![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Active Transport |
Substances moving against a concentration gradient across a semi permeable membrane |
|
|
Diffusion |
Spreading out of particles from high conc to low conc down a concentration gradient |
|
|
Impacts rate of diffusion |
Temperature - more energy Difference in concentration - the greater the difference the greater the gradient quicker rate of diffusion |
|
|
How are nutrients absorbed into the gut ? |
Millions of tiny villi Increase surface area of small intestine increase rate of absorption Pass through wall of small intestine Single layer of surface cell - quick diffusion Good blood supply- assist absorption |
|
|
How does gas exchange take place in plants ? |
Co2 enters through stomata on base of leaf Diffuses into cells Oxygen produced in photosynthesis diffuses out of stomata Guard cells open and close stomata stop water loss Flat shape of leaf increase surface area efficient gas exchange Wall of cell for gas exchange
|
|
|
What is surface area to volume ratio? |
How easy for an organism to exchange substances with environment Larger organism the smaller the surface are to volume ratio |
|
|
Gas exchange in lungs during inspiration |
The smallest bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli These inflate during inspiration oxygen is brought in |
|
|
Gas exchange in lungs during exhalation |
The smallest bronchioles end in air sacs called alveoli Theses deflate in exhalation co2 is given out |
|
|
Job of inspiration and exhalation in lungs |
Transfer o2 to blood and remove co2 |
|
|
How to work out surface are : volume ratio |
Work out surface area Work out volume Simplify Make blocks around object easy workings |
|
|
Turgid |
Normal water levels in plant |
|
|
Flaccid |
Water in and out high pressure |
|
|
Plasmolysed |
Water out |
|
|
Osmosis works by |
Only tiny molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane |
|
|
Osmosis works by |
Only tiny molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane |
|
|
Hypotonic means |
Concentration of solute is lower on outside the cell Expands and bursts |
|
|
Osmosis works by |
Only tiny molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane |
|
|
Hypotonic means |
Concentration of solute is lower on outside the cell Expands and bursts |
|
|
Isotonic means |
Concentration of solute inside and outside is equal |
|
|
Hypertonic means |
Concentration of solute is higher on outside Cell shrivels |
|
|
Animals have ...... and plants do not |
Cell wall Vacuole |
|
|
Animals have ...... and plants do not |
Cell wall Vacuole |
|
|
Function of nucleus |
Contains DNA and controls activity through cell |
|
|
Animals have ...... and plants do not |
Cell wall Vacuole |
|
|
Function of nucleus |
Contains DNA and controls activity through cell |
|
|
function of Mitochondria |
Aerobic respiration takes place to transfer energy |
|
|
Animals have ...... and plants do not |
Cell wall Vacuole |
|
|
Function of nucleus |
Contains DNA and controls activity through cell |
|
|
function of Mitochondria |
Aerobic respiration takes place to transfer energy |
|
|
Function of ribosome |
Where proteins are made in the cell |
|
|
Function of chloroplasts |
Contains chlorophyll which absorbs light for photosynthesis |
|
|
Function of cell wall |
Rigid and made of cellulose to support the cell structure |
|
|
Function of cell wall |
Rigid and made of cellulose to support the cell structure |
|
|
Function of cytoplasm |
Other chemical reactions take place |
|
|
Diagram |
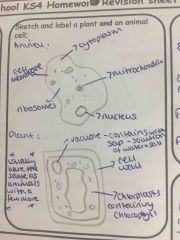
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Specialised cells sperm cell |
Long tail Stream line head for easy movement Lots of mitochondria for energy Enzymes in head to break egg cell membrane |
|
|
Specialised cells sperm cell |
Long tail Stream line head for easy movement Lots of mitochondria for energy Enzymes in head to break egg cell membrane |
|
|
Specialised cell nerve cell |
Long to cover more distance Branches connections at ends to connect to other nerve cells Make network |
|
|
Specialised cells muscle cells |
Long to have space to contact Lots of mitochondria for energy and quick contractions |
|
|
Eukaryotic and Eukaryotes |
Complex cells that are like animal and plant cells Organisms made of eukaryotic cells |
|
|
Eukaryotic and Eukaryotes |
Complex cells that are like animal and plant cells Organisms made of eukaryotic cells |
|
|
Prokaryotes and prokaryotic |
Simple smaller cells like bacteria Prokaryotes are single cell organisms |
|
|
Phloem |
For food Made of elongated cells with small end pores to allow sap in Transports dissolves sugar to the rest of the plant Translocation |
|
|
Phloem |
For food Made of elongated cells with small end pores to allow sap in Transports dissolves sugar to the rest of the plant Translocation |
|
|
Xylem |
Water Made of dead cells No end walls Hole down middle strengthens by lignin Carry mineral ions and water |
|
|
Phloem |
For food Made of elongated cells with small end pores to allow sap in Transports dissolves sugar to the rest of the plant Translocation |
|
|
Xylem |
Water Made of dead cells No end walls Hole down middle strengthens by lignin Carry mineral ions and water |
|
|
Translocation is |
Movement of materials from leaves to other tissue |
|
|
Xylem |
Water Made of dead cells No end walls Hole down middle strengthens by lignin Carry mineral ions and water Transpiration |
|
|
Transpiration is |
Evaporation and diffusion Constant stream of water through plant as diffuse up xylem evaporated and repeated |

