![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Theory |

All organisms are made up of cells, all existing cells are produced by other living cells, the cell is the most basic unit of life. |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
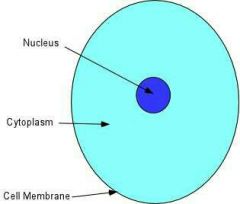
A jelly-like substance that contains dissolved molecular binding blocks. (proteins, nucleic acids, minerals, and ions. |
|
|
Organelles |
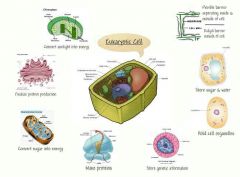
Structures specialized to perform distinct processes within a cell. Most are surrounded by a membrane. |
|
|
Prokaryotic cells |
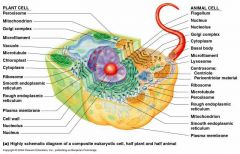
Don't have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. |
|
|
Eukaryotic cells |
Has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Each eukaryotic cell has one. Which is a network of proteins that is constantly changing to meet the needs of a cell. |
|
|
Microtubules |
Long hollow tubes. They give the cell its shape and acts as "tracks" for the movement of organelles, when cells divide, microtubules form fibers that pull half of the DNA into each new cell. |
|
|
Intermediate Filaments |
Are somewhat smaller than microtubules, gives a cell its strength. |
|
|
Microfilaments |
The smallest of the three ( Microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments), are tiny threads that enable cells to move and divide. They play an important role in mucle cells, where they help the muscle contract and relax. |
|
|
Nucleus |
Is the storehouse for most of the genetic information, or DNA(Deoxyribonucleic acid). |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Is an inter connected network of thin folded membranes. |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Tiny organelles that link animo acids together to form proteins. |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Consists of closely layered stacks of membrane-enclosed spaces that process, sort, and deliver proteins. |
|
|
Vesicles |
Is a general name to describe small membrane-bound sacs that divide some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm and transport these materials from place to place within the cell. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Supply energy to cell(singular mitochondrian) are bean shaped and have two membranes. |
|
|
Vacuole |
Is a fluid-filled sac used for the storage of materials needed by a cell. |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Are membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes. They defend a cell from invading bacteria and viruses. They also break down damaged or worn out cell parts. |
|
|
Centrioles |
Are cylinder-shaped organelles made out of short microtubules arranged in a circle. |
|
|
Chloroplasts |
Are organelles that carry out photosynthesis, a series of complex chemical reactions that solar energy into energy-rich molecules the cell can use. |
|
|
Cell wall |
Is a rigid layer that gives protection, support, and shape to the cell. |
|
|
Cell membrane |
(the plasma membrane) Forms a boundary between a cell and the outside environment and controls the passage of materials into and out a cell. |
|
|
Phospholipid |
Is a molecule composed of three basic parts(a charged phosphate group, glycerol, and two fatty acid chains). |
|
|
Fluid mosaic model |
Describes the arrangement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane. |
|
|
Selective permeability |
Means it allows some, but not, all materials to pass. |
|
|
Receptor |
Is a protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response. |
|
|
Intracellular |
Within, or inside, a cell. |
|
|
Passive transport |
Is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane without energy input from the cell. |
|
|
Diffusion |
The movement of molecules in a fluid or gas from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration. |
|
|
Isotonic |
Solution that has an equal concentration of dissolved particles compared with another solution. |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Solution that has a higher concentration of dissolved particles compared with another solution. |
|
|
Hypotonic |
Solution that has lower concentration of dissolved particles compared with another solution. |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Is the diffusion of molecules across a membrane through transport proteins. |
|
|
Active Transport |
Drives molecules across a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Is the process of taking liquids or fairly large molecules into a cell by engulfing them in a membrane. |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Is a type of endocytosis in which the cell membrane engulfs larger particles. |
|
|
Exocytosis |
The opposite of endocytosis, is the release of substances out of the cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane. |

