![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
which NTP have 3 bonds and which have 2
|
G-C pairs have 3 bonds, A-T have 2 (O-NH2 and nH-H bonds form)
|
|
|
which NTP bond to which in dna
|
A bonds to T
G bonds to C |
|
|
G bands are...R bands are...
|
1. G bands are rich in A- T nucleotide pairs; they stain dark.
2. R bands are rich in G-C nucleotide pairs; they stain light. |
|
|
histone proteins...
|
* form a histone octomer
*are positively charged *contain a high proportion of lysine and arginine |
|
|
heterochromatin is...
euchromatin is... |
10%, highly condensed, replicated late
80%, less condensed, replicated early |
|
|
chromosome replication occurs during
|
s-phase of the cell cycle
|
|
|
DNA polymerase copy in which direction and produce in which direction
|
copy (read) DNA in 3to5, produced in 5to3
|
|
|
DNA polymerase delta
|
replicated the leading strand
|
|
|
DNA polymerase alpha
|
uses the RNA primer to synthesize DNA fragments called Okazaki fragements
|
|
|
DNA repair enzyme..
|
replaces the RNA primers with DNA
|
|
|
DNA ligase
|
joins DNA fragments
|
|
|
the TELOMERE nucleotide ewquence is
|
GGGTTA
|
|
|
nuclease
|
cleaves the ends to form double-helix
|
|
|
AP endonuclease
|
recognizes the site of the missing base and nicks the deoxyribose sugar phosphate
|
|
|
phosphodiesterase...
|
excises the deoxyribose sugar phosphate
|
|
|
this enzyme recognizes and removes uracil from DNA
|
uracil-DNA glycosidase
|
|
|
recognizes pyrimidine dimer and excieses a 12-residue oligonucleotide that includes the dimer
|
uvrABC enzyme
|
|
|
integrase
|
recognizes specific nucleotide sequences and cuts the viral DNA
|
|
|
two types of transposable elements
|
alu sequences, LINE-1 sequences
|
|
|
transposase
|
is a recombination enzyme similar to integrase. it cuts the transposable element at sites marked by inverted repeate DNA sequences that are 20 base pairs long
|
|
|
methotrexate inhibits ...
|
dihydrofolate reductase
|
|
|
in sickle cell anemia a ___ is converted to ___
|
glutamic acid is converted to a valine
|
|
|
the gene prmotor DNA sequence...
|
located near the gene upstream, is where RNA polymerase II and transcription factors assemble so that a gene can be transcribed into messenger RNA, contains a TATA box, CAAT box or GC box
|
|
|
the gene regulatory (enhancer) DNA sequence ...
|
located far away from the gene, upstream OR downstream, binds gene regulatory protins
|
|
|
what are the four types of DNA binding proteins..
|
homeodomain proteins, zinc finger proteins, leucine zipper proteins, and helix-loop-helix proteins
|
|
|
homeodomainn proteins ...
|
consist of three linked alpha helices which are arranged in a helix-turn-helix motif in helicies 2 and 3, helix 3 binds specifically to DNA segments that contain ATTA sequence
|
|
|
zinc finger protein..
|
has one alpha helix, contains one zinc atom bound to four cysteine amino acids, contains a hormone-binding region, a 70 AA long region near the zinc atom binds specifically to DNA segments
|
|
|
lucine zipper protein...
|
consistes of an alpha helix that contains a region in which every seventh amino acid is leucine, dimerization and formation of y-shaped dimer, 20 aa logn region that binds DNA
|
|
|
helix-loop-helix protein
|
short alpha helix connected by a looop to a longer alpha helix, loop allows for dimerzation
|
|
|
the lac operon consists of three genes
|
lac Z gene - beta-glactosidase
lac Y gene - lactose permase lac A gene - thioglactosidase transacetylase |
|
|
RNA polymerase I...
RNA polymerase II... RNA polymerase III... |
I: rRNA
II: mRNA, snRNPs III: tRNA and 5S rRNA |
|
|
RNA capping is..
|
addition of methylated guanine nucleotide to the 5' end
|
|
|
RNA polyadenylation
|
addition of repeated adenine nucleotides (poly-A tail) to the 3' end of the RNA transcript
|
|
|
RNA splicing...
|
is performed by snRNPs that are a complex of RNA and protein called a spliceosome
|
|
|
this enzyme links an aminio acid to tRNA
|
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
|
|
|
this enzyme helps form the peptide bond between amino acids during translation
|
peptidyl transferase
|
|
|
start codon is
|
AUG which coes for methionine
|
|
|
the stop codoons are
|
UAA, UAG, UGA
|
|
|
RNA polymeras I transcribes
|
rNA genes to form 45S RNA
|
|
|
RNA polymerase iii TRANSCRIBES
|
5s RNA
|
|
|
the 40S subunit contains
|
18S RNA
|
|
|
the 60S subunit contains
|
5S RNA, 5.8S RNA, 28S RNA
|
|
|
the fibrillar center of the nucleolus contains
|
pale-staining transcriptionally inactive DNA
|
|
|
the dense fibrillar component is..
|
dense-staining and contains transcriptionally active DNA, RNA polymerase I and 45S RNA
|
|
|
the granular component of the nucleolus
|
contains maturining riboslma precursors including 45S rna 5s rna, ribosomal proteins, RNA-binding protiens and snRNPSs
|
|
|
silent mutaions can occur when...
|
mutations occur in spacer DNA, introns, or the third nuclotide codon (sometimes)
|
|
|
missense mutations
|
occur when a change in a single nucleotide alters the codon so that one amino acid in a protein replaces another produce proteins with a compensated function
|
|
|
no9nsense mutations
|
occur when a change in a single nucleotide alters the codon and produces a premature stop codon and produce nonfuctional truncated proteins
|
|
|
frameshift mutations
|
occur when a deletion or an insertion of a single nucleotide alterse the codon and shifts the reading frame, and produce garbled proteins
|
|
|
translocation mutations
|
occur when a section of a gene moves from its original location to another location and may produce no protein
|
|
|
RNA splicting mutations
|
occur when a change in the nucleotdie at the 5' or 3' end of an intron alters the codon and changes the splice site
|
|
|
an oncogene is...
|
is a mutated proto-oncogene it encodes an oncoprotein that disrupts the normal cell cycle anc causes cancer
|
|
|
a proto-oncogene
|
is a normal gene that enoodes a protein that stimulates the cell cycle
|
|
|
the mutation of ras proto-oncogene to oncogene occurs when..
|
a glycine is replaced by a valine
|
|
|
p53...
|
is the anti-oncogene located on chromosome 17, encodes for the normal p53 protein (a zinc finger GRP) that causes the expression of targe genes whose gene products suppresses the cell cycle at stage G1 by inhibiting the activity of Cdk2-cyclin D and Cdk2-cyclin E
|
|
|
G0 is
|
the resting phase of the cell
|
|
|
G1 is..
|
between mitosis and the synthesis of DNA (RNA, protein, lipid, and carbohydrate syntehsis occurs), lasts 5 hours
|
|
|
S phase
|
DNA and chromosomal protein syntheisis occurs lasts 7 hours
|
|
|
G2 phase..
|
between DNA synthesis and M phase lasts 3 hours, ATP synthesis occurs
|
|
|
stages of M phase...,
|
a. Prophase
b. Prometaphase c. Metaphase d. Anaphase e. Telophase f. Cytokinesis |
|
|
the proteins families that control the cell cycle
|
cyclin dependent protein kinases AND cyclins which form Cdk-cyclin complexes
|
|
|
G1 checkpoint
|
*occurs at the G1->ss phase transition
*cdk2-cyclin D and Cdk2-cyclin E mediate this transition *the p53 anti-oncogene suppresses the cell cycle at this checkpoint preventing damaged DNA from entering S phase |
|
|
G2 checkpoint
|
* occurs at the G2->m phase transition
* cdk1-cyclinA and Cdk1-cyclinB mediate this transition * supresses the cell cycle at this checkpoint preventing damaged DNA from entering M phase |
|
|
cyclins are inactivated by ... during
|
by protein deradation during anaphase of M phase, ubiquitin is covalently attached to the lysine residues of cyclin by the enzyme ubiquitin ligase, called polyubiquitination
|
|
|
interphase...
|
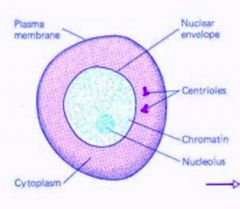
chromatin diffuse nucleus intact
|
|
|
prophase (4 facts)...
|

1. Chromatin condenses to form well-defined chromosomes.
2. Each chromosome is duplicated during the S phase and has a specific DNA sequence (centromere) that is required for proper segregation. 3. A centrosome complex that acts as the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) splits into two halves. The halves move to opposite poles of the cell. 4. The mitotic spindle, which contains microtubules, forms between the centrosomes. 5. nuclear envelope breaks down |
|
|
prometaphase
|
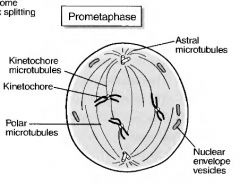
1. The nuelear envelope is disrupted, giving the microtubules access to the chromosomes.
2. The nueleolus disappears. 3. Kinetochores (protein complexes) assemble at each centromere on the chromosomes. 4. Certain microtubules of the mitotic spindle bind to the kinetochores (kinetochore microtubules) . 5. Other microtubules of the mitotic spindle are polar microtubules and astral microtubules. |
|
|
metaphase
|

1. Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate.
2. Cells can be arrested by microtubule inhibitors (e.g., colchicine). 3. Cells can be isolated for karyotype analysis. |
|
|
Anaphase
|
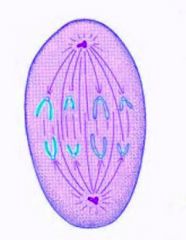
1. The kinetochores separate, and the chromosomes move to opposite poles.
2. The kinetochore microtubules shorten. 3. The polar microtubules lengthen. |
|
|
Telophase
|
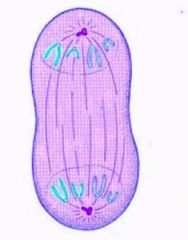
1. Chromosomes decondense to form chromatin.
2. The nuclear envelope re-forms. 3. The nucleolus reappears. 4. The kinetochore microtubules disappear. 5. The polar microtubules continue to lengthen. |
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
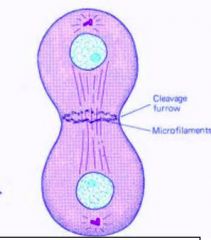
1. Cytoplasm divides through the process of cleavage.
2. A cleavage furrow forms around the center of the cell. 3. A contractile ring forms at the cleavage furrow. The ring is composed of actin and myosin filaments. |
|
|
what are the gene products that are encoded by mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
|
*Two ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs)
* 22 transfer RNAs (tRNAs) corresponding to each amino acid * seven subunits fo teh reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NADH) dehydrogenase complex * three subunits of teh cytochrome oxidases complex * two subunits of the F0 adenosine triphosphate synthase * One subunit (cytochrome b) of the ubiquinone-cytochorme c oxidoreductase complex |
|
|
teen falls while rollarblading and hurts his elbow. He can't feel the medial part of his palm.
What is the nn & what is the injury. |
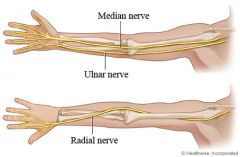
ulnar nn due to broken medial condyle
|

