![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Principle of Genetic Equivalence |
Each cell in our body carries the same genetic information. Why?- mitosis makes identical copies of the genetic information, each of the 10^14 cells in ahuman adult carries all of the same DNA as the zygote. |
|
|
Cloning |
the production of a new organism that is genetically identical to another organism. |
|
|
What is cloning in plants called and how does it occur? |
vegetative propagation, taking a cutting and growing it into a newplant |
|
|
How does cloning occur in animals? |
starting with a diploid zygote and growing an embryo. This can bedone artificially by introducing a diploid nucleus into an egg. Because the diploid nucleus comes from asomatic donor cell, this procedure is called somatic nuclear transfer. The key to the success of such anexperiment is whether or not the reconstructed zygote will develop like a normal zygote. |
|
|
somatic nuclear transfer |
By removing the haploid nucleus of a donor egg,and replacing it with the diploid nucleus of adonor cell. There is usually some treatment tostart development, to make the reconstructedzygote act as if it is the product of fertilization.In mammals, the cloned embryo can grow intoa blastocyst, but it will need to be implantedinto a surrogate mother for completedevelopment. |
|
|
What did Ian Wilmut do |
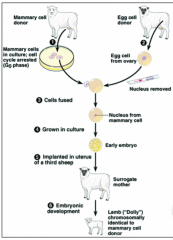
successfully cloned a sheep |
|
|
All of the cells in an individual are identical so why do different cells look and behave differently? |
although all thegenes in the genome are present as DNA in the chromosomes, only a small subset of those genes is actuallyexpressed (i.e. making mRNA and henceprotein). This is the principle of differentialgene expression. |
|
|
Which genes are generally active in ALL cells? what are they called |
glycolysis or transcription, are generally activein all cell types. These are often calledhousekeeping genes |
|
|
What are model organisms? |
Model Organisms are chosen for study because theyhave properties that make it easier to performexperiments, while at the same time having similarityto more complex organisms so that findings can be applied to many other more complex organisms, suchas humans |
|
|
What are some properties that make model organisms useful. name some model organisms |
short generationtime, small size, and ability to do genetics. Examplesinclude Drosophila (fruit fly), mouse, the roundwormC. elegans, the zebrafish Danio rerio, and the plantspecies Arabidopsis thaliana |
|
|
What are the to types of development in model organisms? Explain them |
Regulative and mosaic. For example, if asingle cell is removed from an 8-cell mouse embryo,the remaining cells will still form a complete mouse(regulative development). If the same experiment isdone with the roundworm C. elegans, the animal willdevelop missing a body part specific for the cell thatwas removed (mosaic development). |
|
|
where/when are stem cells found |
They are found during embryonicdevelopment, and also in fully grown organisms. |
|
|
What do adult stem cells do? |
used for growth and the repair ofinjuries. |
|
|
What are some limitations of stem cells |
limited in the range of tissuesthat they can make. For example, stem cells that renew the blood andimmune system do not contribute to other cell types. |
|
|
What is a blastocyst? whats in it? |
Early in mammaliandevelopment, embryos consist of a ball of a few hundred cells called ablastocyst.Within the blastocyst is a clump of cells called the inner cellmass, from which the embryo will develop. |
|
|
What can the blatocysts inner cell mass be used for? |
embryo development and If these cells are harvestedand grown on tissue media that prevents their differentiation, they keeptheir ability to generate almost any tissue. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells |
|
|
What is therapeutic cloning ? What can it accomplish? |
a somatic nuclear transfer experiment is used to generate a clonedembryo, from which the inner cell mass is isolated to generate embryonic stem cells. By using a patient's own cells as a source of the newtissue, there would be no immune rejection of the new cells |
|
|
What are induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS)? |
some body cells can be reprogrammed by changes ingene expression and can behave as if they are stem-cell like. For example, connective tissue cells(fibroblasts) can be made to act like stem cells by the combined expression of a set of transcription factors(Oct-4, Sox-2, Klf-4, c-Myc). These factors cause the differentiated cells to become more like embryoniccells, which can then be programmed to turn into different cells by expression of other factors. |
|
|
What is regenerative medicine and what is it used for? |
If the correct growth conditionscan be found, stem cells could beinduced to express the correctgenes so that they can becomecells of very specific types. Thisfield of regenerative medicineoffers hope for cures for manymedical conditions such asdiabetes, Parkinson’s disease,heart disease and spinal cordinjury. |

