![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Diffusion |
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
|
|
|
Concentration Gradient |
The difference in the concentration of the molecules across a distance |
|
|
|
Cytolosis |
Occurs when the cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to enter the cell |
|
|
|
Active Transport |
Molecules move against the concentration gradient (low to high) and the cell uses energy |
|
|
|
Passive Transport |
Substances that cross the cell membrane w/o any input of energy by the cell (high to low) |
Enters with water |
|
|
Plasmolosis |
The process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution |
|
|
|
Surface Area's Effect on Diffusion |
Larger surface area = Faster diffusion rate |
|
|
|
Hyper/hypo/iso-tonic solutions |
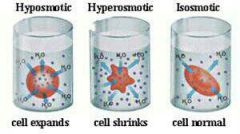
|
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Passive transport - Enter cell through their own ion channel |
|
|
|
Sodium-Potassium Pumps |
Carrier protein that transports Na+ and K- UP their concentration gradients |
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
Calls ingest external fluid, macromolecules and large particles |
|
|
|
Exocytosis |
Process by which substances are released from a cell through a vesicle that fuses with the membrane and forces the substance out |
|
|
|
Ion Channels and Carrier Proteins |
Move charged particles across the cell membrane by using chemical energy from ATP |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
The movement of a stable level of internal conditions |
Ex: Temperature |
|
|
Equilibrium |
Concentration of the molecules will be the same throughout |
|

