![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
First step of Fatty Acid Synthesis using Acetyl-CoA and why is this critical? |
Acetyl-CoA is converted to citrate. Critical because then it can be transported into the cytosol |
|
|
Enzyme that cleaves citrate to create Acetyl-CoA in cytosol? Does it use ATP? |
Citrate Lyase, uses ATP for energy |
|
|
Why is it necessary for oxaloacetate to re-enter mitochondria after Acetyl-CoA is produced? |
NADPH is created for energy use for the creation of fatty acids |
|
|
Does Fatty Acid Synthesis use NADH or NADPH? |
NADPH |
|
|
What are 2 common ways Fatty Acid synthesis gets NADPH for energy? |
1. Malate is converted into pyruvate using pyruvate transporter 2. Pentose Phosphate Pathway which provides 2 times as much NADPH |
|
|
2nd step of Fatty acid synthesis: Acetyl-CoA forms and bicarbonate form... Enzyme? |
Malonyl-CoA. Enzyme is acetyl-CoA carboxylase. RATE LIMITING STEP OF FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS. Highly regulated. |
|
|
Describe 2 features of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
1. Biotin Carrier protein binds bitoin which moves Acetyl-CoA around 2. Other subunits catalyze reaction to put CO2 on Acetyl-CoA |
|
|
3rd Step of Fatty Acid Synthesis: Fatty Acid synthase |
Fatty Acid synthase has four steps which adds 2 carbons to the end of the chain each time. It uses NADPH (twice) for energy to build fatty acids. |
|
|
What are the 4 steps of Fatty Acid Synthase |
Condense, Reduce, Dehydrate, Reduce |
|
|
What are the 2 responsibilities of the Acyl Carrier Protein? |
1. Delivers carbons to Fatty Acid Synthase 2. Shuttles the growing chain to the 4 different active sites of Fatty Acid Synthase |
|
|
Acyl Carrier Protein activation. Enzyme? |
Charged by first 2 carbons which come from Acetyl-CoA. Reaction is catalyzed by MAT or malonyl/acetyl-CoA transferase. Connection of thiol groups really activates the acyl grouups. |
|
|
1st step of Fatty Acid Synthase |
Condensation. Energetically favorable due to coupling with decarboxylation (loss of CO2) makes reaction favorable |
|
|
2nd Step of Fatty Acid Synthase |
Reduction. NADPH is used to reduce Beta-Keto to an alcohol |
|
|
3rd Step of Fatty Acid Synthase |
Dehydration |
|
|
4th Step of Fatty Acid Synthase |
Reduction. NADPH reduces double bond to create saturated alkane. Chain is moved back to original starting point which where steps are repeated. |
|
|
Overall Outcome of Fatty Acid Synthase? |
Repeats 7 times. Palmitate (16:0) is generated. USE A LOT OF ENERGY! 14 NADPH and ATP to get Acetyl-CoA from mitochondria |
|
|
How can fatty acids be desaturated? Is it Fatty Acid that is really reduced? |
fatty acyl-CoA desaturase and input of NADPH. Fatty acids don't interact generally unless bound to Acetyl-CoA. NADPH works through a chain of reactions to reduce oxygen to form water. |
|
|
What is furtherst position humans can desaturate fatty acids? |
Position 9. |
|
|
What fatty acids are essential? |
Generally Linoleate which create PUFAs which are important for signaling and membrane fluidity. Arachidonic acids are also important for pain and inflammatory response |
|
|
What is a major inhibitor and regulator of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase? |
Palmitoyl-CoA is an inhibitor. Citrate allosterically activates ACC and inhibits PFK-1 to reduce glycolysis |
|
|
Synthesis of Phosphatidic Acid |
Reduction of glycerol to Glycerol 3 phosphate, acyl transferase adds fatty acids with Acetyl-CoA attached to those FA |
|
|
Regulation of Triacylglycerol Synthesis is regulated by? |
Insulin! |
|
|
Examples of lipids that use Strategy 1 of Activation of Phosphatidic Acid |
Cardiolipin and Phophatidylinosiol |
|
|
2 Strategies to create phosphatidylcholine |
1st strategy: Use Phosphatidic Acid 2nd strategy: Use diacylglycerol Important to note |
|
|
How many fatty acids are required to make a sphingolipid? |
2 FA. Necessary to make the Sphinganine. |
|
|
The enzyme catalyzing the rate-controlling step in the de novo synthesis of fatty acids is regulated allosterically by the positive modulator |
Citrate |
|
|
If fatty acid synthase made a 20 carbon fatty acid, how many malonyl-CoA molecules would it need? |
9. First 2 carbons always come from Acetyl-CoA |
|
|
How does glucagon and epinephrine affect carboxylase acetyl-CoA? |
It inhibits it's activity by triggering phosphorylation. Phosphorylation deactivates the enzyme. |
|
|
Lipogenesis occurs mostly in the |
Liver |
|
|
Warburg Effect |
Metabolism of cancer cells change. Glucose uptake is increased greatly in cancer cells. A lot also goes to pentose phosphate pathway. Pyruvate ferments lactate more often than entering citric acid cycle. |
|
|
How do cancer cells get citrate to bring Acetyl-CoA into the cytosol to use for Fatty Acid Synthesis? |
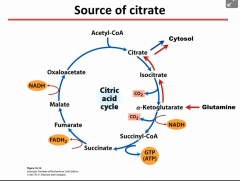
Cancer cells use glutamine to form alpha-ketoglutarate which goes in reverse direction of the TCA cycle and for citrate. |
|
|
Why is an increased amount in fatty acid synthesis poor for prognosis of cancer? |
A lot of fatty acid pathways promote tumor growth |
|
|
Why might lipogenesis be important for cancer growth? 4 factors |
1. Access to exogenous lipids might be limited 2. Greater survival in extreme conditions (hypoxia, low pH) 3. Drug Resistance (packing of membrane changes) 4. Changes in cell signaling pathways |
|
|
siRNA's bind specific regions of _____. If it is a perfect complement of mRNA what does it do the mRNA? |
mRNA. Degrades it |
|
|
are SiRNA's effective on limiting levels of ACC and FAS in cancer cells? |
Yes they are degraded and levels are decreased. |
|
|
Supplementation of Palmitate and Vitamin E can lead to decreased.... |
Apoptosis from FAS and ACC. |
|
|
What is Gibbs Free Energy? What are the two classifications? |
The amount of energy of capable doing work during a reaction. Exergonic, gives off energy. Endergonic absorbs energy. |
|
|
What is enthalpy? Classifications? |
The heat content of the reacting system. Exothermic, gives off heat. Endothermic, brings in heat. |
|
|
Standard Free energy is Negative when... |
Enthalpy is negative and entropy is increased/disordered G = H - TS |
|
|
If Keq is greater than 1, Free energy... |
Free energy is negative and wants to proceed forward. |
|
|
In biochemistry the oxidation of reduced fuels with Oxygen is... |
Stepwise and Controlled |
|
|
The actual free-energy change in process depends on |
1. Standard Free Energy 2. Actual concentrations of reactants and products |
|
|
What actually happens when phosphate is used as energy for a reaction? |
The phosphate is passed on to different reactants and products. They use the phosphate to create an intermediate which then has the energy to drive "another" reaction. Molecules become activated |
|
|
What is Reduction Potential? |
Affinity for electrons, Higher E = Higher affinity. Reactions with a higher reduction potential are more energetically favorable. |
|
|
Which type of bonds activate a molecule? |
1. Phosphate 2. Thioesters |
|
|
When the cell reaches the point of oxygen being used in the electron transport chain, what is blown off by the cell and why is this important? |
The carbon containg reactant has finally been stripped of all electrons and is given off as CO2 |
|
|
NAD and NADP are commonly called? |
Pyridine nucleotides |
|
|
Pellagra |
Niacin deficiency. Dematitis, diarrhea, and dementia and death. |
|
|
What are the feeder pathways for Glycolysis? |
1. Glycogen 2. Lactose 3. Sucrose |
|
|
What is meant by Priming reactions? What reactants are benefitted by priming? |
Priming reactions are when phosphates are added to make reaction energetically favorable. Glucose and Fructose-6-phosphate are activated by phosphate groups (from ATP) and wants to react more. |
|
|
What is the 1st step in Glycolysis? Glucose... Enzyme? Energetically Favorable? What drives reaction? Rationale? |
Glucose is made into Glucose-6-phosphate. Enzyme is Hexokinase Energetically favorable (-16.7kj/mol) and ATP drives reaction. Traps glucose inside the cell and lowers intracellular glucose concentration to allow further uptake |
|
|
Step 2 of Glycolysis: Glucose 6-phosphate... Enzyme? Energetically favorable? What drives reaction? Rationale |
Glucose 6-phosphate is changed into Fructose 6-phosphate. Enzyme is phosphohexose isomerase Unfavorable and reversible Driven forward by product concentration which is kept low
|
|
|
Step 3 of Glycolysis: Fructose 6-phosphate... Enzyme? Energetically favorable? What drives reaction? Rationale? |
Fructose 6-phosphate made into Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. Enzyme is Phosphorfructokinase 1 Energetically favorable (-14.2Kj/mol) RATE LIMITING STEP OF GLYCOLYSIS (dependent on PFK-1) Also 2nd Priming step because coupled to ATP First committed step of glycolysis |
|
|
Step 4 of Glycolysis: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Enzyme? Energetically favoragle? What drives the reaction? Rationale |
Fructose 1-6-bisphosphate is cleaved into Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Enzyme is aldolase Energetically unfavorable GAP concentration is low to pull the reaction forward. |
|
|
Step 5 of Glycolysis: Dihydroxyacetone... Enzyme? Energetically favorable? What drives the reaction? Rationale |
Dihydroxyacetone is converted in to GAP. Enzyme is triose phosphate isomerase Energetically unfavorable Rationale is to get the same products so the process of glycolysis can remain on the same track |
|
|
Step 6 of Glycolysis: GAP.... Enzyme? Energetically faborable? What drives the reaction? Rationale? |
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is combined with inorganic phosphate to form 1,3-bisphosphateglycerate Enzyme is glyceraldehye 3-phosphate dehydrogenase Energetically unfavorable Forms NADH for energy! |
|
|
Step 7 of Glycolysis: 1,3-bisphosphateglycerate.... |
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate becomes 3-phosphoglycerate Enzyme is phosphoglycerate kinase Energetically favorable Forms ATP energy from cleavage of phosphate bond Helps GAP stay low in concentration to pull drive of gylcolysis forward |
|
|
Step 8 of Glycolysis: 3-phosphoglycerate |
3-phosphoglycerate become 2-phosphoglycerate Enyzme is phosphoglycerate mutase Energetically unfavorable Rationale is to form high energy phosphate compound
|
|
|
What is a mutase? |
Catalyze movement of functional group |
|
|
Step 9 of Glycolysis: 2-phosphoglycerate |
2-Phosphoglycerate forms Phosphoenolpyruvate Enzyme is enolase Energetically unfavorable Rationale: Generate high energy phosphate compound. PEP is a good phosphate donor |
|
|
Step 10 of Glycolysis: PEP... |
Pep is dephosphorylated to becom pyruvate. Enzyme is pyruvate kinase Energetically favorable Rationale: Generates ATP for energy use |
|
|
What is the most energetic form of pyruvate...Keto or Enol? |
Keto |
|
|
When does pyruvate become lactate? |
When mitochondria are overwhelmed by great concentrations of pyruvate, lactate is fermented. |
|
|
What are the 3 pathways of Pyruvate? |
1. Ethanol 2. Lactate 3. Acetyl CoA |
|
|
Lactic Acid Fermentation |
Pyruvate to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase Very energetically favorable 9:1 lactate to pyruvate ratio NADH is consumed |
|
|
Why is the conversion of pyruvate to lactate important for enabling glycolysis? |
NAD is replenished |
|
|
Neurons prefer glucose or lactate? |
Lactate |
|
|
Cori Cycle |
Glycogen is reduced to lactate to produce ATP during rapid contraction. When body is resting, lactate is moved to liver where it builds glucose. |
|
|
Yeast fermentation of ethanol. List 2 steps with enzymes |
1. Pyruvate to Acetaldehyde through pyruvate decarboxylase 2. Acetalaldehyde through alcohol dehydrogenase forms ethanol |
|
|
Where does glycolysis normally occur? |
Brain and Muscle |
|
|
Where does gluconeogenesis occur? |
Occurs mainly in the liver |
|
|
How does gluconeogenesis avoid irreversible reactions of glycolysis? |
1. They use different enzymes 2. Differentially regulated to prevent a futile cycle |
|
|
1st critical bypass step of Gluconeogenesis |
Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate couple to ATP Enzyme is Pyruvate Carboxylase Performed in mitochondria Requires a biotin cofactor |
|
|
2nd critical bypass step of Gluconeogenesis |
Oxaloacetate to PEP couple to GTP Enzyme to PEPCK Could be in mitochondria or cytosol Barely energetically favorable
|
|
|
3rd critical bypass step of Gluconeogenesis |
Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate to Fructose 6-bisphosphate Enzyme is fructose bisphosphatase-1 Energetically favorable |
|
|
4th critical bypass step of Gluconeogenesis |
Glucose 6-phosphate to Glucose by Glucose 6-phosphatase Phosphate group makes it favorable because of the activation of by phosphate |
|
|
Cost of Gluconeogenesis |
4 ATP, 2 GTP, 2 NADH |
|
|
Use of Pentose Phosphate Pathway |
1. Formation of NADPH to form reduced glutathione. Important to reduce oxidative stress of cells 2. NADPH is also important for reductive biosynthesis of fatty acids and sterols 3. Ribulose 5-phosphate which promotes nucleotide synthesis |
|
|
What is the important enzyme needed in the Pentose Phosphate Pathway? |
glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase because without it you can't run pentose phosphate pathway and can't get high levels of NADPH to create protection from oxidative species |
|
|
What regulates if glucose 6-phosphate enter glycolysis or pentose phosphate pathway? |
NADPH |
|
|
Rate of the enzyme is more sensitive to high/low concentrations of substrate? |
Low |
|
|
Why do key enzymes operate far from equilibrium? |
They generally are sites of regulation and control flow through the pathway |
|
|
Describe the relationship of the mass action ratio Q and Keq and how it relates to deltaG and direction of reaction |
If mass action ration Q is less than Keq the delta G is negative and the reaction wants to proceed forward. |
|
|
Describe the regulatory power of Enzymes in a chain affect using atp, adp and amp as an example. |
After ATP is used up the concentration doesn't change that much but as it continues down the line to AMP there is a much greater affect on the concentration. ATP and ADP don't see much change but AMP changes 600 fold. Thus AMP is a more potent regulator. |
|
|
Is hexokinase 4 km smaller or greater than km of hexokinase? |
It is greater which means more glucose needed to saturate enzyme. |
|
|
What facilitates the movement of hexokinase 4 from the nucleus of a cell to the cytosol? |
Glucose promotes cytosolic hexokinase 4 to move into the cytosol to promote glycolysis. Fructose 6-phosphate promotes movement of hexokinase 4 into the cytosol. |
|
|
Describe the regulation of PFK-1 and Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase |
Regulation is controlled by levels of AMP and ATP. If levels of AMP are high and ATP is low, go glycolysis. If AMP is low go gluconeogenesis |
|
|
What is the function of Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate? |
It is regulator of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. It promotes glycolysis by activating phosphofructokinase-1 and inhibits fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase |
|
|
PFK-2 and FBP-2 regulation by phosphorylation |
ATP inhibits PFK-2 and activates FBP-2 |
|
|
Glucose rinse produced great accumulation of .... |
Pyruvate |
|
|
Flouride rinse produce great accumulation of... |
3 phosphoglycerate because enolase is inhibited |
|
|
How does glucose become activated before it is added to the glycogen chain? |
UDP activates it |
|
|
Muscle does not do.... |
Gluconegenesis. NO receptors for glucagon. |
|
|
Liver only does.... |
Gluconeogenesis. |
|
|
Where is Acetyl-CoA produced? |
In the mitochondria after glycolysis |
|
|
Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA |
Enzyme is Pyruvate dehydrogenase First carbons of glucose to be fully oxidized NADH is produced |
|
|
Regulation of PDH by phosphorylation |
If phosphorylated it is active. If dephosphorylated it is deactivated. Enzyme has PDH kinase and PDH phosphatase. High ATP activates PDH kinase which phosphorylates PDH which generates more Acetyl-CoA |
|
|
1st step of TCA cycle Acetyl-CoA... |
Acetyl-CoA plus Oxaloacetate to Citrate Enzyme is Citrate synthase Energetically favorable and RATE LIMITING STEP |
|
|
2nd Step of TCA cycle Citrate.... |
Citrate to Iso-Citrate Enzyme is aconitase Energetically unfavorable Isomerization by dehydration/rehydration |
|
|
3rd Step of TCA cycle Isocitrate |
Isocitrate to alphaketolgutarate Enzyme is Isocitrate dehydrogenase Energetically favorable Oxidative Decarboxylation: Lose CO2 and generate NADH |
|
|
4th Step of TCA cycle AlphaKetoglutarate |
Alphaketoglutarate to Succinyl-CoA AKDH is the enzyme Energetically favorable NADH is produced Final Oxidative decarboxylation |
|
|
5th Step of TCA cycle Succinyl CoA |
Succinyl CoA to Succinate Enzyme is Succinyl CoA Synthease Big thing IS GTP FORMED Favorable |
|
|
6th step of TCA cycle Succinate |
Succinate to Fumarate Enzyme is Succinate dehydrogenase FADH2 is formed! but is covalently bound Part of Complex 2 of ECT
|
|
|
7th Step of TCA cycle Fumarate |
Fumarate to Malate Enzyme Fumarase Energetically favorable barely |
|
|
Last step of TCA cycle Malate |
Malate to Oxaloacetate Enzyme is malate dehydrogenase Energetically Unfavorable NADH is formed |
|
|
Describe relationship of glucagon and phosphorylase? |
Glucagon activates phosphorylase to active form of phosphorylase a. Phosphorylase b is less active form. |
|
|
What is an anaplerotic reaction? Give an example |
Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate. All of CAC is skipped. Pyruvate carboxylase is the intermediate. Helps drive gluconeogenesis. |
|
|
What are prosthetic groups? |
Iron containing compounds that move electrons within the complexes |
|
|
What differs in the electron flow from NADH and FADH2? |
NADH has its electrons move into complex 1 which than is shuttle by Q to Ubiquinone that is reduced. FADH2 is shuttle to complex 2 where the electrons are put on ubiquinone right away |
|
|
How many hydrogens are pumped by each complex in the ETC? |
Complex 1 pumps 10 hydrogens per 2 electrons. Complex 2 pumps 6 hydrogens per 2 electrons. |
|
|
In ATP synthase, proton translocation causes a rotation of the F0 subunit and central shaft gamma |
This cause a conformational change in the 3 subunits of F1 which bind ATP |
|
|
How are NADH Molecules brought into the mitochondria? |
NADH molecules are brought in on the Malate Aspartate shuttle |
|
|
How are FADH2 molecules directly put into ubiquinone? |
FADH2 molecules are brought into ECT by Glycerol 3-Phosphate shuttle |
|
|
Why does pyruvate require a carrier into the mitochondrial matrix? |
Because the intermembrane space is impermeable |

