![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how can you recover and continue making glycogen from a false alarm?
|
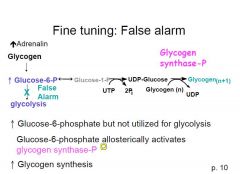
activate the P form of glycogen synthase
|
|
|
where do you get ATP from during strenuous exercise?
|
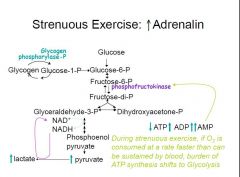
AMP activates PFK
|
|
|
how do you get lactose, maltose, sucrose increase
|
First you MUST break it down to a monosac. To do this- lactase maltase su
|
|
|
what is the main problem in classic galactosemia?
|
UDP transferase so G1P builds up
|
|
|
how do you get from galactose to galacitol?
|
aldose reductase
NADPH |
|
|
What general classes of disease should always be considered in the differential diagnosis of
any sick infant less than one month of age? |
metabolic disease
bacterial disease |
|
|
why are infants usually jaundiced at birth
|
insufficient bilirubin glucuronyl transferase activity at birth
|
|
|
how do you treat jaundice?
|
UV light
|
|
|
What other diseases frequently cause liver dysfunction in newborns?
|
glycogen storage diseases
|
|
|
How do we screen for galactosemia in Wisconsin? How is the diagnosis confirmed?
|
Historically by measuring Galactose-1-P levels in the blood. Now by measuring
UDP transferase activity in leukocytes, and if low, sequencing the DNA. |
|
|
what are the long term effects of galatosemia?
|
Neural (e.g. sensory, speech), fine motor, tremor, learning disabilities, mental
impairment, infertility. |

