![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who was Friedrich Mischer?
|
Swiss biochemist.
*Noticed septic patients had a lot more of a compound with high phosphate content. *Discovered the "nuclein" (DNA) in WBCs |
|
|
What did Griffith contribute to the study of DNA?
|
In 1928, Griffith discovered that genetic information could be passed from one bacteria to another; "transforming" principle
|
|
|
What did Avery and MacLeod and McCarty contribute?
|
Transforming material was pure DNA, not protein, lipid or carbs
*Worked with Drosophilia |
|
|
What did Watson and Crick contribute to the study of DNA?
|
It's structure!
*No actual experiments, looked at other people's data |
|
|
What are the components of DNA?
|
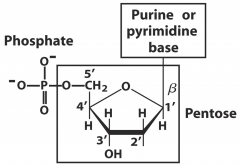
DNA is a polymer of nucleotides
*Pentose sugar *Purine or pyrimidine (nitrogenous base) attached to 1C * Phosphate (attached to 5C) |
|
|
What type of bond forms between phosphate and pentose?
|
Phosphoester
|
|
|
What is a nitrogenous base + pentose sugar called?
|
Nucleoside
|
|
|
What is the bond between pentose and base called?
|
N-beta-glycosyl bond
|
|
|
What are the components of nitrogenous bases?
|
* Ring structure
*Heterocyclic (2N, 4C) *Hydrophobic *Planar *Exists in 2 tautomeric forms *Strongly absorbs in UV range *Purine or pyrimidine |
|
|
How can you tell the difference between purine and pyrimidine?
|
Small name= big structure (2 rings)
Big name= small structure (1 ring= pyrimidine) |
|
|
What are the 5 nitrogenous bases?
|
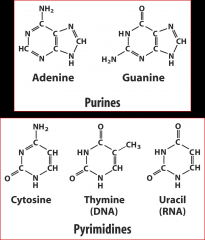
Adenine, Guanine; Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil (RNA)
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a pentose sugar?
|
*Heterocyclic
*Furanose (closed, 5C ring) *Hydrophillic *Non-planar |
|
|
Why is a pentose sugar NON-PLANAR, but a base is planar?
|
No double bonds in pentose sugar, so it is slightly puckered
|
|
|
What are the 3 conformations of pentose sugar?
|
2,2 endo
3,3 exo 2 endo, 3 exo |
|
|
What are the 2 conformations of base and sugar?
|
Anti (opposite) and syn (same side)
Syn conformation only happens in certain conditions |
|
|
What links nucleotides?
|
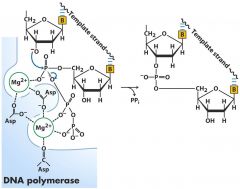
Phosphodiester bond
Deprotonated hydroxyl on pentose ring attacks alpha phosphoryl group (DNA polymerase facilitates) This is a type of metal-ion and acid-base catalysis (Asp residues and Mg2+ are in the active site) *Diphosphate is released |
|
|
Where are phosphodiester bonds formed?
|
3' end
|
|
|
What constitutes the backbone?
|
Phosphate+ Sugar
The backbone is hydrophillic |
|
|
True or False: Nucleotides are planar
|
TRUE. They roject out of plane on axis of backbone.
|
|
|
Who discovered the structure of DNA?
|
Rosalind Franklin via X-ray diffraction analysis.
*She noticed that 2 chains crossed each other |
|
|
What is the Watson Crick model of DNA?
|
*Each DNA molecule has 2 helical polynucleotides
*R-handed double helix *Hydrophillic backbone of alternating deoxyribose and phosphate *C-2 endo deoxyribose *Bases are hydrophobic and stacked away from water *Bases are perpendicular to the helical axis *Major and minor groove *Antiparallel *Complementary *3.4A minor periodicity (between two adjacent bp), 34A major periodicity, one complete turn with 10 bases |
|
|
Why the helical conformation?
|
It minimizes the exposure of the bases to water
|
|
|
How many bases are there per turn?
|
10.5 /turn
|
|
|
What is the translational rise?
|
3.4A
|
|
|
What is the pitch?
|
36A
|
|
|
What is Chargraff's Rule?
|
A pairs with T, C pairs with G
DNA from different tissues of the same species have the same base composition DNA base composition does not change with age, nutritional state, or change altered environment |
|
|
True or False: Bases are directly in the center of DNA?
|
FALSE. Bases lie more to one side. This is due to major and minor groove
|
|
|
How many H bonds do G-C have? A-T?
|
3 for GC, 2 for AT
|
|
|
What type of DNA is found in cells?
|
B-form DNA (10.5 bp/turn)
|
|
|
What is the distance between a purine and pyrmidine bonded?
|
20A
|
|
|
What forces affect the stability of the DNA double helix?
|
Hydrophobic interactions- stabilize inside
Stacking Interactions- these are VDW forces H-bond: facilitates stacking |
|
|
What destabilizes DNA?
|
Electrostatic interactions (due to the negative phosphate). These can be neutralized by positive charged Na+ or proteins
|
|
|
What are the 3 forms of DNA?
|
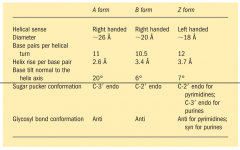
A-form (R-handed, in ethanol, 2.6A between bp)
B-form (R-handed, in cells) Z-form (L-handed, more elongated, less diameter |
|
|
What is the purpose of minor types of DNA structure?
|
Z-like structure observed where transcription starts
Runs of multiple G are A-like Structural variations play a role in DNA-protein interactions |
|
|
What is a palindrome? What is a mirror repeat?
|
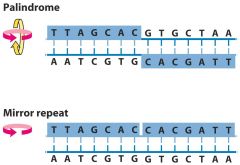
Palindrome= 2 fold symmetry on different strands
Mirror repeat= 2 fold symmetry on same strand. |
|
|
What is a hairpin? What is a cruciform?
|
A bend in the DNA causes complementary bp to bind.
A cruciform is 2 hairpins. |
|
|
What is a triple helix? What type of bonding occurs? Why does it occur?
|
2 polypeptides are bound. The third is bound to the helix by a Hoogstein base pair.
It occurs to regulate transcription (prevent it) |
|
|
When does a tetraplex occur?
|
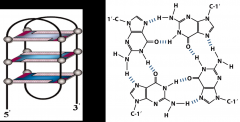
When there are a series of guanine residues, which make the DNA twist and it gets stabilized.
It is found at the end of the chromosome by telomers |
|
|
What does monocistronic mean? Where are these found? What does polycistronic mean?
|
Monocistronic= 1 gene encoding for polypeptide. Mostly in eukaryotes.
Polycistronic= multiple genes encoding for a protein. These are mostly in prokaryotes. |
|
|
What are hte classes of RNA?
|
1. mRNA
2. tRNA 3. rRNA 4. siRNA 5. miRNA 6. Ribozymes |
|
|
What is the secondary structure of RNA?
|
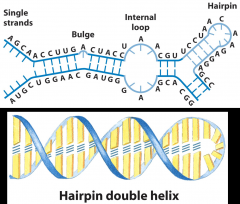
Single Strand
*Can fold onto self to form a double helix (if it does, it forms A-form, R-handed) |
|
|
Which bp denature first?
|
A-T (because only 2 H bonds).
*Unwinding is cooperative |
|
|
What is hyperchromisity?
|
denatured DNA absorbs more UV
|
|
|
What is hypochromisity?
|
A decrease in absorbance due to renaturation of DNA
|
|
|
How many steps are in renaturation?
|
2. The first is the RDS, which is second order of finding complementary sequence to nucleate base pairing.
The second is faster, zippering reaction to form long molecules |
|
|
What can mutgens do to bp?
|
Thymine dimers! Mutation
|
|
|
What level of structure is supercoiling?
|
Tertiary
|
|
|
When does supercoiling occur?
|
When two strands are constrained in any way
2 ends of the DNA need to be anchored or fixed (either to a scaffold or to eachother) |
|
|
What is the difference between R and L-handed supercoiling?
|

Right-handed= + Supercoiling (OVERWOUND)
Left-handed= - Supercoiling (UNDERWOUND) |
|
|
What is the linking number?
|
Lk= Tw+ Wr
Tw= number of times two strands pass each other in a double helix Wr= number of times the double helix pass each other in supercoiled DNA |
|
|
What does a negative supercoil mean for writhe?
|
NEGATIVE WRITHE
|
|
|
If a relaxed DNA had Lk=200 and delta Lk=2, what type of supercoil?
|
POSITIVE. It would be 200+2=202
If delta Lk was -2, Lk= 198, and would be a negative supercoil. |
|
|
How can you tell the difference between + and - supercoil experimentally?
|
Run in a 2-D gel electrophoresis.
Increase the number of supercoils, the DNA moves faster |
|
|
What is the purpose of supercoiling during transcription
|
Helps determine transcription direction
+ Supercoils occur ahead of RNA polymerase. Topoisomerase remove these supercoils |
|
|
What are DNA topoisomerases?
|
Enzymes that remove supercoils from DNa and control the degree of supercoiling in the cell
|
|
|
What are the two types of topoisomerases?
|
I. Type 1
-breaks one of the strands, pass unbroken through it, rejoins strand. It changes Lk by 1 No ATP required II. Type 2 ATP required Both strands are broken. Changes Lk by 2 |

