![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is cellular respiration? |
When O2 is consumed, and sugar is broken down to CO2 and H2O; the cell captures the energy released in ATP.
The aerobic harvesting of energy from food molecules. |
|
|
What is misleading about the following statement? "Plant cells perform photosynthesis, and animal cells perform cellular respiration" |
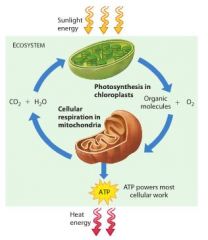
The statement implies that cellular respiration does not occur in plant cells. In fat, almost all eukaryotic cells use cellular respiration to obtain energy for their cellular work.
Photosynthesis and respiration are reactions that complement each other in the environment. They are in reality the same reactions but occurring in reverse. While in photosynthesis carbon dioxide and water yield glucose and oxygen, through the respiration process glucose and oxygen yield carbon dioxide and water. |
|
|
How is breathing (human) related to cellular respiration? |
In breathing, CO2 and O2 are exchanged between your lungs and the air. In cellular respiration, cells use the O2 obtained through breathing to break down fuel releasing CO2 as a waste product.
You breath in O2, cells use O2 for respiration, waste product is CO2, you breathe out CO2 |
|
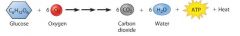
What does this equation tell us? |
Summary of cellular respiration. The equation tells use that the atoms of the reactant sugar molecule (C6H12O6) are rearranged to form the products CO2 and H2O. |
|
|
Cellular respiration can produce up to how many ATP molecules for each glucose molecule?
BONUS: about what % of the energy originally stored in glucose? |
Up to 32.
BONUS: about 34% of the original energy. |
|
|
Why are sweating and other body-cooling mechanisms necessary during vigorous exercise? |
The demand for ATP is supported by an increased rate of cellular respiration, but about 66% of the energy released from food produces heat instead of ATP. |
|
|
What are kilocalories? |
A measure of the quantity of HEAT required to raise temperature to 1 kg of water by 1 degree Celcius.
(the calories in food packages are actually kilocalories). |
|
|
Walking at 3MPH (burns 245cal/hr), how far would you have to travel to burn off the equivalent of an extra slice of pizza, which is about 475kcal? How long would that take? |
You would have to walk about 6 miles, which would take about 2 hours. |
|
|
What is a redox reaction? |
An oxidation-reduction reaction, where there is movement of electrons from one molecule to another. |
|
|
In a redox reaction what is oxidation and what is reduction? |
LEO and GER - losing electrons is oxidation, and gaining electrons is reduction. |
|
|
In the cellular respiration equation, you do not see any electron transfers, instead you see changes in what? |
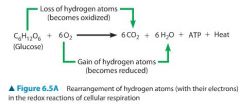
The location of hydrogen atoms:
|
|
|
What is NAD+ and what role does it play in the oxidizing of glucose? |
NAD+ is a coenzyme.
It ACCEPTS electrons and becomes REDUCED to NADH. |
|
|
What is the electron transport chain? |
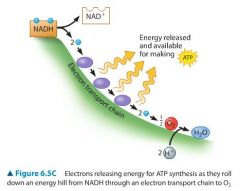
NADH is formed it delivers the electrons to a STRING of ELECTRON CARRIER MOLECULES, forming an electron transport chain (purple in image). |
|
|
What chemical characteristic of the element oxygen accounts for its function in cellular respiration? |
Oxygen is extremely electronegative, making it very powerful in pulling electrons down the electron transport chain. |
|
|
What are the three main stages of Cellular Respiration? |
Stage 1: Glycolysis
Stage 2: Citric Acid Cycle (which includes pyruvate oxidation)
Stage 3: Oxidative Phosphorylation |
|
|
What occurs in the first stage of cellular respiration: glycolysis? |
It occurs in the cytosol of the cell. Glycolysis begins cellular respiration by breaking glucose into two molecules of a 3-carbon compound called pyruvate (2).
Glycolysis means "splitting" of "sugar" |
|
|
Where does the citric acid cycle occur and what happens during this second stage of cellular respiration? |
Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle occur in the mitrochondria.
Pyruvate is oxidized to a 2 carbon compound. The citric acid cycle then completes the breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide.
Thus the CO2 that you exhale is formed in the mitochondria of your cells during this SECOND stage.
This chemical cycle COMPLETES the metabolic breakdown of the glucose molecule. |
|
|
What is the MAIN function of the first 2 stages of cellular respiration? |
To supply the third stage (oxidative phosphorylation), with electrons. |
|
|
What happens during the oxidative phosphorlyation stage of cellular respiration? |
Involves electron transport and a process known as chemiosmosis. NADH and a related electron carrier, FADH2 shuttle electrons to an electron transport chain, embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. |
|
|
Provide an overview of cellular respiration |
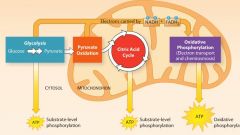
|
|
|
What is chemiosmosis? |
An energy-coupling mechanisms (2nd part of oxidative phosphorylation) that uses the energy of hydrogen ion (H+) gradients across membranes to drive cellular work, such as the phosphorylation of ADP; powers most ATP synthesis in cells. |
|
|
Of the three main stages of cellular respiration, which is the only that uses oxygen? |
Oxidative phosphorylation, in which the electron transport chain ultimately transfers electrons to oxygen. |
|
|
How does glycolysis harvest chemical energy? |
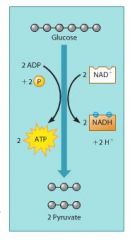
By oxidizing glucose to form 2 pyruvates (each with 3 carbons). |
|
|
How is ATP formed in glycolysis? |
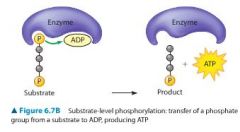
Through a process called substrate-level phosphorylation. In this process an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule directly to ADP, forming ATP |
|
|
What are intermediates within glycolosis? |
Compounds that form between the initial reactant, glucose and the final product, pyruvate. |
|
|
For each glucose molecule processed, what are the net molecular products of glycolysis? |
Two molecules of pyruvate, two molcules of ATP, and two molecules of NADH |
|
|
What is acetyl coenzyme A, what role does it play in pyruvate oxidation (prior to citric acid cycle) |
The pyruvate created during glycolysis is "groomed" during pyruvate oxidation, in which 3 reactions occur: including step 3 coenzyme A (derived from a B vitamin) joins with the 2 carbon group to form a molecule called acteyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Since 2 pyruvates enter, 2 acetyl CoA's are produced, and those enter the citric acid cycle. |
|
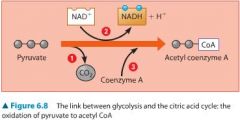
What molecule has been reduced in this reaction? |
NAD+ has been reduced (i.e. it has GAINED an electron) to become NADH. |
|
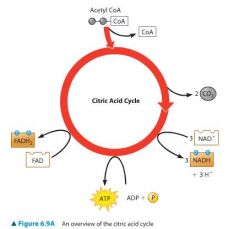
What is the yield of the citric acid cycle? |
2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2 |
|
|
What is the total number of NADH and FADH2 molcules generated during the complete breakdown of one glucose molecule to six molecules of CO2. |
10 NADH, 2 from glycolysis, 2 from the oxidation of pyruvate, 6 from the citric acid cycle
2 FADH2, from the citric acid cycle |
|
|
What is ATP Synthase? |
An enzyme embedded in the membrane which synthesizes ATP, through chemiosmosis with adjacent electron transport chains, using the energy of a hydrogen ion concentration gradient to make ATP
Act like mini turbines, with the rush of H+ ions down their concentration gradient turning the wheels. |
|
|
What are the two main processes in oxidative phosphorlyation? |
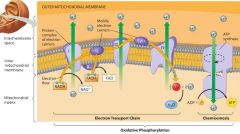
1. Electron transport chain, the hydrogens are pushed outside the membrane.
2. Chemiosmosis, the hydrogens are pulled back into mitochondria, generating ATP as they do so. |
|
|
What effect would an absence of Oxygen (O2) have on the process "electron transport chain" within the oxidative phosphorylation stage? |
Without oxygen to "pull" electrons down the electron transport chain, the energy stored in NADH and FADH2 could not be harnessed for ATP syntesis. |
|
|
The initial study discussed (identifying brown fat in adults) identified brown fat in less than 10% of the patients whose scans were analyzed. The second study identified brown fat in 96% of participants. What accounts for this difference? |
Brown fat is activated in response to cold temperatures, and the second study involved cold treatments. |
|
|
Explain where O2 is used and CO2 is produced in cellular respiration |
O2 accepts electrons at the end of the electron transport chain, CO2 is released during the oxidation of intermediate compounds in pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle. |
|
|
What is anaerobic harvesting of energy? and what is ONE example? |
Harvesting of energy WITHOUT oxygen.
Fermentation is ONE example. |
|
|
Which metabolic pathway generates ATP during fermentation? |
GLYCOLYSIS |
|
|
What are two types of fermentation? |
Lactic Acid Fermentation - used by muscle cells and certain bacteria. It is glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to lactate, regenerating NAD+
Alcohol fermentation - brewing, winemaking, and YEAST. Yeasts are single cell fungi that normally use AEROBIC respiration, BUT can also use anaerobic processes. It is Glycolsis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to ethyl alcohol regenerating NAD+ and releasing carbon dioxide. |
|
|
A glucose-fed yeast cell is moved from an aerobic environment to an anaerobic one. For the cell to continue generating ATP at the same rate, how would its rte of glucose consumption need to change? |
The cell would have to consume glucose at a rate about 16 times the consumption rate in the aerobic environment (2 ATP per glucose molecule is made by fermentation vs 32 ATP by cellular respiration) |
|
|
List some of the characteristics of glycolysis that indicate that it is an ancient metabolic pathway |
Glycolysis occurs universally (functining in both fermentation and respiration), does not require oxygen, and does not occur in a membrane enclosed organelle. |
|
|
Animals store most of their energy reserves as fats, not as polysaccharides. What is the advantage of this mode of storage for an animal? |
Most animals are mobile and benefit from a compact and concentrated form of energy storage. Also, because fats are hydrophobic, they can be stored without extra water associated with them. |
|
|
What is biosynthesis? |
The production of organic molecules using energy-requiring metabolic pathways. |
|
|
Explain how someone can gain weight and store fat even when on a low-fat diet. |
If caloric intake is excessive, body cells use metabolic pathways to convert the excess to fat. The glycerol and fatty acids of fats are made from G3P and acetyl CoA, respectively, both produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates. |
|
|
What is the electron transport chain? |
The first part of oxidative phosphorlyation stage, in which a series of electron carrier molecules that shuttle electrons during a series of redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP; located in the inner membrane of mitochondria, the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, and the plasma membranes of prokaryotes. |
|
|
What does the oxidative phosphorylation stage entail? |
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration. |
|
|
What is substrate-level phosphorlyation |
substrate-level phosphorylation. In this process an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule directly to ADP, forming ATP
For example, one of the intermediates in glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. |
|
|
Cellular respiration oxidizes glucose and organic fuels to what two molecules?
In what molecule does the oxygen breathed in FIRST show up in? |
CO2 and H20!
H2O, CO2 is whats breathed out at the end |
|
|
In glycolysis what is REDUCED |
NADH+ because it GAINS an electron and becomes NADH |
|
|
When is the most immediate source of energy for making MOST of the ATP in your cells? |
MOST- happens during third stage (oxidative phosphorylation)
When H+ moves across membrane down concentration (turns the turbine) |
|
|
In cellular respiration, which stage is the ONLY stage that REQUIRES ATP to make ATP? |
glycolysis |
|
|
During fermentation,what is generated during glycolysis?
What is this then converted back into? |
NADH, NAD+ |
|
|
What is fat is the most efficient molecule for long-term energy storage even compared to carbohydrates? |
with their numerous hydrogen atoms, fats provide an abundant source of high-energy electrons |
|
|
What are the intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle?
When these are siphoned off, what can they then be used for? |
pyruvate and acetyl COA
can be siphoned off to build amino acids, fats, and sugars |

