![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Non vascular plants (bryophytes) |
plant that has no xylem and pholem; reproduce through spores |
|
|
no roots, stems or leaves |
What non-vascular plants do not have that vascular plants have only? |
|
|
Non-vascular plants (bryophytes) |
Examples of these plants are mosses, liverworts and hornworts |
|
|
Pteridophyte and seed plants |
Two types of vascular plants |
|
|
Pteridophytes |
A vascular plant that has mostly ferns ; only have roots, stems and fronds and reproduce by spores |
|
|
Angiosperms |
A seed plant that have flowering plants |
|
|
Gymnosperms |
A seed plant that is non-flowering mostly conifers (pine tree, ginkgo, cycad) |
|
|
Phylum porifera |
Animals: sponges |
|
|
Phylum Cnidaria |
Animals: corals, jellyfish, sea anemone |
|
|
Phylum Platyhelminthes |
Animals: Flatworms (liver fluke, planaria) |
|
|
Phylum nematoda |
Animals: roundworms (ascaris) |
|
|
Phylum annelida |
Animals: Segmented worms (earthworm, leech) |
|
|
Cold-blooded vertebrates |
Type of phylum chordata that is poikilothermic/ectothermic; rely on environment for body heat |
|
|
Class Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) |
Class of cold-blooded vertebrates that have sharks and rays |
|
|
Class Osteichthyes (bony fish) |
Class of cold-blooded vertebrates that have all fish except cartilaginous fish |
|
|
Class amphibia |
Class of cold-blooded vertebrates that have moist skin; lung-breathing adult stage |
|
|
Class reptilia |
Class of cold-blooded vertebrates that have scales, lung-breathing |
|
|
Warm-blooded vertebrates |
Type of phylum chordata that is homeothermic/endothermic; can maintain a constantly high body temperature |
|
|
Class Aves (Birds) |
Class of warm-blooded vertebrates that have feathers |
|
|
Class Mammalia |
Class of warm-blooded vertebrates that have hair, mammary glands |
|
|
Phylum mollusca |
Animals: snail, squid, clam |
|
|
Phylum echinodermata |
Animals: starfish, sea urchin |
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda |
Animals: jointed legs; biggest group |
|
|
Class insecta |
Class of Phylum Arthropoda that has 6 legs |
|
|
Class arachnida |
Class of Phylum Arthropoda that has 8 legs; spiders; ticks |
|
|
Class crustacea |
Class of Phylum Arthropoda that has 10 or more legs; crab, lobster, shrimp |
|
|
Class diplopoda (millipedes) |
Class of Phylum Arthropoda that has 2 pairs of legs per segment |
|
|
Class chilopoda (centipedes) |
Class of Phylum Arthropoda that has 1 pair of legs per segment |
|
|
Phylum chordata |
Animals: notochord; pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail, dorsal hollow nerve cord (sea squirts, lancelets and vertebrates) |
|
|
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Subphylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species |
Levels of classification in taxonomy |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Ethylene |
This plant hormone function is in charge of ripening of fruit |
|
|
Abscisic acid |
This plant hormone function is in charge of water control and control of stomata |
|
|
Cytokinin |
This plant hormone function is for cell division and cell repair |
|
|
Benthos |
This ocean life form are organisms on the seabed (starfish, corals, crab) |
|
|
Nekton |
This ocean life form are organisms that swim (fish, squid, shrimp) |
|
|
Plankton |
This ocean life form are organisms that float or drift on the water surface (algae, bacteria, sea urchin, starfish, fish and crustacean larvae) |
|
|
Adaptation |
“Fitness” for an organism to survive in its environment; possession of favorable characteristics |
|
|
Inheritance of acquired characteristics |
This theory by Lamark says that traits develop or acquired during an organisms life time or pass on to its offspring |
|
|
Darwins theory of evolution |
Diverse groups of organisms evolved from a common ancestor or descent |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Natural selection |
What is the main mechanism for evolution? |
|
|
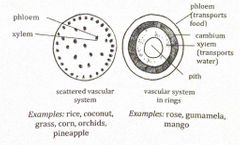
Monocot and dicot |
Types of angiosperms |
|
|
1 cotyledon, parallel veins, petals and sepals in 3s and fibrous roots |
Characteristics of monocot angiosperm |
|
|
2 cotyledons, netted veins, petals and sepals in 4s or 5s; and taproot |
Characteristics of dicot angiosperm |
|
|
Slow and permanent reaction by plants |
Tropism |
|
|
Phototropism |
Tropism to light |
|
|
Geotropism |
Tropism to gravity |
|
|
Thigmotropism |
Tropism to touch |
|
|
Auxin |
This plant hormone function is in charge of cell differentiation, cell elevation and plant growth |

