![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the living things checklist? |
1. Movement 2. Respiration 3. Sensitivity 4. Growth 5. Reproduction 6. Excretion 7. Nutrition |
|
|
What is the cell theory? |
1. All organisms are composed of cells 2. Cells are the smallest units of life 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells |
|
|
What is the difference between light and electron microscopes? |
An electron microscopes have much shorter wave lengths than light microscopes, in order to produce higher-resolution images |
|
|
What are organelles? |
Any number of specialised or organised structures within a living cell |
|
|
Difference between pro and eukaryotic cells? |
Prokaryotic cells are unicellular and don’t have a nucleus, whereas eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane enclosed organelles |
|
|
Label an animal cell |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Label a plant cell |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Function of cell wall |
Gives structure and support to cells. Made of cellulose |
|
|
function of cell membrane |
holds to contents of the cell in place and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. |
|
|
function of nucleus |
Controls the cell activities e.g. cell division, metabolism, and contains genetic information (DNA). |
|
|
function of nucleolus |
Manufactures ribosomes which move out of the nucleus to the ER of protein synthesis. Appears as a darkly stained part of the nucleus. |
|
|
function of vacuole |
Involved in digestion, storage and release of cellular waste products. In animals cells they are very small, but in plants can be very large and play a role in turgor pressure and maintaining the shape of the cell. |
|
|
function of mitochondria |
The site of aerobic respiration, make energy. Oval shaped. Inner membrane is highly folded to increase surface area for site of chemical reactions. |
|
|
function of chloroplast |
Site of photosynthesis in plants. Contain stacks or 'grana' containing chlorophyll to trap sunlight. |
|
|
function of ribosomes |
The site of protein synthesis. Very small, often found attached or Endoplasmic Reticulum. |
|
|
function of endoplasmic reticulum |
(ER) involved in synthesis and transport of materials within the cell. Smooth ER has no ribosomes attached. Rough ER has ribosomes attached. |
|
|
function of golgi apparatus |
Modifies, sorts and packages substances made by the cell to be exported. |
|
|
function of lysosomes |
Pick up and break down unwanted materials (old organelles, bacteria) |
|
|
function of cytoplasm |
Jelly like cytoplasm that fills up the interior of the cell and supports the organelles. Site for chemical reactions |
|
|
function of cytosol |
The fluid that surrounds the organelles. |
|
|
what is the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol? |
Cytoplasm fills in the empty space and supports the organelles within the cell. It also regulates what enters and exits the cell. Cytosol surrounds just the organelles but does not regulate them as a collective. |
|
|
what is meant by an 'organic' molecule? |
contains carbon carbohydrates, hydrogen and oxygen atoms |
|
|
the plasma membrane forms: |
- The membrane controls the exchange of materials between the internal and external environments of the cell. - Membranes are selectively permeable (allows some substances through but not others) |
|
|
label the parts of the membrane |
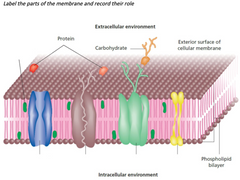
|
|
|
what is diffusion |
it is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. it moves substances down the concentration gradient |
|
|
Diffusion will continue until.... |
it will continue until the concentration gradient has been eliminated |
|
|
what particles can easily go through a membrane? |
uncharged particles such as water and oxygen |
|
|
What is facilitated diffusion? |
the substance is attached to a specific carrier molecule to move across a membrane |
|
|
what is osmosis? |
the movement of semi permeable membranes from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
|
|
what is a hypotonic solution? |
lower solute, higher water |
|
|
what is a hypertonic solution? |
higher solute, lower water |
|
|
define active transport |
the deliberate movement of molecules across the membrane from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration |
|
|
what is the surface area to volume ratio? |
The larger a cell is, the greater the surface area available for diffusion. ... Smaller cells have a much greater surface area to volume ratio allowing material to diffuse throughout the entire volume of the cell quickly and efficiently. |
|
|
what is an enzyme? |
a substance that acts as a catalyst to enact a chemical reaction |
|
|
what is a catalyst? |
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing chemical change |
|
|
what is an anabolic reaction? |
one that builds up complex molecules |
|
|
what is a catabolic reaction? |
the breakdown of complex molecules to simpler products |
|
|
label the diagram |
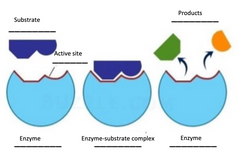
|
|
|
list the four factors that effect enzyme activity |
1. pH 2. temperature 3. Substrate and enzyme concentration 4. Cofactors and coenzymes can either promote or prevent reactions occurring |
|
|
what is a competitive inhibitor |
a molecule that competes with a substrate for an enzyme active site and impairs enzyme function |
|
|
what is a non-competitive inhibitor? |
a molecule that binds to an enzyme at a site other an the active site, that still impairs enzyme function |
|
|
label the different parts of chloroplast |
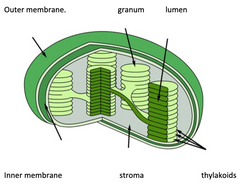
|
|
|
define respiration |
a series of chemical reactions which release energy from complex carbohydrates |
|
|
define photosynthesis |
a series of reactions that converts carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light and chlorophyll into sugars and oxygen |
|
|
cells to multicellular organisms steps: |
atoms make up molecules make up organelles make up cells |
|
|
what are the four main functions of the circulatory system |
1. Circulates oxygen and water and the removal of carbon dioxide 2. Provides the cells with nutrients 3. Protects the body against disease and infection by removal of the waste products 4. The maintenance of homeostasis |
|
|
what are the three main components of the circulatory system |
1. heart 2. blood 3. blood vessels - veins, arteries and capillaries |
|
|
label the components of the blood |
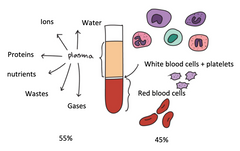
|
|
|
label the features of red blood cells |
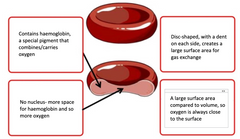
|
|
|
label the heart |
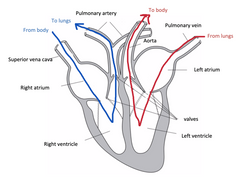
|
|
|
what is countercurrent gas exchange? (in a fish) |
the blood flows through the gills in the opposite direction as the water flowing over the gills |
|
|
what is an open circulatory system? |
pumps blood into a hemocoel with the blood diffusing back to the circulatory system between cells. blood is pumped by a heart into the body cavities, where tissues are surrounded by blood. (insects) |
|
|
what is a closed circulatory system? |
(vertebrates) have the blood closed at all times within vessels of different sizes and wall thickness. the blood is pumped by the heart through vessels and does not fill up cavities |
|
|
label the human respiratory system |
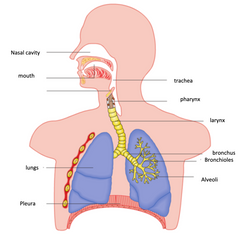
|
|
|
what are the four main roles of the digestive system? |
1. ingestion of food into the body 2. digestion of food 3. absorption of nutrients 4. egestion of waste |
|
|
what are the two types of digestion? |
mechanical digestion - physical movements of the teeth to make the food smaller chemical digestion - enzymes continue to break down the food |
|
|
label the human digestive system |
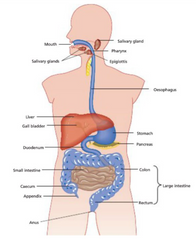
|
|
|
what is excretion? |
a process by which metabolic waste is eliminated from an organism |
|
|
a person has been in a car crash and lost the function of the kidneys. explain why they must undergo dialysis? |
the body can no longer pass waste as urine and filter blood, so dialysis is essential to ensure these waste products are removed and excess fluid does not build up in the body |
|
|
what is deamination? |
the removal of an amino group from an amino acid or other compound |
|
|
what is toxic ammonia? |
when there is too much ammonia in the body that the kidneys cannot eliminate it from the body |
|
|
label the human kidney diagram |
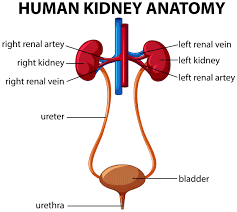
|
|
|
explain the countercurrent arrangement found in fish that facilitates diffusion of respiratory gasses |
The blood flows through the gills in the opposite direction to the water flowing over the gills. This then facilitates counter current oxygen exchange and creates a diffusion gradient and allows maximum extraction of oxygen from water that flows over the gills |

