![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
muscle types |
smooth skeletal cardiac |
|
|
skeletal muscle structure |
muscle, muscle fiber, myofibril, sarcomeres |
|
|
sarcomere |
contractile units of muscles z-line to z-line striations are visible z-lines |
|
|
actin |
thin protein filaments
attatched to z-lines has myosin binding sites |
|
|
myosin |
thick protein filaments binds to actin |
|
|
troponin complex |
has Ca²⁺ receptors when triggered causes shape change in tropomyosin exposing binding sites on actin |
|
|
muscle contraction |
a neural impulse transmitted across synapse to muscle cell by acetylcholine neural impulse passes down t-tubules to SR SR releases Ca²⁺ into cytosol Ca²⁺ binds to troponin complex and binding sites on actin are exposed myosin uses ATP to ¨walk¨ along actin (contraction) neural impulse ends; SR pumps Ca²⁺ back from cytosol tropomyosin blocks binding sites on actin; relaxation occurs |
|
|
osmoregulation |
regulation of water and solutes |
|
|
interstitial fluid |
watery liquid that surrounds cells contains water and solutes aids in exchange with capillaries |
|
|
osmoconformers |
interstitial fluids resemble seawater isotonic marine invertabrates |
|
|
osmoregulators |
interstitial fluids are different from the environment hyper- or hypotonic use energy to transport water or solutes |
|
|
metabolites |
waste from metabolic processes |
|
|
Ammonia |
water soluble gas toxic in small amounts must be excreted quickly requires lots of water |
|
|
Urea
|
toxic in large amounts takes a lot of water |
|
|
Uric Acid |
non-toxic takes very little water secreted as paste |
|
|
Urine |
95% water |
|
|
Kidneys |
regulate water and solutes by filtering blood |
|
|
Ureters |
tubes from kidneys to bladder |
|
|
Bladder |
stores urine |
|
|
Urethra |
drains bladder |
|
|
nephron |
functional unit of kidney |
|
|
glomerous |
network of capillaries per nephron |
|
|
filtration |
plasma and solutes removed |
|
|
reabsorption |
vital solutes and water are reclaimed and return to capillary |
|
|
hemolyph |
circulatory fluid and interstitial fluid are the same open circulatory system |
|
|
blood |
circulatory fluid and interstitial fluid are seperate closed system |
|
|
single circulation |
heart pumps blood through one circuit 2 chambered heart 2 classes of fish |
|
|
double circulation |
pulmonary and systemic circuits 3 or 4 chambered hearts |
|
|
human blood circulation |
superior/inferior vena cava right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary arteries lungs pulmonary veiins left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta body |
|
|
lub sound |
atrioventricle valves closing |
|
|
dub sound |
semilunar valves closing |
|
|
blood pressure affected by |
salt intake stress plaque build-up |
|
|
sinoatrial node |
¨Pacemaker¨ generates electrical signal for atria |
|
|
atrioventricular node |
passes signal to ventricles |
|
|
ECG |
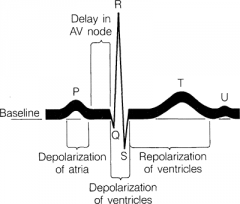
|
|
|
lymphatic system |
collects lymph that leaks from capillaries |
|
|
lymph nodes |
organs that filter lymph have resident leukocytes |
|
|
nasal cavity |
filters, warms, and moistens air |
|
|
trachea |
wind pipe |
|
|
larynx |
upper part of trachea contains vocal cords mobile pushes epiglottis to cover glottis |
|
|
glottis |
opening to trachae |
|
|
bronchi |
tubes from trachae to lung |
|
|
bronchioles |
tube network in lungs |
|
|
alveoli |
sites of gas exchange small air sacs |
|
|
control of breathing |
medulla oblongatta pons |
|
|
gas transport |
90% of CO₂ is in bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) |

