![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
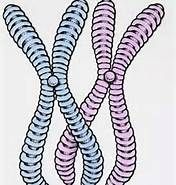
tetrad |
structure containing four chromatids that forms during meiosis |
|
|
mitosis |
cellular division that produces 2 identical cells that may be used for growth or repair |
|
|
meiosis |
cellular division that produces 4 unique cells that are used in sexual reproduction |
|
|
diploid |
describes a cell that has 2 full sets of chromosomes |
|
|
haploid |
describes a cell that has 1 full set of chromosomes |
|
|
somatic cells |
body cells; NOT reproductive cells |
|
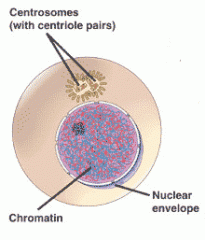
interphase |
cell cycle phase in which the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis |
|
|
m phase |
cell cycle phase in which the nucleus and the cytoplasm divide into two cells |
|
|
PMAT |
the 4 subphases of mitosis |
|
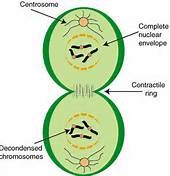
cytokinesis |
division of the cytoplasm |
|
|
meiosis |
process by which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half |
|
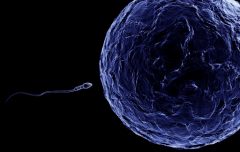
gamete |
specialized cell involved in sexual reproduction |
|
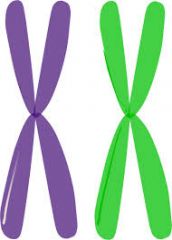
homologous |
term used to refer to chromosomes that each have a corresponding chromosomes from the opposite-sex parent |
|
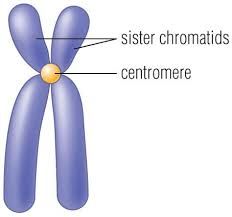
chromatid |
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome |
|
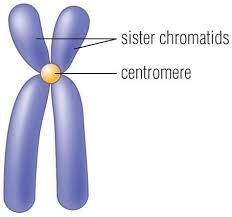
centromere |
area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached |
|
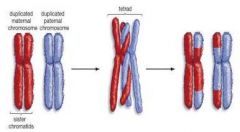
crossing over |
process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis |

