![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two major div in nervous system?
|
CNS (brain, spinal cord) peripheral (the rest)
|
|
|
What does a dendrite do?
|
Lots of sa to pick up impulse and conduct towards cell body
|
|
|
What is cell body
|
metabolic centre of cell, cellular respiration and protein synth
|
|
|
Function of myeline sheat
|
Made of lipids around axon to insulate
|
|
|
Schwann cell function
|
Produces myelin sheath, tightly packed around forms layers of myelin
|
|
|
what does nodes of ranvier allow
|
more rapid nerve conduction along axon
|
|
|
What are synaptic endings
|
End of axon, vesicles containing neurotransmitters here
|
|
|
described three types of neurons
|
Sensory, motor, interneuron (conveys between parts of system)
|
|
|
during resting potential w hat is concentration of ions? how is it maintained?
|
Na+ more concentrated, K+ inside. Active transport
|
|
|
Described action potential?
|
With stimuli, impulse is generated with voltage change. Upswing (-60->40), membrane is permeable to Na+. They move from outside to inside. this is depolarization.
|
|
|
Describe recovery phase.
|
In b etween nerve impulses, K+ returned inside axon, Na+ back to original position. this requires ATP.
|
|
|
Why is myelin sheath faster?
|
Because the impulse jumps from note to node. nonmyelinated, the impulse must depolarize and repolarize on each point.
|
|
|
What happens when nerve impulse reaches end of axon?
|
Synaptic endings release neurotransmitters that affect potnetial of next neuron.
|
|
|
Describe structure of axon.
|
Synaptic endings are the swollen knobs, presynaptic is before, post synaptic is next neuron. Cleft is between.
|
|
|
What do excitatory transmitters do?
|
Make post synaptic more permeable to Na+
|
|
|
What doe inhibitory transmitters do?
|
Make post synpatic less permeable to Na+
|
|
|
What are synaptic vesicles?
|
They contain neurotransmitters
|
|
|
summarized synapse in pre synaptic
|
impulse reaches synpatic ending (action potential), Ca+2 flows into ending. Ca+2 ions cause contractile proteins to pull synaptic vesicles into inner surface. These fuse with membrane to release neurotransmitters via ATP.
|
|
|
SUmmarize synapse in cleft and post synaptic (before enzymatic)
|
Diffuse accross the cleft to receptors on post synaptic, the post have selective ion channels with lock and key. Ion flux changes voltage to move closer to action potential.
|
|
|
Summarize synapse in post synaptic after absorption
|
The NT are broken down and degraded by enzymes. synaptic ending reabsorbs NT. other enzymes break down after it is absorbed.
|
|
|
What cell part makes NT?
|
Protein (ribosome)
|
|
|
5 actions of drugs in synapse?
|
Stimulates, blocks, combines preventing breakdown, mimics, blocks receptor
|
|
|
3 types of nerves?
|
Sensory, motor, mixed.
|
|
|
What is the dorsal root?
|
Dorsal root ganglion, contains cell bodies of sensory neurons whose dendrites conduct impulse towards spinal cord.
|
|
|
What is ventral root?
|
Each spinal nerves contains axons of motor neurons that conduct impulses away from cord.
|
|
|
What is somatic nervous system?
|
Includes all nerves that serve muscoloskeletal and exterior sense organs.
|
|
|
Describe a reflex action (5 steps)
|
Stimuli, impulse via dorsal root ganglion to spinal cord, synapse with gray matter of spinal cord, interneuron synapses with motor neuron, impulse carried by ventral root to muscle/gland
|
|
|
What is autonomic nervous system divided into?
|
Sympathetic and parasympathetic.
|
|
|
Describe sympathetic nervous system
|
Emergency, fight or flight. Noradrenalin released by postganglionic axon. e.g. bladder constrict
|
|
|
Describe parasympathetic
|
All internal response associated with relaxed state. Include acetylcholine, released by post ganglionic axon. e.g. bladder relax
|
|
|
CNS contains?
|
Brain, spinal cord. Protected by bone, dura mater menignes, arachnoid menings, pia mater meninges. Spaces between filled with spinal fluid.
|
|
|
Difference between gray and white matter?
|
Gray is cell bodies --> synapes, interneurons
White matter ---> mylelinated nerve tracts |
|
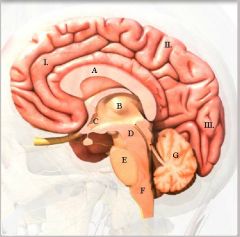
label
|

|
|
|
Medulla oblongata is?
|
Primitive brain. Controls heart rate, bp, reflex like vomiting, sneezing
|
|
|
What is cerebellum?
|
Controls balance and movement. Muscle movement.
|
|
|
What does pons do?
|
It relays between forebrain, hindbrain and medulla oblongata
|
|
|
What does thalamus do, and then hypothalamus?
|
Receive sensory info to channel to cerebrum. Thalamus receives sensory impulses except smell and sends to appropriate regions. Hypothalamus --> homeostasis.
|
|
|
What does corpus callosum do?
|
Space between two hemispheres of brain. Transmit impulses between hemispheres.
|
|
|
Describe cerebrum.
|
Largest, conscious brain. Intellect, memory.
|
|
|
Four parts of consciousness?
|
Frontal: movement, higher intellect, parietal: senses and speech, temporal: hearing smell, memory of visual, occipital: vvision, visual experience
|

