![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
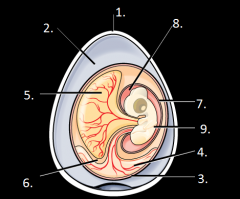
|
1. Egg shell 2. Albumen 3. Chorion 4. Allantois 5. Yolk 6. Yolk sac 7. Amnion 8. Amniotic cavity 9. Embryo |
|
|
Benefits of placenta |
Greater protection Greater mobility Favors evolution of few large offspring |
|
|
How does the placenta form? |
Forms from embryonic/maternal tissues |
|
|
Who are the amniotes? |
Reptiles Mammals |
|
|
Temporal Feresteral |
Openings in skull behind eyes |
|
|
Diapsid vs. Syapsid vs. Anapsid |
Diapsid: 2 openings in skull (most reptiles) Synapsid: 1 opening in skull (humans) Anapsid: 0 openings in skull (turtles) |
|
|
Reptile Traits |
Scales Amniotic egg Tetrapod 3-4 chambered Flight (in birds) |
|
|
Benefit of scales (scutes) |
Horny scales composed of keratin Used for waterproofing |
|
|
Traits of Lepidosaurs |
Replaceable overlapping scales Limbs are reduced/lost Autotomy Hemipenis Parthenogenesis |
|
|
Autotomy |
Self amputation of limbs (tail in lepidosaurs) |
|
|
Hemipenis |
Pair of retractable sex organs near tail |
|
|
Parthenogenesis |
Female cloning of egg that can be fertilized by polar bodies |
|
|
Testudinia Traits |
0 temporal fenesterae Presence of shell Terrestrial (tortoises) and aquatic (turtles) No placental care |
|
|
Shell parts in Testudinia |
Dorsal: Plastron (underside of shell) Ventral: Carapace (hard upper shell) |
|
|
Crocodilia traits |
Thick, non-overlapping scales Laterally compressed tails Oviparous 4 chambered heart |
|
|
Differences in crocodilian snouts |
Crocs: Narrow Gator: Broad |
|
|
Aves traits |
Evolved flight Feathers Convergent evolution Hollow bones 4 chambered heart Bird lung connected to anterior and posterior sacs |
|
|
Bird breathing step 1 |
Inhalation 1: Air fills posterior sacs Exhalation 1: Air moves to lung, new air in posterior |
|
|
Bird breathing step 2 |
Inhalation 2: Air from lung moves to anterior sac Exhalation 2: Air leaves anterior sac and moves to lung |
|
|
Endothermy |
Generate heat via metabolism and retain it viause of fur/hair (ex. Birds, mammals) |
|
|
Ectothermy |
All other tetrapod animals in which temperature is comparable to ambient temperature |
|
|
Temperature regulation increases... |
Enzyme rates significantly |
|
|
If cold... |
Shivering response Muscular activity produces heat Vasoconstriction reduces heat loss |
|
|
If hot... |
Sweating uses heat to evaporate water Vasolidation loses heat |
|
|
How does body surface play an important role in thermoregulation? |
Smaller body= a larger SA to volume ratio vs, large body |
|
|
What do infants use to retain heat? |
Infants use brown fat which has a higher amount of mitochondria |
|
|
Mammary Gland |
exocrine organ that produces nutrients for offspring Increases maternal investment |
|
|
Exocrine |
Ducted gland releases secretory material into duct (salviary, sweat, etc.)
|
|
|
Endocrine |
Ductless glands release secretory material into extracellular environment (bloodstream) |
|
|
Monotreme traits |
Platypus and 4 species of echidnia Egg layers Produce small eggs |
|
|
Platypus traits |
Beack has electro/mechno sensory structures used for foraging Rear limbs contain venom glands (males only) |
|
|
Marsupial |
Pouched animals Initially live bearing Nourish embryos using placenta but born under developed |
|
|
What happens after marsupial young are born? |
After birth, offspring get in pouch (marsupium) or attach to mom and suckle to continue devlopment |
|
|
Unique reproductive traits of Marsupials |
Female: 2 uteri and 2 vagina with 3rd "psuedo" vagina Male: 2 prong penis used only for copulation |
|
|
Eutherian Mammal Traits |
Placental viviparity using chorio-allontric placenta Better developed embryos |
|
|
Cons of eutherian placental mammals |
Long gestation/Premature loss Energetically expensive |
|
|
Trends of eutherian mammal evolution |
Amphibian lung- sac with folds Reptile lung- complex with accessory air sacs Mammalian lung- increased surface area by grape like clusters known as alveoli |
|
|
Mammalisn circulation |
Double pump system 4 chambered heart Oxygenated blood |
|
|
Primates trends |
Opposable thumbs Arboreal Tails Extensive parental care Large brain to body size ratio Color vision Eyes face forward |
|
|
Prosimians |
Before monkeys Lemurs, lorises Small, arboreal |
|
|
Anthropoids |
Human like Old world monkeys: africa and asia New world monkeys: central and south america Lesser apes: Gibbons Great apes (hominids): gorilla, orangutan, chimps, bonobo, humans |
|
|
Great Apes |
Hand walkers- orangutan
Knuckle walkers- gorilla, bonobos, chimps Bipedalism- humans |
|
|
Benefits of bipedalism |
Frees up hands greater mobility greater sensitivity of hands greater field of view |
|
|
Types of Hominins |
Gracitie Australopithecines Robust Australopithecines Early Homo sp. Recent Homo sp. |
|
|
Gracitie Australopithecines |
3-4 ft in height Slender Large jaw and teeth |
|
|
Robust Australopithecines |
~3-1.5 mYA Large sagittal crest that attaches to jaw muscles Large jaw met an evolutionary dead end |
|
|
Early Homo sp. |
Taller, more narrow face Smaller jaw and teeth Brain case increases in size Coincides with first appearance of stone tools |
|
|
Recent Homo sp. |
1 mYA to present Longer limbs More streamlined body Narrowing of face Increased cranial capacity |
|
|
Major trends in primate evolution |
Increased height/overall body size Reduction in jaw/tooth size Increased cranium and brain size |
|
|
Out of Africa Hypothesis |
Homo sapiens evolved in Africa and dispersed inmultiple waves Evidence of interbreeding between Neanderthalmales and H. sapiens females Large, rounder body- low surface area/vol ratio |
|
|
Differences in SA/V ratio |
High SA/V ratio= adaptation for dissipating heat Low SA/V ratio= adaptation for conserving heat |
|
|
Sunlight differences in evolved humans |
Greater sunlight= more UV light= selectivepressure that favors dark skin
Lower sunlight= lower, UV light= selective pressurethat favors light skin |
|
|
Cultural selection |
Lactosetolerance evolved in adult humans due to cattle/use of milk
|

