![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Mitosis |
Divide nucleus |
|
|
|
Chromosome |
Is made up by 2 sister chromtaids |
|
|
|
Prophase |
Nucleur membrand breaks down a spindle fibers start to form |
|
|
|
Metaphase |
Chromosome are line up along the equator & spinder fibers are attach to the centromere of the chromosome |
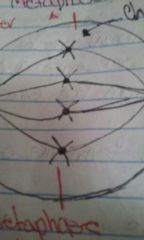
|
|
|
Anaphase |
Chromosomes are spirted into 2 becoming chromtaids & our the opposite poles sides |
|
|
|
Telophase |
Nuclear enevlope around each retorms & cytoplasm forms |
|
|
|
Cytokines |
Cytoplasm how the cell divides |
|
|
|
Cytokines in plant |
A line is form through the cell to slipt |
|
|
|
Cytokines in animal |
Cleavage furrow is form (like a pinch in each side) where the cell splits |
|
|
|
Where does the cell spends most of its time? |
The cells spend most of its time in interphase |
|
|
|
What is interphase? |
G1, S, G2 |
|
|
|
G1 |
Cell is growing, builds organelles, & continue carrying regular function |
|
|
|
S |
Dna is copied |
Synthesis |
|
|
G2 |
Continues to grow and prepares to split the nucleus into 2 |
|
|
|
Karyotype |
A display of individual somatic cell chromsome of metaphase |
|
|
|
Somatic cell |
Any other cell is not sperm or an egg cell |
|
|
|
Homologous chromosomes (terad) |
A pair of chromosomes that have the same size and shape |
|
|
|
Autosome |
Other then a sex chromosome |
|
|
|
Sex chromosomes |
Determines individuals |
|
|
|
Sex chromosomes XX IS ? |
A female |
|
|
|
Sex chromosomes XY is a ? |
A male |
|
|
|
Diaploid |
All the chromosome |
46 |
|
|
Hiploid |
Half the chromosomes |
23 |
|
|
Meiosis |
Sexual reproduction |
|
|
|
Meiosis 1 |
Stays the same as mitosis but stays in 2 sets of chromosomes |
|
|
|
Meiosis 2 |
Same thing like mitosis but you have 4 hapliod cells with half as many chromosomes |
|
|
|
Genetics |
The study of heredity |
|
|
|
What is heredity |
the passing on of physical or mental characteristics genetically from one generation to another. |
|
|
|
Allele |
Alternate forms of a gene/ factor |
|
|
|
Phenotype |
What you can see from a organism |
Features |
|
|
Genotypes |
The dna the organism has |
|
|
|
Dominant |
An allele takes over |
Captial letter |
|
|
Recessive |
An allele which is present but remains expressed masks |
Lowercase |
|
|
Homozygous |
Both alleles for a trait our the same |
|
|
|
Heterozygous |
The organism alleles for a trait different |
|
|
|
Punnet square |
A tool calculating genetic probability |
Math |
|
|
Genotypic ratio |
We have 3 genotypes ( TT, Tt, & tt) |
1:2::1 |
|
|
Phenotypic ratio |
When the Dominant takes over the recessive trait the 3 is the dominat and 1 is recessive |
3:1 |
|
|
Dihybrid Cross |

|
|
|
|
RH |
Positive- can accept positive or negative Negative- only can accept negative |
|
|
|
Antigens |
What fights different type blood which is not the same blood type |
|
|
|
Evolution |
Change over time |
|
|
|
Natural selection |
Individuals better adapted to their environment and are able to survive better |
A.K.A survival of the fittest |
|
|
Population |
A group of individuals of same species that interbread |
|
|
|
Gene Pool |
Common group of all genes present in a population |
|
|
|
Mutation |
Change in dna sequence |
|
|
|
Gene Shuffling |
From sexual reproduction |
|
|
|
Gene Flow |
Due to the imigration of the fertile indiviuals or gamates between population |
Gene imgration |
|
|
Nonrandom mating |
Inbreeding and assortive mating |
|
|
|
Speciation |
The formation of new species |
|
|
|
Reproduction Isolation |
Members of 2 population cannot interbreed and produce fertile offsping |
|
|
|
Behavioral Isolation |
Cabable of breeding but have differences in courtship rituals |
|
|
|
Geographical isolation |
Separated by geographical barriers lile a river, mountains, or bodies of water |
Grey & black squirrel that live opposite sides of the great canyon |
|
|
Temporal Isolation |
2 or more specoes reproduce at different times. |
|
|
|
Ecology isolation |
Species occur in the same area, but they have different habitats and rarely encounter each other |
|
|
|
What's Charlie Darwin father of..? |
Charlie dawer is founding father of evolution |
|
|
|
What is speciation Darwins? |
Charlie Darwin collected different Finches and saw how the change and how they act and became in population because gene pool |
Finches ( type of bird) |
|
|
Relative Dating |
Determines the fossil age by how deep it was in dirt. |

|
|
|
Absolute Dating |
Detemines the age of the fossil by a number |
Numerical dating |
|
|
If you want to know how long a person is died you check for ? |
You check for Nitrogen-14 because bones have Carbon-14 in them so over time the carbon will change to nitrogen |
|
|
|
Big Bang Theory |
A cosmic explosion that created the universe |
|
|
|
What's the evidence of the big bang theory ? |
-Everything in galaxy is traveling away from each other -cosmic radiation from the explosion can be observed |
|
|
|
What was early earth like ? |
- Earth was hot! - Little or no oxygen -Gasses in atmosphere °Hydrogen cyanided(poision for human) °Hydrogen sulfide °Carbon Doxide ° Carbon monoxide ° nitrogen ° water |
|
|
|
How did earth get oxygen? |
°chemical separation ° photosyntheic cyanobacteria °water vapor |
|
|
|
How did life begin? |
Miller and ureys experiment °vapor °water °Lighting °gas Made amino acid that created life. |
|
|
|
Positive stimulus |
The feedback is increased |
|
|
|
Negative feedback |
The number decreased on negative feedback |
|

