![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cm- What features do animal cells have (5) |
Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane Mitochondria Ribosomes |
|
|
|
Cm- What features does a plant cell have? (5) + (3) |
Everything an animal cell has plus cell wall Vacuole Chloroplasts |
|
|
|
Cm- What's a nucleus |
Brain (contains genetic material) |
|
|
|
Cm- What's cytoplasm |
Gel like substance where most of the chemical reactions happen. It contains enzymes which control these chemical reactions |
|
|
|
Cm- What's mitochondria |
Where most of the reactions for aerobic respiration takes place |
|
|
|
Cm- What are ribosomes |
These are where proteins are made in the cell. |
|
|
|
Cm- What does a cell wall do |
It supports the cell and strengthens it |
|
|
|
Cm- What occurs in chloroplasts and what does it contain? |
Photosynthesis, it makes food for the plant. It contains chlorophyll which absorbs light needed for photosynthesis |
|
|
|
Cm- What are all living things made out of |
Cells |
|
|
|
Cm- Name 2 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells |
1) prokaryotic cells are smaller 2) prokaryotic cells don't have a true nucleus but the other one does 3) eukaryotic cells are complex (like animal and plant cells) while prokaryotic cells are simpler (like bacteria) |
|
|
|
Cm- What's are eukaryotes |
Organisms made up of eukaryotic cells |
|
|
|
Cm- What's a prokaryote |
A prokaryotic cell ( a single-celled organism) |
|
|
|
Cm- What's a cell membrane |
It holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out |
|
|
|
M- how do you calculate magnification? What's the triangle for it. |

Image size divided by real size |
|
|
|
What are root hair cells specialised for? Explain further How? (1) |
Absorbing water and minerals. They're on the surface of plant roots which stick out into the soil ( to absorb water and minerals) |
|
|
|
M- how do you convert micrometers to millimetres? |

Divide um by 1000 |
|
|
|
What are subcellular structures? |
The different parts of a cell |
|
|
|
Cd- What is mitosis? What’s it a form of? (2) |
The splitting up of chromosomes (Asexual reproduction or the human body making new, identical cells) |
|
|
|
Cd- Describe the events of the cell cycle that need to occur before mitosis can begin |
The cell needs to double its subcellular structures (organelles) and then duplicate its Chromosomes (and then it can split) |
|
|
|
M- what is resolution? |
The ability to distinguish between two points, a higher resolution gives a sharper image. |
|
|
|
M- how do you convert micrometers to millimetres? |
Divide um by 1000 |
|
|
|
Ds- what are nerve cells specialised for? Explain further. How? (2) |

Rapid signalling. They carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another. They're long to cover distance and hey have branched connections to connect to other nerve cells and form a network. |
|
|
|
Ds- what are muscle cells specialised for? How? (2) |
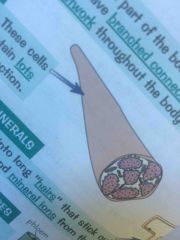
Contraction. They're long so that they have space to contract and contain lots of mitochondria to generate energy needed for contraction. |
|
|
|
Ds- What are root hair cells specialised for? Explain further How? (1) |

Absorbing water and minerals. They're on the surface of plant roots which stick out into the soil ( to absorb water and minerals) |
|
|
|
Ds- What are phloem and xylem cells specialised for? How? (3) |

Transporting substances (such as water and food). They're long and join end to end. Xylem cells are hollow in the centre and phloem cells have few subcellular structures so that stuff can flow through them. |
|
|
|
Ds- What are subcellular structures? |
The different parts of a cell |
|
|
|
Ds- what are nerve cells specialised for? Explain further. How? (2) |
Rapid signalling. They carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another. They're long to cover distance and hey have branched connections to connect to other nerve cells and form a network. |
|
|
|
Cd- Describe the events of the cell cycle that need to occur before mitosis can begin |
The plant has to increase the amount of its subcellular structures and duplicate it's DNA |
|
|
|
Ds- What type of cell can turn into any type of cell? |
Embryonic stem cells |
|
|
|
Ds- what are things that stem cells are used for? (3) |
1) To cure diseases 2) therapeutic cloning 3) nerve cells are used for for people paralysed by spinal injuries |
|
|
|
Ds- why are some people against using embryonic stem cells? |
They feel that human embryos shouldn't be used for experiments since each one is a potential human life. |
|
|
|
Ds- where are stem cells found in plants |
In the meristems |
|
|
|
Ct- What's diffusion? |
Diffusion is the spreading out of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration |
|
|
|
Ct- where can diffusion happen? |
In gases or solutions |
|
|
|
Ct- how exchange surfaces adapted to maximise effectiveness? (3) |
1) They have a thin membrane 2) they have a large surface area so lots of a substance can diffuse at once 3)in animals, they have a lot of blood vessels, to get stuff into and out of the blood quickly |
|
|
|
Ct- how is alveoli specialised to maximise the diffusion? (4) |
1) an enormous surface area 2) a moist lining for dissolving gases 3) very thin walls 4) a good blood supply |
|
|
|
Ct- how is the small intestine maximised for absorption? |
There's millions of tiny villi that increase the surface area in a big way |
|
|
|
Ct- where is the exchange surface on a leaf? (2) |
1) Underneath the leaf 2) the walls of the cells inside the leaf |
|
|
|
Ct- where does most of the oxygen and water vapour diffuse out of in a leaf? |
Through the stomata ( little holes underneath the leaf) |
|
|
|
What is diffused in through the stomata in leaves? What is diffused out of it?
|
-Carbon dioxide -oxygen and water vapour |
|
|
|
Where is stomata located in a leaf? |
Underneath the leaf (on the exchange surface) |
|
|
|
How is the structure adapted in a leaf so that diffusion can happen easily? |
It's flat which increases the surface area (and makes diffusion happen quicker) |
|
|
|
Ct- What can affect the rate of diffusion? (3) |
1) the bigger the concentration gradient (the difference in concentration), the faster the diffusion rate. 2) The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion because the particles have more energy. 3) if it was happening in the cell membrane then the bigger the surface area of the membrane, the faster the rate of diffusion |
|
|
|
Ct- what's osmosis? |
Osmosis is a type of diffusion. Osmosis is passive movement of water particles from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration |
|
|
|
Ct- what's a partially permeable membrane? |
A membrane with very small holes in it ( only tiny molecules like water can pass through them) |
|
|
|
Ct- how can you reduce the effects of errors in experiments? (2) |
1) By repeating the experiment. 2) By calculating the mean for the results |
|
|
|
Ct- what is active transport? |
The movement of substances from a lower to a higher concentration, diffusion and osmosis is the other way round. |
|
|
|
Ct- what does active transport need for it to work that osmosis and diffusion don't need? |
It needs energy from respiration |
|
|
|
Ct- What is diffused in through the stomata in leaves? What is diffused out of it?
|
-Carbon dioxide -oxygen and water vapour |
|
|
|
Ct- Where is stomata located in a leaf? |
Underneath the leaf (on he exchange surface) |
|
|
|
Ct- How is the structure adapted in a leaf so that diffusion can happen easily? |
It's flat which increases the surface area (and makes diffusion happen quicker) |
|
|
|
Cm- What features do bacteria cells have? (6) |
Cell membrane Cell wall Cytoplasm Plasmids Chromosomal DNA Ribosomes |
|
|
|
Cm- What are plasmids? |
Small rings of DNA |
|
|
|
Ct - what experiment can you do for osmosis? |
Observing the effects of a sugar solution on plant tissue (potato slices) |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what's a catalyst |
A substance that increases the speed of a reaction, without being changed or used up. |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what do you call the thing that reacts with the enzyme that fit into the active site? |
Substrate |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what do enzymes need to work well (2) |
The right temperature and ph |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what do enzymes need to work well (2) |
The right temperature and ph |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what's ph do most enzymes work best at? |
Ph 7 but not always |
|
|
|
Enzymes - how do you work out the rate of reaction? |
1000 divided by time in seconds |
|
|
|
Enzymes- What do carbohydrates do? |
Convert carbs to simple sugars |
|
|
|
Enzymes - What do digestive enzymes do? |
Break down molecules that are too big to pass through the walls of the digestive system |
|
|
|
Enzymes- What does amylase do (carbohydrase) |
Breaks down starch |
|
|
|
Enzymes - What does bile do? |
It neutralises the acid and makes conditions alkaline in the stomach |
|
|
|
Enzymes - Why is hydrochloric acid produced in the stomach? (2) |
- kill bacteria - to give the right ph for the protease enzyme to work (ph 2) |
|
|
|
Enzymes - What else happens in the liver? (Apart from the bile neutralising stomach acids) |
Emulsified fats (breaks it down and turns it into droplets) |
|
|
|
Food tests- When you test for sugar what colour does the solution turn when you add the Benedicts solution? |
From blue to green, yellow or red (depending on how much sugar is in the food) |
|
|
|
What colour does it turn when you add iodine solution? |
From browny orange to bluey black |
|
|
|
Food tests - What colour does the solution turn when you add iodine solution? |
From browny orange to bluey black |
|
|
|
Food tests - What colour does the solution turn when you do the biuret test for proteins? |
From blue to pink or purple |
|
|
|
Food tests - What does the Benedicts test test for? |
Sugars (reducing sugars) |
|
|
|
What is iodine solution used to test for? |
Starch |
|
|
|
Food tests - What is iodine solution used to test for? |
Starch |
|
|
|
Food tests - What do use a biuret test to test for |
Proteins |
|
|
|
What do use the Sudan III test to test for |
Lipids |
|
|
|
Food tests -What do use the Sudan III test to test for |
Lipids |
|
|
|
Food tests - How will you know if a sample contains lipids |
The mixture will separate out into two layers and the top layer will be bright red |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what parts of the digestive system produces amylase |
Salivary glands, pancreas and stomach |
(3) |
|
|
Enzymes - what's a protease |
An enzyme that breaks down protein into amino acids |
|
|
|
Enzymes - in the digestive system, in what organs would you find protease |
The stomach, pancreas and small intestine |
(3) |
|
|
Enzymes - What do you lipase do and where are they produced |
They break down fats into fatty acid's and glycerol and it is produced in the pancreas and the Small intestine |
|
|
|
Enzymes - what happens in the large intestine |
Excess water is absorbed from the food |
|
|
|
Specialise cells carry out a particular function. How do they make up a tissue and what do tissues make up etc |
Similar cells work together to carry out a particular function and make up a tissue - tissues make up organs - organs make up organ systems |
|
|
|
What's the order for digestive system and what happens in each organ |
- salivary glands - gullet - stomach -pancreas, liver and gallbladder which prepares stuff to go into the - small interesting -large intestine - rectum (faeces are stored here) then they go through the anus |
Look at the other flash cards to see what happens in the organs |
|
|
What does the Benedicts test test for ? What colour does it turn to? |
Sugars From blue to green, yellow or red |
|
|
|
What does iodine solution test for and what colour would it turn to? |
Starch From browny orange to black or blue |
|
|
|
What are organelles |
Subcellular structures in cells |
|
|
|
What’s the difference between genotype and phenotype |
Genotype is the set of genes which gives us characteristics while the phenotype gives a physical trait |
|

