![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What was the griffith experiment? What did he find? |
Studied mice. Two strains of bacteria- smooth and rough. Smooth killer. heat affected. transformation - dead smooth cells transformed live rough cells |
|
|
What was the Avery, MacLeod and McCarty experiment? |
only DNAses destroyed the ability of the purifiedmaterial to transform rough cells. Therefore,DNA was the transforming principle |
|
|
What was the Hershey-Chase Experiment? |
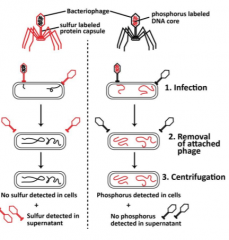
Answers: what part of the bacteriophage isresponsible for transferring the information needed to make more T2? |
|
|
what are chargoffs rules? |
% of A bases is similar to the % of T bases, and %C is similar to %G. The ratio of [A]+[T] to [G]+[C] (calledthe base composition) varies between different species, but is constant for different individuals within agiven species. |
|
|
The info stored in DNA is _____. |
the order of basepairs. |
|
|
What was the Meselson Stahl exp? |
DNA replication is semi conservative. (strands separate, bases are added, two new daughter strands). THey added heavy N to DNA constantly then switched it up to light nitrogen |

