![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function of nervous system (4) |
-Receive info about external & internal environment -process and integrate that info -store info as necessary -command responses (mainly by signals to muscles and glands) |
|
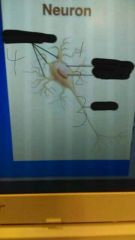
|
1. Cell body 2. Nucleus 3. Axon 4. Dendrites |
|
|
Look over how neurons receive and conduct signals on topic 20 |
(: |
|
|
Neurons keep a______ ____ _____ (polarized membrane) |
Resting membrane potential |
|
|
Neurons have a_____ ____ between possible action potentials, because it takes time for the sodium potassium pump to reestablish ion gradients |
Refractory period |
|
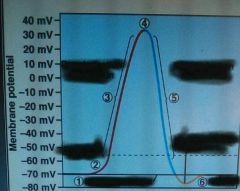
? |
1. Resting potential 2. Threshold 3. Depolarization (Na+ flows in) 4 & 5 Repolarization Hyperpolarization (undershoot) 6. Resting |
|
|
Action potentials propagate along_____ usually thru____ _____ and down______ to the synapse |
Dendrites Cell body Axons |
|
|
Intercellular junctions between an axon and either a muscle cell, gland cell, or dendrites of another neuron |
Synapses |
|
|
Carry signal to the next cell |
Neurotransmitters |
|
|
Binds to an ion channel in muscle cell, allowing Na+ & K+ out, starting an action potential in the muscle cell |
Ach (acetylcholine) |
|
|
Excitation neurotransmitter; MSG added to food to enhance flavor is this |
Glutamate |
|
|
Inhibitory neurotransmitters |
Glycine and GABA |
|
|
Transmits action potentiaks |
Excitatory |
|
|
Reduce likelihood of action potentials |
Inhibitory |
|
|
Major function is control of body movements |
Dopamine |
|
|
Major function is regulation of sleep and emotional state |
Serotonin |
|
|
If neurotransmitter level stays too high, the receptor # is______ and re-take or destruction mechanisms are______. What about when levels stay too low? |
Reduced ; increased Increased, reduced |
|
|
Drug molecules prevent____ and cause____ of the postsynaptic membrane |
Reabsorption Overstimulation |
|
|
Supporting celka |
Neuroglia |
|
|
Major role of supporting cells |
To produce myelin sheaths around axons |
|
|
Layers of membrane that insulate the axon |
Myelin sheath |
|
|
Gaps every 1-2 mm; action potentials "jump" from one of these to the next. |
Nodes of Ranvier |
|
|
Action potentials "jumping" from one node to the next allow for |
Action potentials to travel faster along myelinated axons compared to unmyelinated axons |
|
|
Animals that don't have a nervous system |
Sponges |
|
|
Both have neural nets; which one has a central neural ring? |
Cnidaria Echinoderms (cnr) |
|
|
Typically have a CNS with a centralized control center (brain) located in the head |
Bilateria |
|
|
Brain and spinal cord; mainly association neurons |
Central nervous system (CNS) |
|
|
Everything besides brain and spinal cord ; mainly sensory and motor neurons |
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) |
|
|
Control skeletal muscles |
Somatic motor neurons |
|
|
Regulate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands |
Autonomic motor neurons |
|
|
Integrates brain with spinal cord, controls breathing; aka brain stem |
Medulla oblongata |
|
|
Associated with medulla oblongata , involved in coordination and motion memory |
Cerebellum |
|
|
Motor control, memory, emotion, higher functions (in cerebral cortex) -greatly enlarged in humans |
Cerebrum |
|
|
Integrates the hemispheres of the brain |
Corpus callosum |

