![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a species? |
A group of organisms that can breed together to produce fertile offspring. |
|
|
What are adaptations? |
Features that help living organisms survive in their environments |
|
|
What are the benefits of adaptions? |
They increase a species chance of survival making it more likely that they will survive and reproduce |
|
|
What is a habitat? |
Where an organism lives |
|
|
What do organisms compete for? |
Resources |
|
|
What do animal species compete for? |
Food or shelter |
|
|
What do plants compete for? |
Space and light |
|
|
What does an interdependent species mean? |
Species in a habitat that rely on each other, and on the environment for food and other needs |
|
|
What does a food web show? |
What eats what in a habitat |
|
|
What can changes in a food web do? |
Affect other species that are also in the foodweb |
|
|
How much light energy do plants absorb? |
1-3% that falls on their leaves. |
|
|
What do plants use sun energy for? |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
Why do plants photosynthesise? |
So they can produce the chemicals that make up plant cells and store energy
|
|
|
What are plants in the food web? |
Producers |
|
|
What depends on plants for food? |
Animals, bacteria and fungi |
|
|
What is almost all life dependent on? |
The sun |
|
|
How is energy transferred between organisms? |
-When animals (consumers) eat other animals. -When decay organisms (decomposers and detritivores) eat dead organisms and waste materials. |
|
|
How much energy is passed on at each level of a food chain? |
A small percentage |
|
|
What happens to the rest of the energy in a food chain? |
-Its used for life processes (MRS GREN) -It escapes to the surroundings as heat -It is exreted as waste and passed onto decomposers. -It cant be eaten and is passed down to decomposers. |
|
|
Why do food chains have no more than four species? |
Because so much energy passes out? |
|
|
Lots of energy passes out of a food chain, what effect does this have? |
The food chain has no more than 4 species. |
|
|
What is the 'path' for energy in a foodchain? |
Sun -> producers -> consumers -> etc. |
|
|
What is the equation for percentage efficiency of energy transfer at different stages of a food chain? |
(Amount transferred/Total amount) X100 |
|
|
How is carbon recycled? |
Through the environment |
|
|
What is the 'basic' carbon cycle's parts? 4 |
-Plants take in CO2 through photosynthesis, and make glucose -Animals and plants break down glucose in respiration and return CO2 to the atmosphere. -Microorganisms break down the molecules of dead organisms by decomposition. -Combustion of wood and fossil fuels adds CO2. |
|
|
How is nitrogen recycled? |
In the environment. |
|
|
Why are microorganisms vital in the nitrogen cycle? |
Because decomposer bacteria break down proteins in dead organisms, |
|
|
What are the processes that are part of the nitrogen cycle? |
-nitrogen fixing bacteria converting nitrogen into nitrogen compounds like nitrates. -Plants using nitrates to make proteins that animals can digest to make animal proteins. -Denitryfying bacteria break down nitrates in the soil to release Nitrogen back to the air. This is Denitrification. |
|
|
Where are nitrogen fixing bacteria found? What do they do? |
Found in some plant roots. They convert nitrogen into nitrogen compounds like nitrates. |
|
|
How do plants use nitrogen? |
To make proteins |
|
|
What do denitrifying bacteria do? |
Break down the nitrates in the soil and release nitrogen into the air |
|
|
What does denitrification mean? |
Removal of nitrogen from the soil. Bacteria break down nitrates in the soil, converting them back to nitrogen. |
|
|
How do scientists measure environmental change? |
Using indicators. |
|
|
What do living indicators include? |
-Phytoplankton, to measure ocean temperatures -Lichens, to monitor air quality -Mayfly nymphs, to monitor O2 levels in rivers |
|
|
What do non-living indicators include? |
-Nitrate levels in streams, rivers and lakes -CO2 levels and temperature in air and oceans. |
|
|
When did life begin? |
3500 mil. years ago |
|
|
What have all species evolved from? |
simple living things |
|
|
What provides evidence for evolution? |
Fossils and DNA analysis of living organisms. |
|
|
What is another word for differences between individuals of a species? |
Variation |
|
|
What causes genetic variation? |
mutations in the genes |
|
|
What do mutations in the genes of a species cause? |
Variation |
|
|
How are mutations passed on? |
Through the sex cells, passing the genes onto offspring |
|
|
What do genetic mutations occassionally cause? |
New characteristics |
|
|
What makes species change over time? |
Evolution |
|
|
What may happen due to evolution over time? |
New species may develop |
|
|
What changes can cause evolution? |
-Mutations and natural selection -Environmental changes -Isolation |
|
|
How is natural selection different to selective breeding? |
Because selective breeding is due to human intervention, when they chose the characteristics of the living thing. |
|
|
Recall the general outline for how natural selection works. |
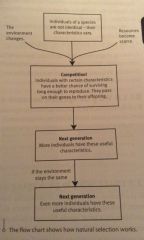
|
|
|
What was Darwins theory? |
Evolution |
|
|
How did Darwin develop the theory of evolution? |
By natural selection |
|
|
What did Darwin do to come up with his theory? |
He made many observations and used createive thought |
|
|
Why is Darwins theory better than Lamarks? |
Because it fits with modern genetics ad is supported by more evidence |
|
|
What was Lamarcks theory? |
That an organism can pass on characteristics that the organism has acquires in its lifetime and can oass on these characteristics to its offspring |
|
|
What is biodiversity? |
The great variety of living things, both within a species and between different species. |
|
|
How do scientists group organisms? |
By using similarities and differences between the organisms physical appearnace and DNA. |
|
|
What is classification? |
Grouping of organisms |
|
|
What does classifying help to do? |
Make sense of the diversity of life whilst showing how organisms have evolved. |
|
|
What is the biggest group for animals? |
The animal kingdom |
|
|
What are other groups for organisms? |
Vertebrates, non-vertebrates, mammals, amphibians, carnivores, omnivores etc. |
|
|
Define sustainability |
Metting the needs of people today without damaging the earth for people in the future. |
|
|
Why is preserving biodiverity important? |
-We use wild varieties of plant species to develop new varieties of food crops -We use plant substances as medicines |
|
|
What is monoculture? |
Growing single crops in large fields |
|
|
Is monoculture sustainable? Why not? |
No. The crops can be easily attacked by pests and diseases. |
|
|
Why is growing varied crops more sustainable? |
Because their alleles will be more varied, so are likely to include som eresistant plants. |
|
|
Define extinct |
When all members of a species die out |
|
|
What can cause a species to become extinct? |
-A change in the environment -A new species arrives that competes/eats or causes disease. -Another species in the food web becomes extinct |
|
|
Why is packaging a problem? |
It uses huge amounts of energy and creates a lot of waste. |
|
|
What happens to packaging in landfill sites? |
It takes up a lot of space and biodegradable packaging fails to decompose because there isnt enough oxygen. |
|
|
What is a sustainable approach to packaging? |
To reduce it. |

