![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a cell? |
Basic structural, functional unit Small membrane compartment Smallest form of life e.g. multicellular cells, single celled organisms (virus) |
|
|
What are the three domains of cellular life |
Archaea and Bacteria (prokaryotic) Before the nucleus, single celled organisms, their DNA is not enclosed in a membrane Eukarya (eukaryotic) true nucleus, their DNA is enclosed |
|
|
Prokaryotic Cells, Eukaryotic cellsb Surface Area |
1-5 um 10-100 um |
|
|
Surface Area to volume ratio |
Cells need high VA:V exchanging molecules with the environment Increasing internal surface SA for biochemical reaction, the more membrane you have the more reactions you have and the more surface area you need. SA is very important |
|
|
Animal cell, what do you know? |
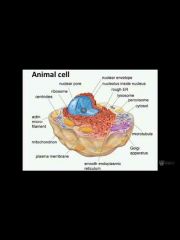
Other things, -cytoplasm, everything inside a cell except the nucleus |
|
|
Plant cell, what do you know? |
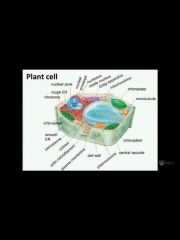
Chloroplasts, cellulose, plasmodesma, central vacuole |
|
|
What are cellular membranes bound by? |
Plasma membrane Made up of phospholipids, forms a phospholipid bilayer |
|
|
Nucleus, what is it composed of? |
DNA, tells the cell what to do Surrounded by the nuclear envelope (doublelipid bilayer) Nuclear pores , allows bsubstances in and out Stores genetic information in the form of chromatin (DNA+protein) Nucleolus, DNA excluded from this region, makes ribosomalcomponents (rRNA and ribosomal proteins) |
|
|
Ribosomes, what is its functions? |
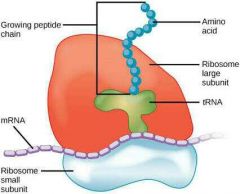
Synthesize proteins from amino acids, following the instructions of mRNA , ribosome reads and translates mRna, Two types , free ribosomes. Are made in the cytotoxic, mostly making cytosolic proteins. Bound ribosomes associated with the endoplasmic reticulum, mostly making proteins for membranes , export and some organelles |
|
|
The Endo membrane system, what is it? |
Series of interconnected membrane bound organelles. Nuclear envelope, ER, golgi, vesicles, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane Each compartment contains a unique set of proteins |
|
|
The Endoplasmic Reticulum, what is it? |
Rough, (spotty) ribosomes Smooth, (no ribosomes) |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, describe. |
No associated ribosomes Tubular structure Present in all cell, however it is rare Diverse functions, lipids (phospholipids, steroids , hormones, triglycerides), detoxification (liver), calcium storage (muscles) |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum |
Rough ER membrane is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane |
|
|
Which is bigger chloroplast or mitochondria |
Chloroplast |
|
|
What two organelles have their own DNA? |
Mitochondria and Chloroplast |
|
|
Cytoskeleton, what is is function, what is it made out of? |
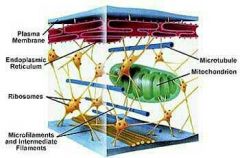
Function, Structure and support Motility Anchorage Three protein based fibres, Microfilaments (7-8nm) Intermediate filaments (8-12nm) Microtubules (25nm) |
|
|
Microtubules |
Comprising of the protein tubulim Diverse functions, tracks for organelle movement, whole cell movement as a part of the cilia and flagella (tail in sperm,microtubules male it move) , spectating chromosomes during mitosis. They are very important as they seperate chromosomes during mitosis |
|
|
Microfilaments (actin filaments) |
Formed from a protein called actin Functions, Form a network just inside of plasma membrane to maintain cell shape Contraction of muscle cells, b cytoplasmic Streaming |
|
|
Intermediate filaments |
Many different proteins for the different structural functions E.g. kamin, keratin |
|
|
Describe Prokaryotic Cells |
Don't have membrane bound organelles, DNA is as big circle coiled into the nucleoid region, mostly unicellular. diverse cells, metabolism and habitats |
|
|
Biology levels |
Molecule Organelles Cells Organ Organism |
|
|
Overarching themes in biology |

|
|
|
How do lupus and proteins male there way outside of the cell |
Vesicles transport of proteins and lipids outside the cell |
|
|
Phospholipids |
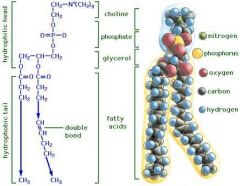
Are amphipathic (have hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts) Polar hydrophobic head, non polar hydrophobic tales |
|
|
Phospholipids in water |
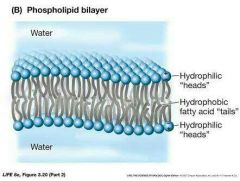
They'll form a structure,this is our phospholipid bilayer, there are two layers, traps are pointed inwards |
|
|
Phospholipids sometimes spontaneously form strictures to hide their tales from water, what ate these? |
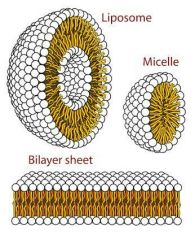
Vesicle (liposomes) micelle and bilayer |
|
|
Membrane why are they referred to add a fluid mosaic |
They are fluid, are able to move around because Lipid molecules can move laterally within membranes, as well as as the irregular arrangement of proteins |
|
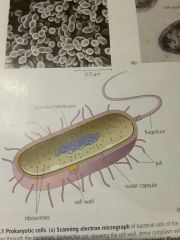
Flagellum, of a prokaryotic cell |
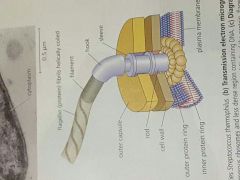
|

