![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the Fat soluble Vitamins? |
A, D, E, K |
|
|
|
What are the Water Soluble Vitamins? |
B, C |
|
|
|
What are the levels of organization? |
Tissue, organ, organ system, organism. |
4 |
|
|
What are the minerals in animal nutrition? |
Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, & Magnesium. |
|
|
|
What is a Herbivore? |
Animal that maintains their diet from eating plants and algae. |
|
|
|
What is a Carnivore? |
Animal that maintains their diet from eating other animals. |
|
|
|
What is a Omnivore? |
Maintains diet from eating plants and animals. |
|
|
|
What are the essential Nutrients an animal needs and which are the energy producing ones? |
Carbohydrates, Protein, Lipids are the energy producing ones and Minerals, Vitamins, and Water are the other essential nutrients needed by animals. |
|
|
|
How many Amino Acids are needed by animals? |
20 Amino Acids and half are synthesized from molecules in their diet. |
|
|
|
What does the Pancreas produce? |
It produces proteases trypsin chymotrypsin |
|
|
|
In the small Intestine, Bile aids in? |
Digestion and Absorption in fats. |
|
|
|
Bile is made in the ____?____ and stored in the ____?____. |
Bile is made in the Liver and stored in the Gallbladder. |
|
|
|
What are the main stages of food processing? |
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption, Elimination. |
|
|
|
What is Ingestion? |
It is the act of eating. |
|
|
|
What are substrate feeders? |
Animals that live in or on their food source. |
|
|
|
What are fluid feeders? |
Fluid feeders are animals that suck fluid from a living host. |
|
|
|
What do Bulk Feeders eat? |
Bulk Feeders eat large pieces of food. |
|
|
|
What is digestion? |
Digestion comes after ingestion and it is the process of breaking down food into molecules small enough to absorb. |
|
|
|
What comes after Digestion but before Elimination? Define it. |
Absorption. It is the uptake of nutrients by the cells in the body. |
|
|
|
What is The last stage of food processing? |
Elimination. It is the passage of undigested material. |
|
|
|
What happens in Intracellular Digestion? |
In Intracellular Digestion food particles that are being broken down of substances within the cytoplasm of a cell. |
|
|
|
What goes on in Extracellular digestion? |
In Extracellular digestion food particles are broken down outside of the cells. |
|
|
|
What are the Classification of Nutrients?
|
Carbohydrates, Protein, Lipids, Vitamins, Minerals, Water.
|
|
|
|
What are Macronutrients?
|
A substance required in large amounts by living organisms. A type of food: Carbohydrates, Protein, Lipids.
|
|
|
|
What are Micronutrients?
|
Vitamins and Minerals that are required in small amounts.
|
|
|
|
What is the other name of Vitamin A and which foods are high in the Vitamin?
|
Retinol. Dark Green and orange vegetables and fruits, dairy products. |
|
|
|
What are symptoms of Deficiency of Vitamin A (Retinol)?
|
Blindness, Skin disorders, impaired immunity. |
|
|
|
What is the vitamin associated with Rickets Disease?
|
Vitamin D. Rickets: A disease of children caused by vitamin D deficiency, characterized by imperfect calcification, softening, and distortion of the bones typically resulting in bow legs. |
|
|
|
What is the other name for Vitamin E?
|
Tocopherol |
|
|
|
What are the Vitamin requirements in Humans?
|
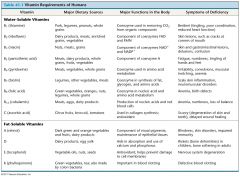
|
|
|
|
What are the Mineral Requirements in Humans?
|
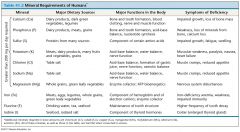
|
|
|
|
What is the most important gland?
|
Pancreas because it secretes insulin. |
|
|
|
Most of digestion occurs in the...?
|
small intestine Enzymes secreted by the pancreas are squirted into the duodenum, where fat, protein, and carbohydrate digestion continues. The last site of digestion occurs on the brush border of the small intestine, where the last of the fat, protein and carbohydrate digestion occurs. There are no digestive enzymes in the colon.Feb 12, 2013 |
|
|
|
What is the function of the Liver?
|
Many vital functions have been identified with the liver. Some of the more well-known functions include the following: Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion. Production of certain proteins for blood plasma.
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the Gallbladder?
|
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped, hollow structure located under the liver and on the right side of the abdomen. Its primary function is to store and concentrate bile, a yellow-brown digestive enzyme produced by the liver. The gallbladder is part of the biliary tract
|
|
|
|
What are the parts of the small intestine?
|
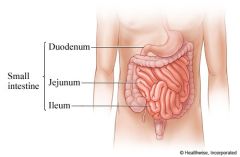
The small intestine consists of three parts. The first part, called the duodenum, connects to the stomach. The middle part is the jejunum. The third part, called the ileum, attaches to the colon.
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the Large intestine?
|
The major function of the large intestine is to absorb water from the remaining indigestible food matter and transmit the useless waste material from the body.
|
|

