![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The building blocks of nucleic acids are |
Nucleotides |
|
|
Name three major components of which adenine nucleotides are a component of |
NAD, FAD, CoA |
|
|
In biosynthetic processes of (UDP-GLUCOSE! , SAM) |
Nucleotides derivatives are activated intermediates |
|
|
Roles of nucleotides in cellular processes |
*serve as metabolic regulators *serve as major currency of energy in all cells (ATP and GTP) |
|
|
Components of nucleic acids |
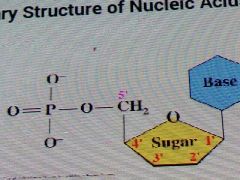
They consist of nucleotides that have a sugar, nitrogen base, and phosphate. |
|
|
Nucleic acids are |
Large molecules consisting of long chains of monomers called nucleotides, that store information for cellular growth and reproduction |
|
|
The nitrogen bases in DNA and RNA are |
*purine Adenine(A) and Guanine(G) *pyrimidine Cytosine (C) , THYMINE (T) , and Uracil(U)
|
|
|
The difference between the nitrogen bases in DNA and RNA is |
THYMINE IN DNA URACIL IN RNA |
|
|
The pentose sugars for DNA and RNA |
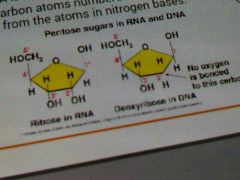
In RNA is ribose In DNA is deoxyribose with no O atom on carbon 2'. |
|
|
What is a nucleoside |
It is a molecule that has a nitrogen base linked by a glycosidic bond to C1' of a sugar. It is named by changing the nitrogen base ending to - osine for purines - idine for pyrimidines |
|
|
What is a nucleotide |
It is a nucleoside that forms a phosphate Ester with the C5' - OH group of a sugar It is named using the name of the nucleoside followed by 5'-monophosphate |
|
|
A nucleotide is formed, |
When the - OH on C5' of a sugar bonds to phosphoric acid |
|
|
In the primary structure of nucleic acids, nucleotides are joined by |
phosphodiester bonds The 3' -OH group of the sugar in one nucleotide forms an Ester bond to the phosphate group on the 5' - carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide |
|
|
Structure of Nucleic acids |
A nucleic acid has a free 5'-phosphate group at one end and and a free 3' - OH group at the other end. It is read from the free 5' end using the letters of the bases. |
|
|
The structure of RNA |
It is a single strand of nucleotides with bases A, C, G, and U. It is linked by phosphodiester bonds between ribose and phosphate |
|
|
DNA structure |
nucleotides containing bases A, C, G, and T linked by Ester bonds between deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups |
|
|
Double helix of DNA |
Two strands of nucleotides form a double helix structure like a spiral staircase. The bases along one strand complement the bases along the other. |
|
|
Describe DNA replication |
*genetic information is maintained each time a cell divides *the DNA strands unwind *each parent strand bonds with new complementary bases* two new DNA strands form that are exact copies of the original DNA |
|
|
Percentage total of the three types of RNA |
Ribosomal RNA 75 Messenger RNA 5-10 Transfer RNA 10-15 |

