second stage of mitosis |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
Type of RNA that makes up the major part of ribosomes |
|
|
|
Anaphase |
During this phase the centromeres that joined the sister chromatids split allowing the sister chromatids to separate and become individual chromosomes |
Third phase of mitosis |
|
|
Telophase |
During this phase, the chromosomes which were distinct and condensed begin to disperse into a tangle of dense material |
4th and final phase of mitosis |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
Type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis |
|
|
|
Cyclin |
One of a family of closely related proteins that regulate the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells |
|
|
|
Cancer |
Disorder in which some of the body's own cells lose the ability to control growth |
|
|
|
Transcription |
Process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence in RNA |
|
|
|
Transformation |
Process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria |
|
|
|
Bacteriophage |
A virus that infects bacteria |
|
|
|
RNA polymerase |
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription |
|
|
|
Nucleotides |
Monomer of nucleic acid made up of a 5 carbon sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base |
|
|
|
Base pairing |
Principle that bonds in DNA can form only between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine |
|
|
|
Genes |
A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait |
|
|
|
Promoters |
Region of DNA that indicates to an enzyme where to bind to make RNA |
|
|
|
Introns |
Sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein |
|
|
|
Exons |
Expressed sequence of DNA, codes for a protein |
|
|
|
Codon |
Three nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid |
|
|
|
Translation |
Decoding of a messenger RNA message into a polypeptide chain |
|
|
|
What does translation take place on? |
Ribosomes |
|
|
|
Anticodon |
Group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that is complementary to an mRNA codon |
|
|
|
Mutations |
Any change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information |
|
|
|
Point mutations |
Gene mutation involving changes in one or a few nucleotides |
|
|
|
Frameshift mutations |
Mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide |
|
|
|
Polyploidy |
Condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes |
|
|
|
Operon |
Group of genes operating together |
|
|
|
Operator |
Region of chromosomes in an operon to which the repressor binds when the operon is "turned off" |
|
|
|
Differentiation |
Process in which cells become specialized in structure and function |
|
|
|
Hox genes |
Series of genes that controls the differentiation of cells and tissues in an embryo |
|
|
|
Process where DNA makes copies of itself |
Replication |
|
|
|
What controls the cell cycle? |
Cyclins |
|
|
|
Why is it bad to damage nervous tissue? |
Nervous tissue does not go through cell replication and it cannot heal itself |
|
|
|
What is the shape of DNA? |
double helix |
|
|
|
What controls the cell cycle? |
Cyclins |
|
|
|
What are the problems growth causes for cells? |
* DNA can't control cells activities * Surface area to volume ratio limits cell size because a cells volume increases faster than its surface * Diffusion of nutrients can't take place fast enough |
|
|
|
What is the shape of a spindle? |
A football shape |
|
|
|
4 stages if mitosos |
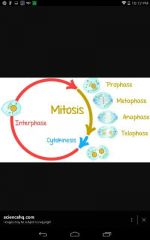
Learn phases |
|
|
|
What are some things that happen during prophase? |
* The chromatin condenses into chromosomes. * The centrioles separate, & a spindle begins to form. * The nuclear envelope breaks down |
|
|
|
What happens during metaphase |
The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere |
|
|
|
What happens during anaphase |
The sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart |
|
|
|
What happens during telophase |
The chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell and lose their distinct shapes two nuclear envelopes will form |
|
|
|
What happens during cytokinesis |
The cytoplasm pinches in half. Each daughter cell has an identical set of duplicated chromosomes |
|
|
|
What happens during interphase |
The cell grows and replicates its DNA and centrioles |
|
|
|
What does the spindle help with? |
Separating chromosomes |
|
|
|
Mitosis |
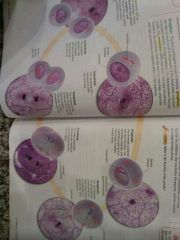
(: |
|
|
|
Cytokenisis |
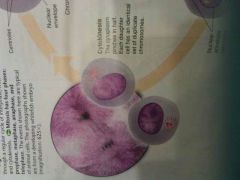
(: |
|

