![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a polar molecule
|
Molecule with uneven distribution of charge
|
|
|
Why is water a valuable solvent
|
- most of cell reactions take place in aqeous solution
- can act as transport mediumin living organism - different effect it has on hydrophobic + hydrophilic molecules |
|
|
What is a buffer
|
Chemical/substance that resists changes to pH + ensures environment maintains pH
|
|
|
What is the function of calcium
|
Plants: component of middle lamella of cell walls
Animals: component of bones and teeth, essential in blood clotting and muscle contraction |
|
|
What is the function of iron
|
part of haem group of haemoglobin, important part of electron carriers in respiration
|
|
|
What is the function of magnesium
|
gives chlorophyll light absorbing properties
|
|
|
What is the function of potassium
|
important in maintaining electrical gradients across neurones
|
|
|
What is the function of nitrate
|
component of amino acids, nucleic acids and chlorophyll
|
|
|
What is the function of phosphate
|
important component of cell membrane as phospholipids
major component of ATP and nucleic acids |
|
|
What is the function of hydrogencarbonate
|
important as natural buffer
|
|
|
What is the formula of glucose
|
C6H12O6
|
|
|
Draw alpha glucose
|
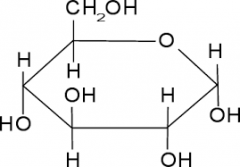
|
|
|
Draw beta glucose
|
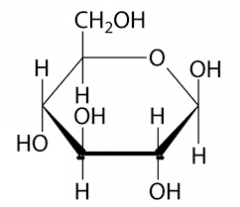
|
|
|
What is an isomer
|
Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
|
|
|
How are disaccharides formed
|
Condensation reaction of two monosaccharides
|
|
|
What is a condensaton reaction
|
Loss of one water molecule
|
|
|
What is a hydrolysis reaction
|
Gain of one water molecule
|
|
|
What is a glycosidic bond
|
Bond formed between two hexose sugars in a disaccharide
|
|
|
What is the general formula of disaccharide
|
C12H22O11
|
|
|
How is maltose formed
|
2 a-glucose molecules linked through condensation reaction
|
|
|
How is fructose sucrose formed
|
a-glucose condenses with fructose
|
|
|
What is the general formula of polysaccharides + general properties
|
(C6H10O5)n
Not sweet and insoluble in water |
|
|
What does starch consist of (approx.%)
|
20% amylose
80% amylopectin |
|
|
Properties of amylose
|
- a-glucose molecules linked by a-1,4 glycosidic bonds
- chains coiled in spiral, held in place by hydrogen bonds - long unbranched chains - coiled due to prescence of bulky side groups, so molecules lie at different angles |
|
|
Properties of amylopectin
|
- also uses a-1,4 glycosidic bonds
- a-1,6 glycosidic bonds form side branches (occcur approx one every ten molecules) - also coiled |
|
|
Why is starch a good storage molecule
|
- amylose + amylopectin very compact due to coiled config, so rich store of glucose in small space
- insoluble, so will not affcet water relations in cell (lots of carbs would cause lots of water to enter via osmosis) - large molecule so will not easily pass through cell membrane and will remain in cell - amylopectin branches creates many terminal ends that are easily hydrolysed, allowing rapid breakdown of starch into glucose |
|
|
Properties of glycogen
|
- similar to amylopectin
- more, shorter branches - stored in liver and muscles of mammals - no unbranched chains so more terminal ends, faster hydrolysis |
|
|
Properties of cellulose
|
- purely structural
- made of b-glucose - alternating molecules rotated 180 degrees, causing straighter chains as bulky side groups alternate being below and above chain, and hydrogen bonds can form cross linkages between adjacent chains - grouped together in microfibrils, forming cell walls in lattice to increases tensile strength |
|
|
General properties + 2 main types of lipids
|
triglycerides + phospholipids, hydrophobic + large
|
|
|
Properties of triglycerides
|
- 3 fatty acids joined to 1 glycerol in condensation, linked by ester bonds
- fatty acids are organic acids, form hydrophobic tails with hydrophobic carboxyl (COOH) group at one end - condensation occurs between glycerol OH group and fatty acid COOH group - excellent energy store as release more energy per unit mass than carbs - insulate and stored in layer below body surface in many animals - protects many body organs |
|
|
What is a saturated fatty acid
|
Contain max number of hydrogen atoms, and carbons linked via C-C single bonds
|
|
|
What is an unsaturated fatty acid
|
Has at least one C=C double bond
|
|
|
What are fats and oils
|
Triglycerides
fats usually animal products and saturated oils usually plant products and unsaturated |
|
|
Properties of phospholipids
|
- similar to triglycerides but 1 fatty acid replaced with phosphate
- polar, as phosphate is hydrophilic and fatty acids hydrophobic |
|
|
Draw structure of amino acids
|
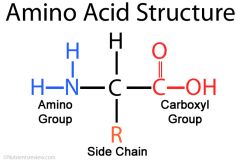
|
|
|
Properties of proteins
|
- amino acids linked by peptide bonds
- formed by condensation reactions - has 4 possible structures |
|
|
Properties of primary structure
|
- sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
- end in NH2 (phosphate) and COOH (carboxyl) on either side |
|
|
Properties of secondary structure
|
- either side of peptide bond has NH and C=O, H pos and O neg, forming hydrogen bonds
- alpha-helix formed by hydrogen bonds at regular intervals, twisting chain into spiral - beta-pleated sheets less rigid and and less flexible, formed by adjacent sections of chain orientated anti-parallel to each other |
|
|
Properties of tertiary structure
|
- further folding of secondary structure, giving unique 3D shape due to bonds formed by range of R groups in chain
- hydrogen bonds (relatively weak and easy broke) - ionic bonds (between amino and carboxyl groups, stronger but damaged by pH changes) - disulphide bonds (covalent, formed between sulfide containing R groups, very strong and very important in giving strength to fibrous proteins) - hydrophobic interactions |
|
|
Properties of quaternary structure
|
2 or more polypeptide chains bonded together (mostly by disulfide bonds)
|
|
|
What are conjugated proteins
|
Quaternary proteins containing prosthetic groups
|
|
|
What are fibrous proteins
|
- polypeptides arranged in form of fibres or sheets
- parallel chains linked by cross-bridges to form very strong, stable molecules - structural function eg collagen found in tendon in bones |
|
|
What are globular proteins
|
- metabolic role eg enzymes, antibodies and haemoglobin
- ability to form specific 3D shapes is crucial |
|
|
What are prions
|
Type of protein found in mammals and some other animal groups, in nervous system and thought to be involved in synaptic transmission
|
|
|
How can prions cause disease
|
- normals form of prion (PrP^c) can convert to a misfolded, disease casuing form (PrP^Sc)
- PrP^Sc acts as template causing other prions to convert to this type - once present, will lead to a chain reaction causing prions to increase - number of prions with tightly packed beta sheets increases to a threshold level that causes neurodegenerative diseases in brain and nervous tissues, eventually death |
|
|
How can prion-disease arise
|
- PrP^c spontaneously adopts PrP^Sc form
- mutations in DNA that codes for prion protein, passes form onto offspring from parent - through eating food contaminated with the PrP^Sc form |
|
|
Name 3 types of prion diseases
|
- scrapie in sheep
- bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) aka mad cow disease, usually cattle affected by eating -variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) human version of BSE usually from eating PrP^Sc contaminated beef products |
|
|
What is the structure of nucleic acid
|
- pentose sugar
- phosphate group - nitrogenous base |
|
|
How are nucleic acids formed and what is the bond that forms
|
Condensation, phosphodiester bonds
|
|
|
What is the structure of DNA
|
2 anti-parallel strands of nucleic acids with deoxyribose sugar being held together by hydrogen bonds between adjacent bases (double helix structure)
|
|
|
What are the bases in DNA
|
adenine with thymine (2 H bonds)
guanine with cytosine (3 H bonds) |
|
|
What is the function of DNA
|
Genetic code, regulates development of living organisms through control of protein synthesis, particularly the regulation of enzymes
|
|
|
What does the sequence of DNA bases determine
|
The primary structure of polypeptides (the amino acid sequence)
|
|
|
What is a gene
|
Sequence of DNA that codes for a polypeptide
|
|
|
What is RNA
|
- single strand of nucleic acid with ribose sugar
- much shorter than DNA - the base uracil replaces thymine |
|
|
What are the 3 types of RNA
|
- messenger RNA (carries code of DNA in nucleus to ribosome)
- transfer RNA (carries amino acids to ribosome for protein synthesis) - ribosomal RNA (made in nucleolus, forms over half the mass of each ribosome) |
|
|
How is DNA replicated
|
- DNA helicase enzyme unzips the strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between bases (allowing each strand to become a template for formation of 2 DNA molecules)
- Free nucleotides are linked to template strands in correct sequence as a conseuence of teh bases on free nucleotides following same base pairing rules as DNA - Nucleotides of each strand joined together by enzyme DNA polymerase - Each DNA molecule contains one original strand and one new one (semi-conservative replication) |
|
|
Describe the Meselson and Stahl experiment
|
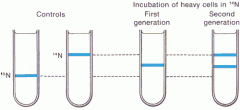
- Meselson and Stahl cultured the bacterium E.coli using the heavy isotope of nitrogen, ^15N
- The heavy nitrogen was incorporated into bases of DNA in all the bacteria over time, as older bacteria containing normal nitrogen ^14N died and were replaced - Bacteria was transferred to a medium of normal nitrogen, and bacterial DNA was then extracted at intervals and analysed - Density-gradient centrifugation was used to seperate the DNA following sampling, and the different isotopes of nitrogen would accumulate at the top (normal) or bottom (heavy) of the centrifuge tube - After one gen, intermdiate position is because all DNA has 1 strand with only normal N bases, and 1 with only heavy N bases - After second gen, about half of the DNA consists of both normal and heavy N, and other half only normal N |

